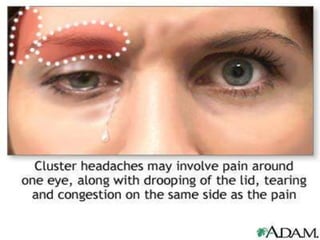
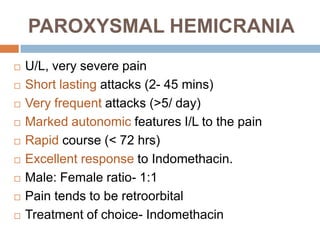
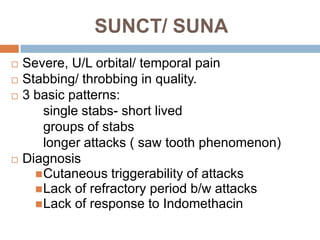
This document summarizes several types of primary headaches including trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs). TACs are short-lasting headache attacks associated with cranial autonomic symptoms and include cluster headache, paroxysmal hemicrania, and SUNCT. Cluster headaches are characterized by severe, unilateral pain and periodicity with daily bouts. Paroxysmal hemicrania causes very severe, short-lasting unilateral headaches very frequently and responds well to indomethacin. SUNCT involves severe orbital or temporal pain with stabbing or throbbing quality and cutaneous triggerability of attacks. The document also briefly outlines other primary headache types such as hemicrania continua,