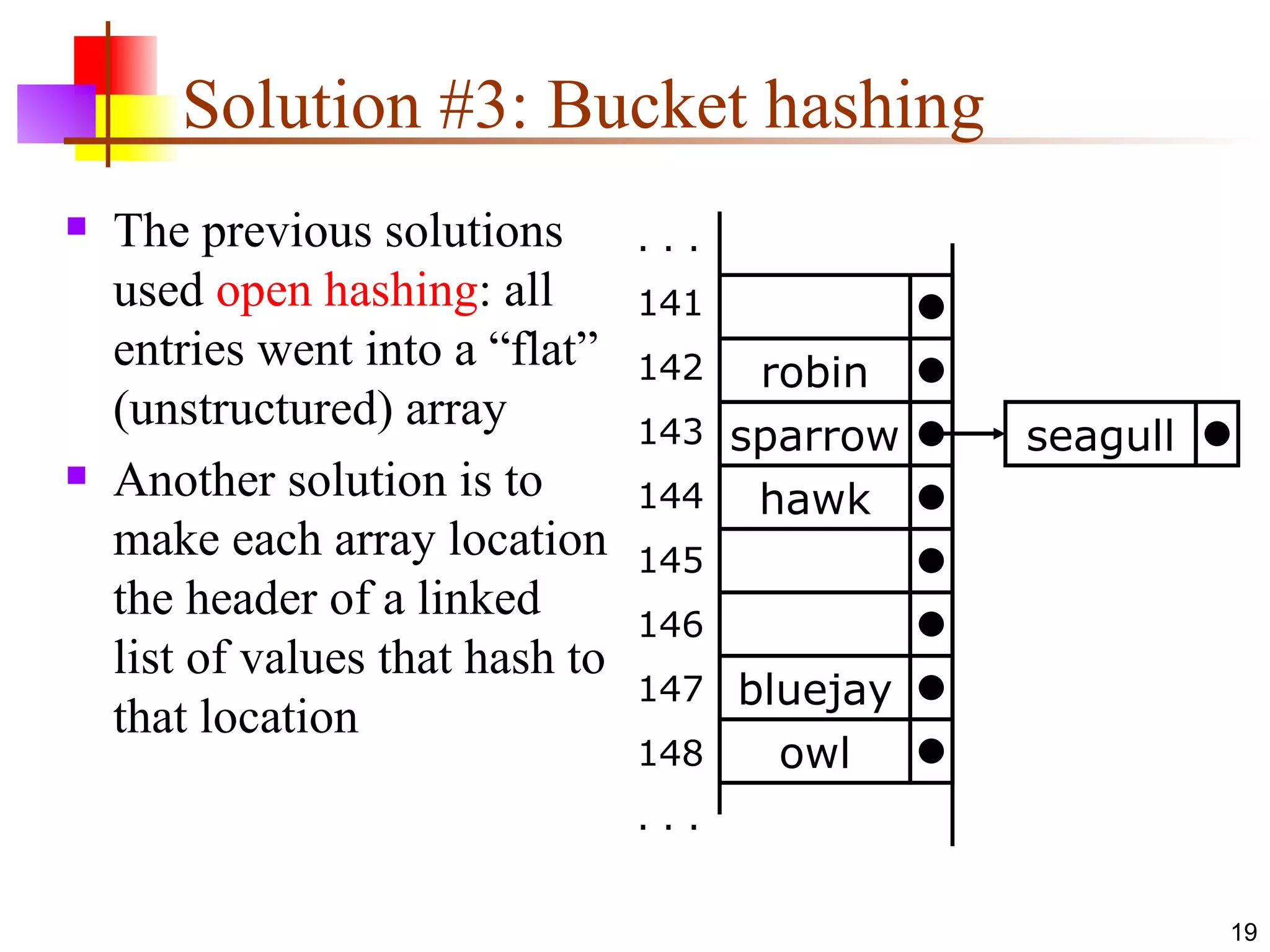
Hashing involves using a hash function to map objects to integer indices in an array. An ideal hash function would map equal objects to the same index, allowing constant-time lookups. However, collisions where unequal objects map to the same index are inevitable. Common techniques for handling collisions include open addressing, which searches for the next available index, and bucket hashing, which uses each index as a linked list header. To use Java's hash-based collections like HashMap, user-defined classes must override hashCode() consistently with equals().









![Insertion, I Suppose you want to add seagull to this hash table Also suppose: hashCode(seagull) = 143 table[143] is not empty table[143] != seagull table[144] is not empty table[144] != seagull table[145] is empty Therefore, put seagull at location 145 seagull robin sparrow hawk bluejay owl . . . 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 . . .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18-hashing-110503060921-phpapp02/75/18-hashing-11-2048.jpg)
![Searching, I Suppose you want to look up seagull in this hash table Also suppose: hashCode(seagull) = 143 table[143] is not empty table[143] != seagull table[144] is not empty table[144] != seagull table[145] is not empty table[145] == seagull ! We found seagull at location 145 robin sparrow hawk bluejay owl . . . 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 . . . seagull](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18-hashing-110503060921-phpapp02/75/18-hashing-12-2048.jpg)
![Searching, II Suppose you want to look up cow in this hash table Also suppose: hashCode(cow) = 144 table[144] is not empty table[144] != cow table[145] is not empty table[145] != cow table[146] is empty If cow were in the table, we should have found it by now Therefore, it isn’t here robin sparrow hawk bluejay owl . . . 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 . . . seagull](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18-hashing-110503060921-phpapp02/75/18-hashing-13-2048.jpg)
![Insertion, II Suppose you want to add hawk to this hash table Also suppose hashCode(hawk) = 143 table[143] is not empty table[143] != hawk table[144] is not empty table[144] == hawk hawk is already in the table, so do nothing robin sparrow hawk seagull bluejay owl . . . 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 . . .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18-hashing-110503060921-phpapp02/75/18-hashing-14-2048.jpg)