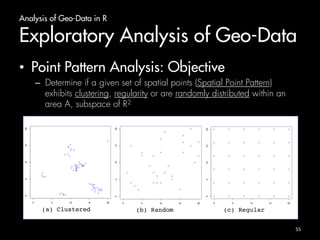
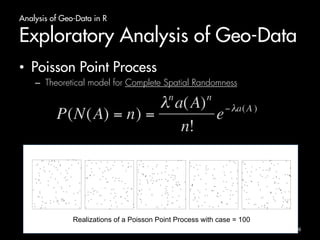
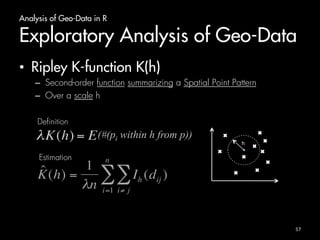
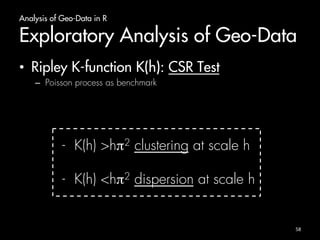
The document outlines an introduction to analyzing and visualizing geo-data in R. It discusses exploring the structure of spatially distributed point data through point process statistics like the Complete Spatial Randomness test and Ripley's K-function. It also covers visualizing maps and point patterns with packages like maps, ggmap, rworldmap, and ggplot2. The document provides examples of mapping different regions, geocoding location data, and plotting point patterns on maps in R.










![Basic R
Basic operations
> 1+1 # Addition
[1] 2
> 4 - 3 # Subtraction
[1] 1
> 4 * 2 + 1 # Operator precedence
[1] 9
> 6 ^ 2 # Exponentiation
[1] 36
> sqrt(5) # Math function
[1] 2.236068
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatacourse-141008143905-conversion-gate01/85/Big-datacourse-12-320.jpg)


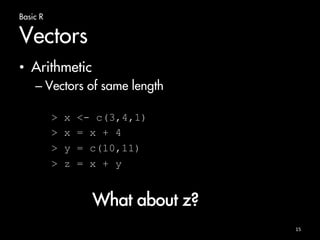

![Basic R
Vectors
• Sequence
17
> 1:10
[1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
> 10:1
[1] 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
> seq(from = 1, to = 10)
[1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
> seq(from = 10, to = 1)
[1] 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
> seq(from = 1, length = 10, by =4)
[1] 1 5 9 13 17 21 25 29 33 37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatacourse-141008143905-conversion-gate01/85/Big-datacourse-17-320.jpg)
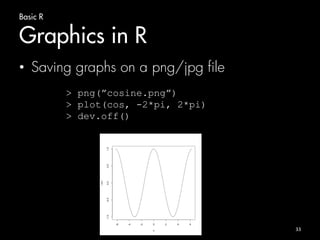
![Basic R
Vectors
• Logical vectors
> x = seq(from=1, to=10)
> x
[1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
> y = (x %% 3 == 0)
> y
[1] FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE
FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatacourse-141008143905-conversion-gate01/85/Big-datacourse-18-320.jpg)
![Basic R
Vectors
• Index vectors
– Access by index
– From 1
– Logical condition
19
> x = c(2,5,7,9)
> x[1]
[1] 2
> x[c(2,4)]
[1] 5 9
> x[x<7]
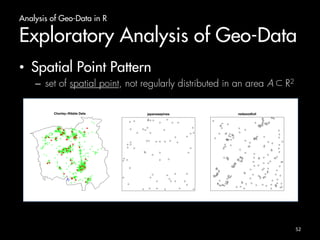
[1] 2 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatacourse-141008143905-conversion-gate01/85/Big-datacourse-19-320.jpg)
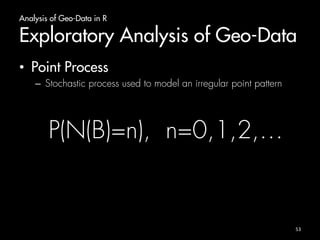
![Basic R
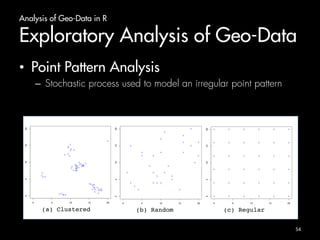
Arrays and Matrices in R
• Matrix
– A matrix is a two-dimensional object
– matrix function
20
> matrixA = matrix(data = c(1:10), ncol = 2, nrow = 5)
> matrixA
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 1 6
[2,] 2 7
[3,] 3 8
[4,] 4 9
[5,] 5 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatacourse-141008143905-conversion-gate01/85/Big-datacourse-20-320.jpg)
![Basic R
Arrays and Matrices in R
• Array
– A matrix is a n-dimensional object
– array function + dim
> x = c(1:18)
> x
[1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
> y = array(data=x, dim=c(2,3,3))
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatacourse-141008143905-conversion-gate01/85/Big-datacourse-21-320.jpg)
![Basic R
Arrays and Matrices in R
• Accessing by index
22
> x <- array(data=c(1:12), dim=c(3,4)) #generate 3 by 4 matrix
> x
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
[1,] 1 4 7 10
[2,] 2 5 8 11
[3,] 3 6 9 12
> i <- array(c(1:3,3:1), dim=c(3,2))
> i
> [,1] [,2]
> [1,] 1 3
> [2,] 2 2
> [3,] 3 1
> x[i]
[1] 7 5 3
> x[i] <- -1
> x
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
[1,] 1 4 -1 10
[2,] 2 -1 8 11
[3,] -1 6 9 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatacourse-141008143905-conversion-gate01/85/Big-datacourse-22-320.jpg)

![Basic R
Lists
• Example:
24
> lst = list(name="Massimiliano", surname="Ruocco",
> age=99, birthplace="Italy")
> lst$name
[1] "Massimiliano”
> lst[1]
$name
[1] "Massimiliano"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatacourse-141008143905-conversion-gate01/85/Big-datacourse-24-320.jpg)

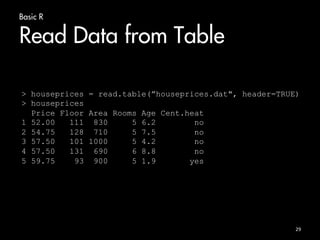
![Basic R
Data Frames
• Accessing as a normal matrix
26
> apartmentPrices[2,1]
[1] Trondheim
Levels: Bergen Oslo Trondheim
> apartmentPrices[1,]
cities squaremeters prices
1 Trondheim 80 3
> apartmentPrices$prices
[1] 3.0 4.5 5.1 3.7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatacourse-141008143905-conversion-gate01/85/Big-datacourse-26-320.jpg)
































![Koan 3
Basic R (2)
• create a vector with only odd numbers
from 1 to 100
• create a vector [1,2,3,...,100]. Extract
from this the vector with only odd
numbers
• Compare the two resulting vectors
78](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatacourse-141008143905-conversion-gate01/85/Big-datacourse-79-320.jpg)