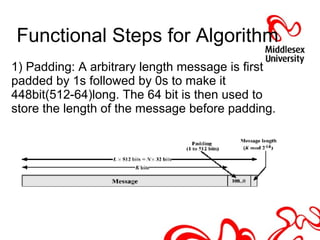
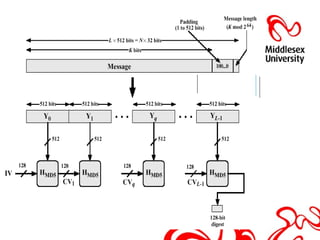
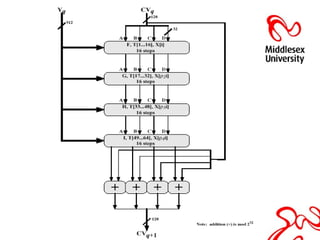
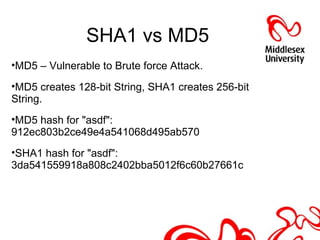
This document discusses hash functions and their analysis for a network security seminar. It begins by defining a hash function as a mathematical function that converts a large amount of data into a small string of integers. Common applications of hash functions include hash tables for quickly searching data, eliminating data redundancy, caches, bloom filters, and pattern matching. Cryptographic hash functions have properties like preimage and second preimage resistance as well as collision resistance. Popular cryptographic hash functions discussed include MD2, MD4, MD5, SHA-1, and SHA-2, along with their advantages, limitations, and examples of attacks.