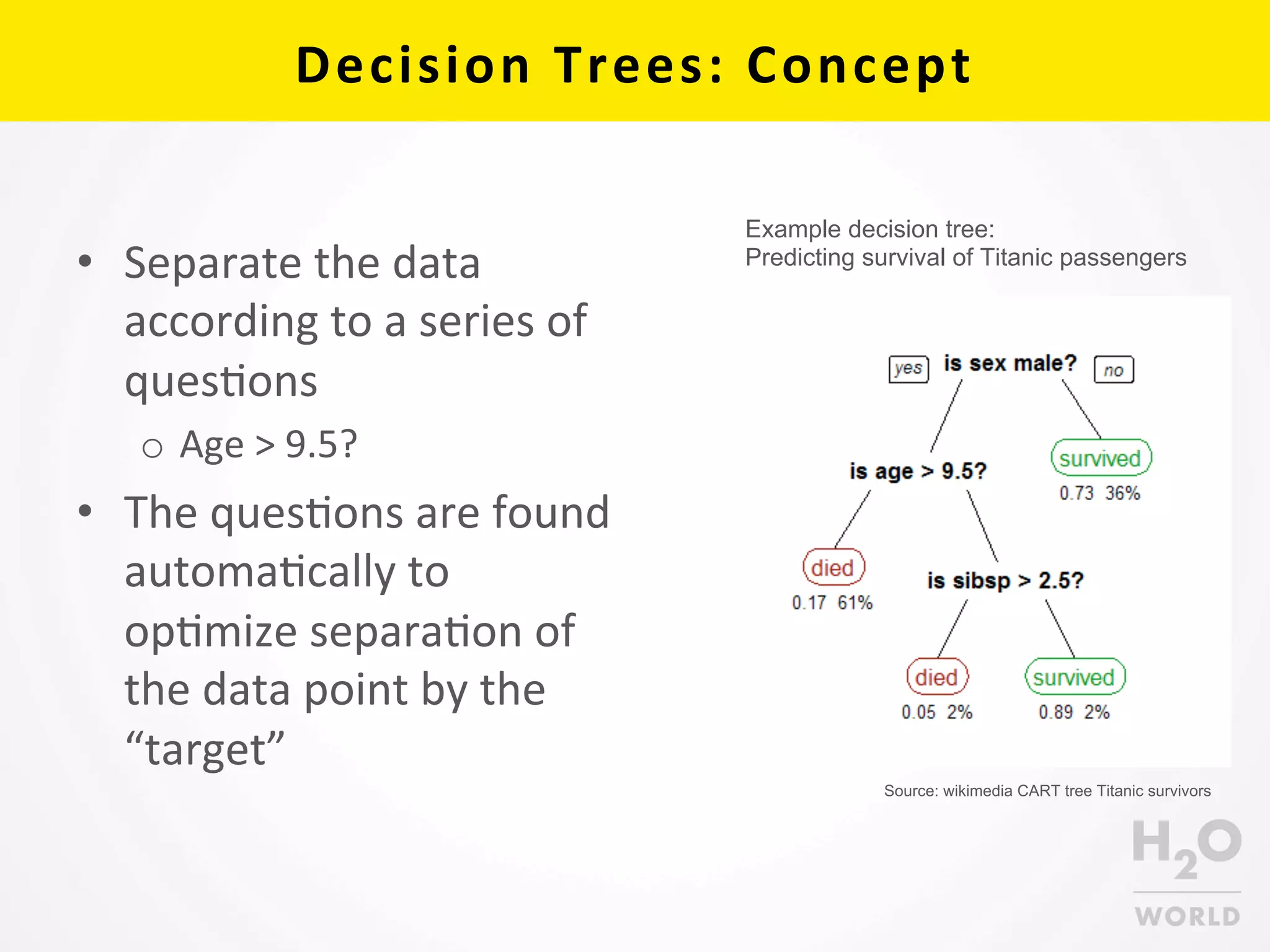
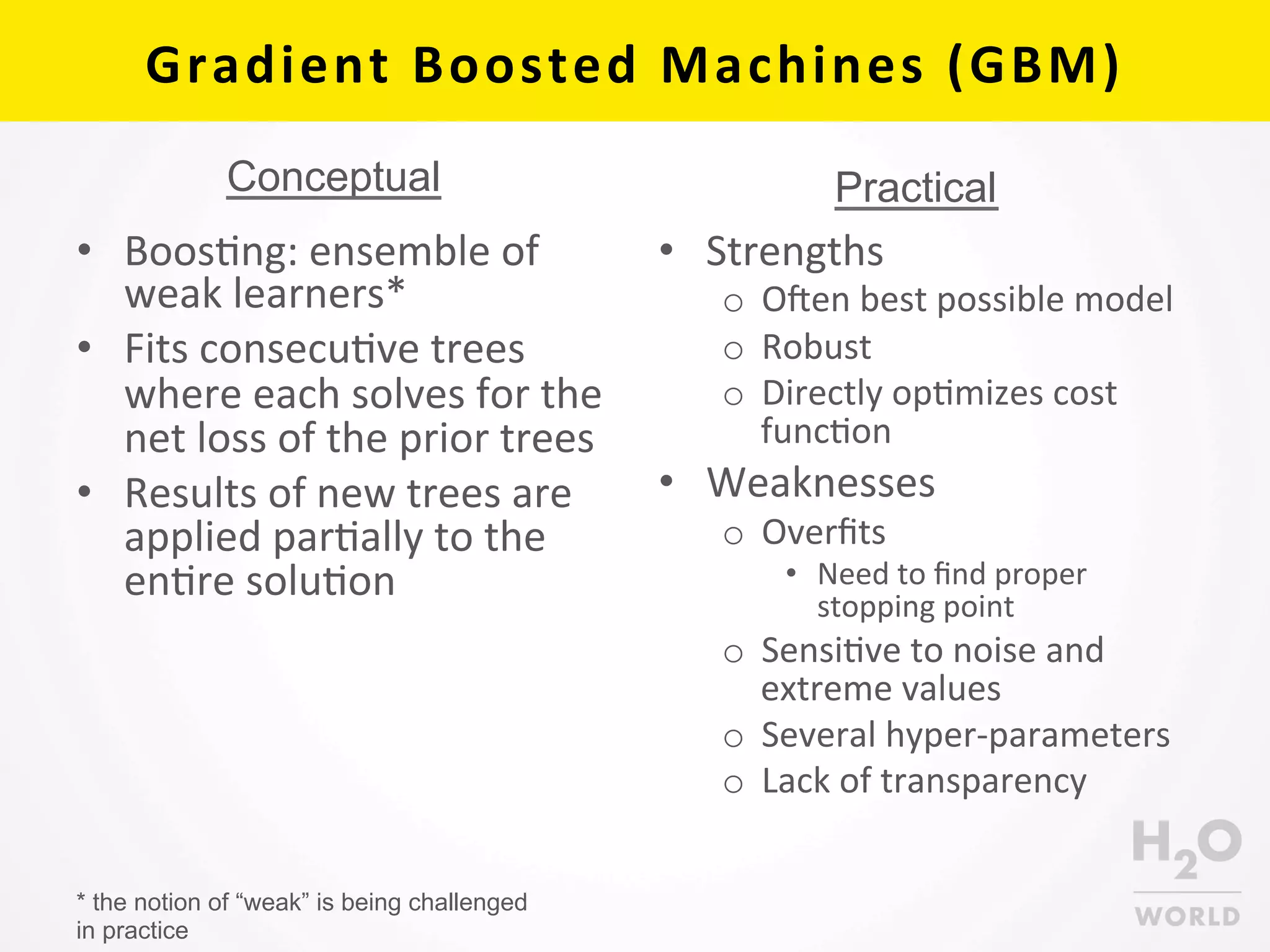
This document provides an overview of random forest and gradient boosted machine (GBM) algorithms in H2O. It begins with background on decision trees, random forest, and GBM. It then discusses H2O implementations, including code examples and parameter descriptions. Key aspects of decision trees, random forest, and GBM concepts and practical uses are outlined. The document concludes by noting trees in H2O are fitted in parallel using shared histograms to calculate cut-points, optimizing squared error through greedy searches. Further exploration of these algorithms is encouraged through examples.