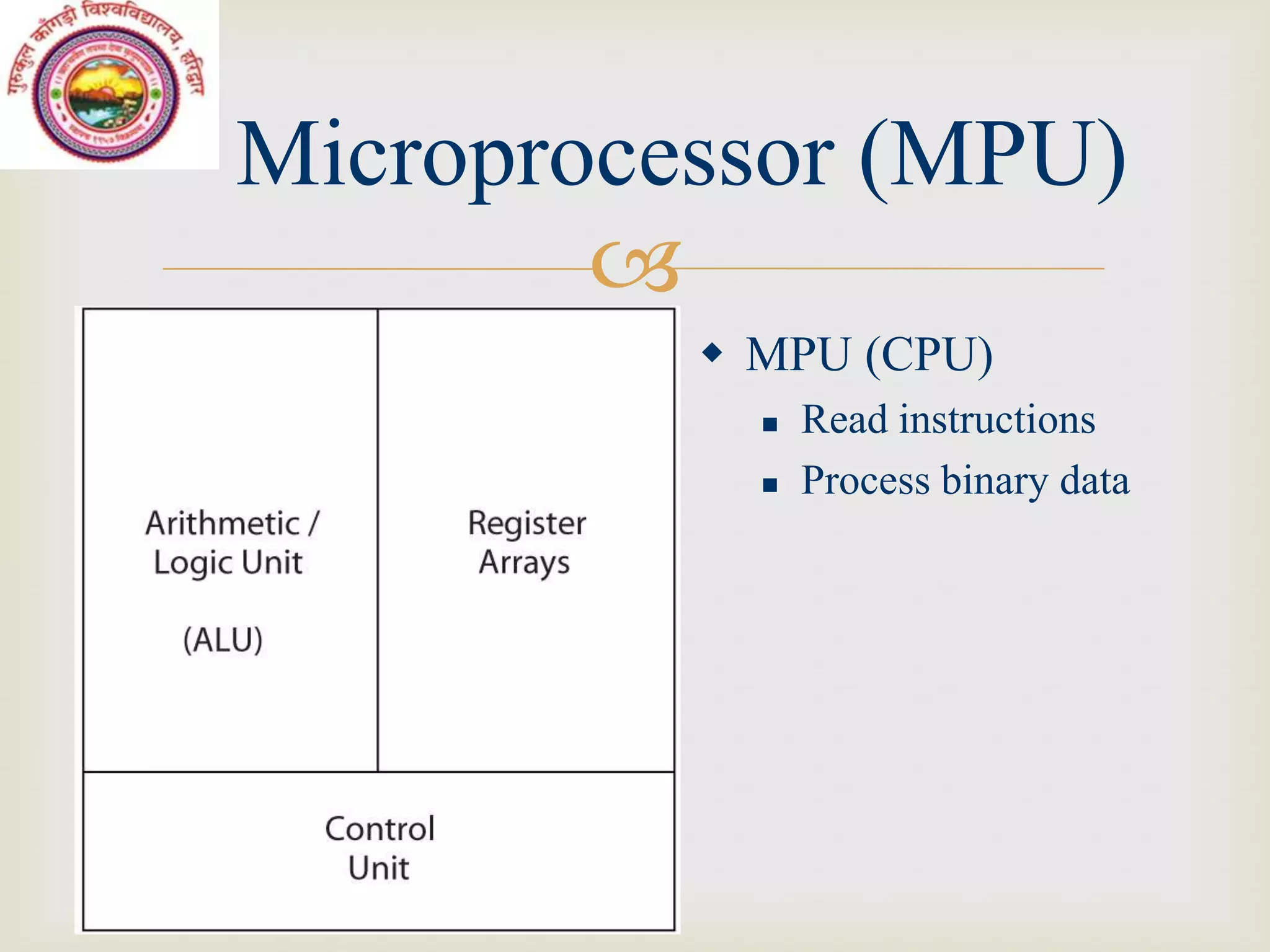
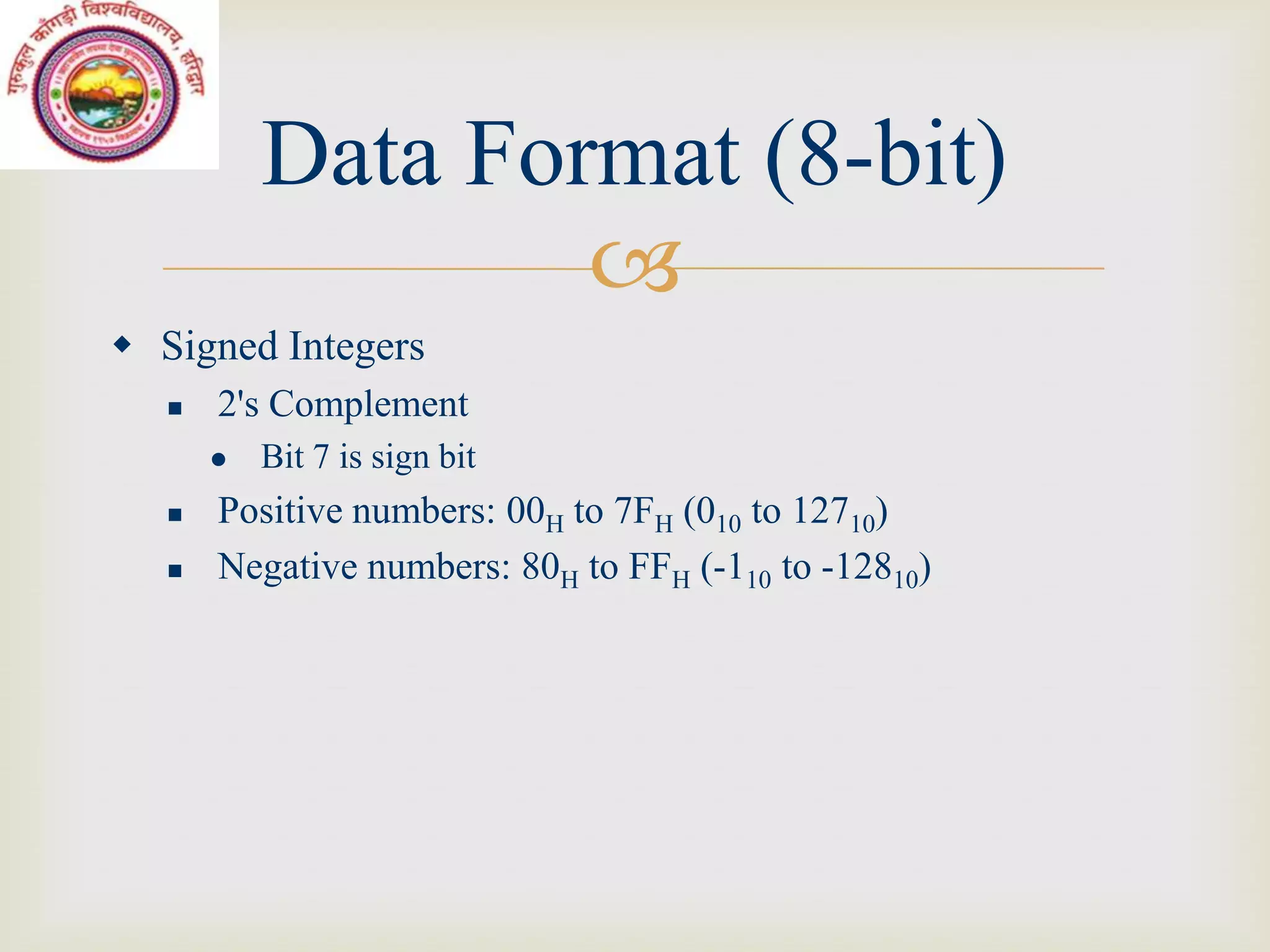
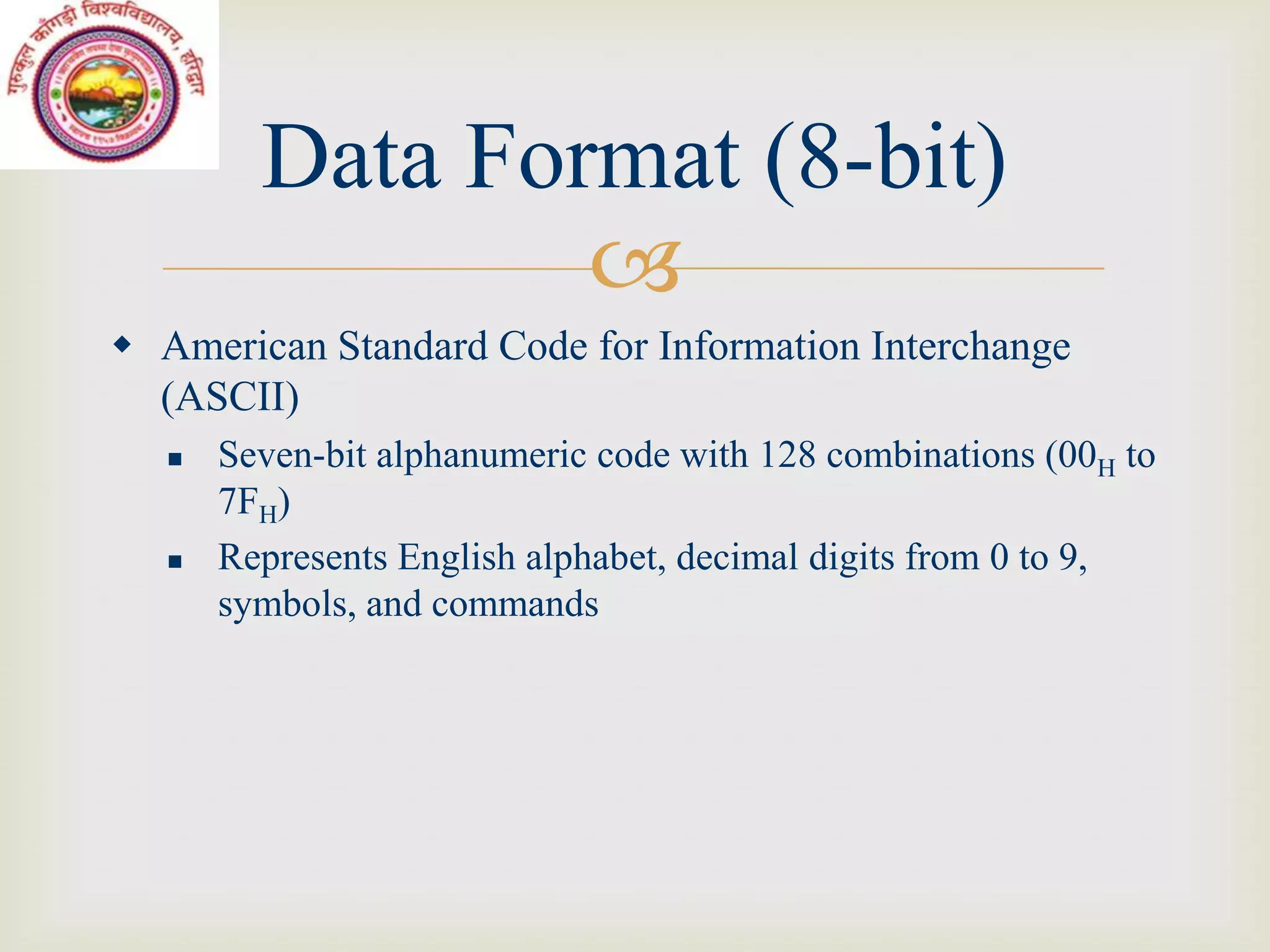
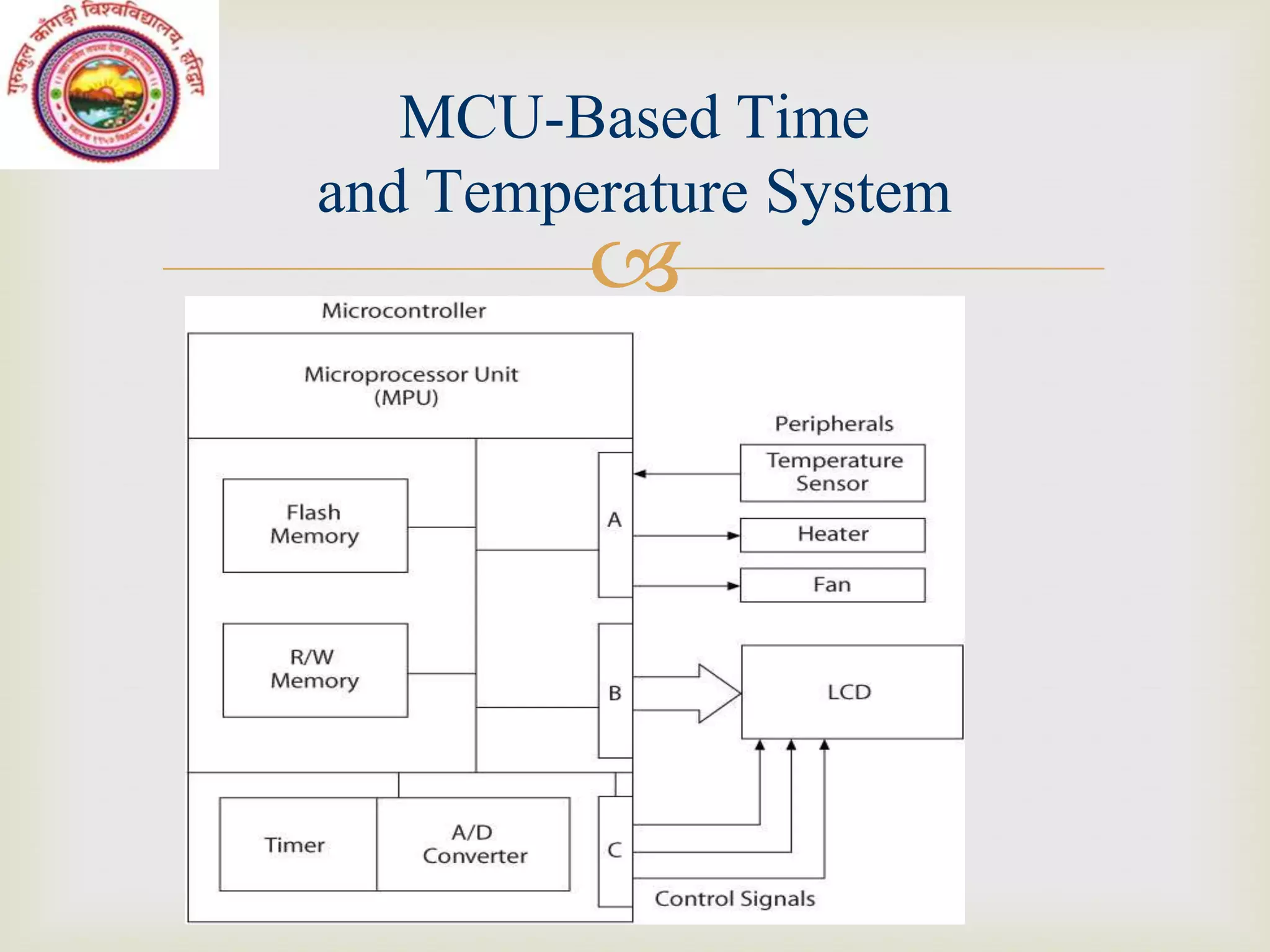
This document discusses microcontrollers and microprocessor-based systems. It defines a microcontroller as an integrated circuit that combines a microprocessor, memory, and input/output ports on a single chip. It also describes the components of microprocessor-based systems including the microprocessor, memory, I/O devices, and system bus. The document provides examples of data formats, programming languages, and common applications like a time and temperature measurement system.