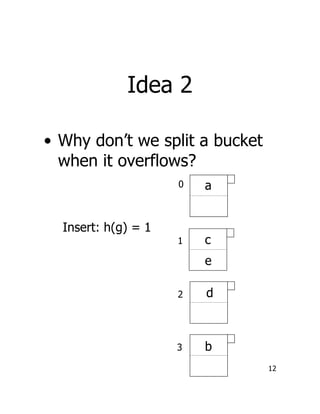
This document discusses hash indexes and extendible hashing. It begins by explaining basic hash tables and how they allow direct access to records via a hash function. It then describes how hashing can be used in a database management system by storing records in disk blocks based on their hashed key value. The major challenges with static hashing are overflow blocks and coping with data growth. Extendible hashing is presented as a solution that dynamically splits buckets as they overflow and uses an indirection directory that doubles in size as needed to accommodate more data.

![2
What is a Hash Table?
• Hash Table
– Hash function
• h(k): key ‡ integer [0…n]
• e.g., h(‘Susan’) = 7
– Array for keys: T[0…n]
– Given a key k, store it in
T[h(k)]
5
Susan4
James3
2
Neil1
0
h(Susan) = 4
h(James) = 3
h(Neil) = 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hash-101022040258-phpapp01/85/Hash-2-320.jpg)