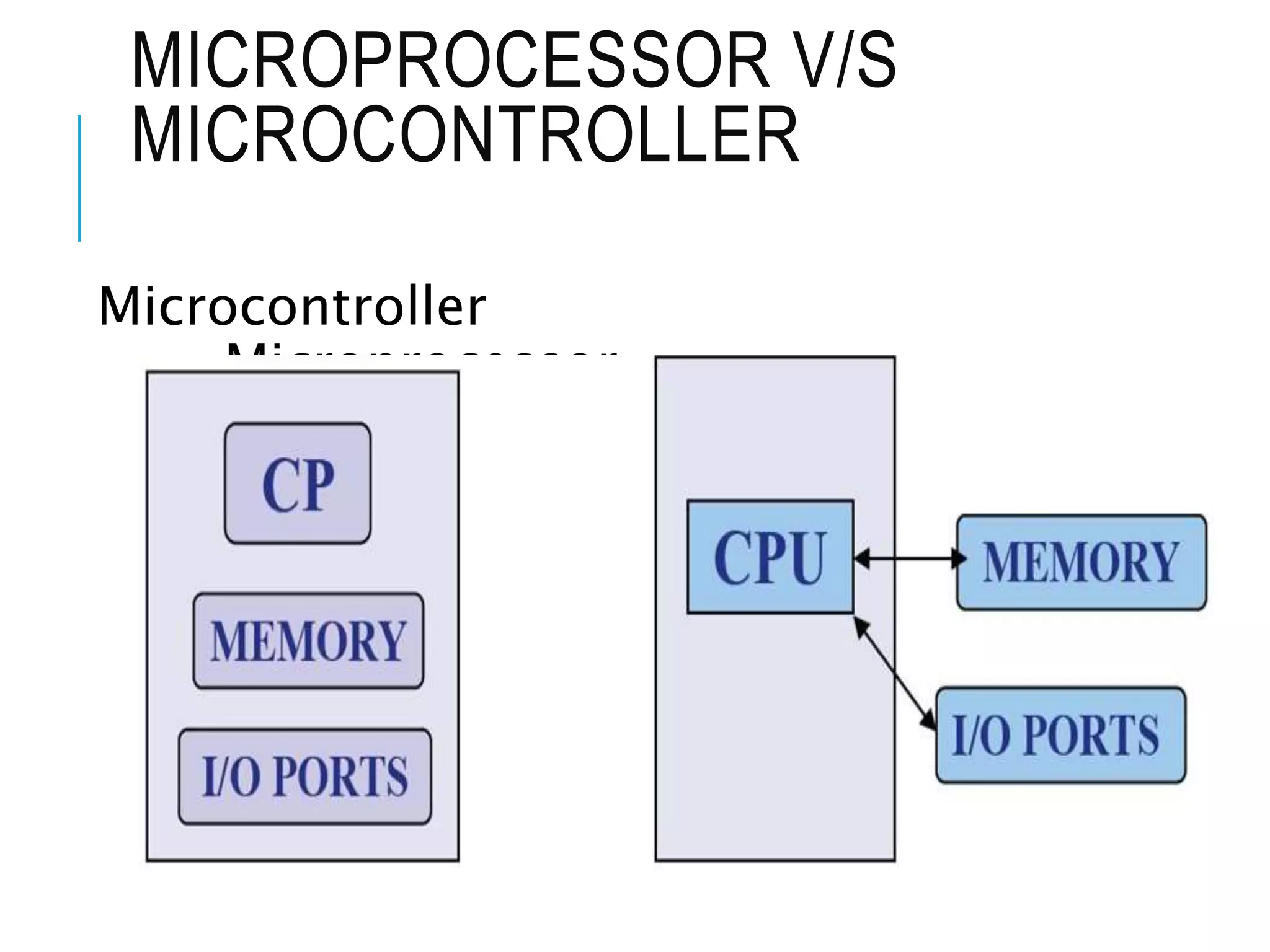
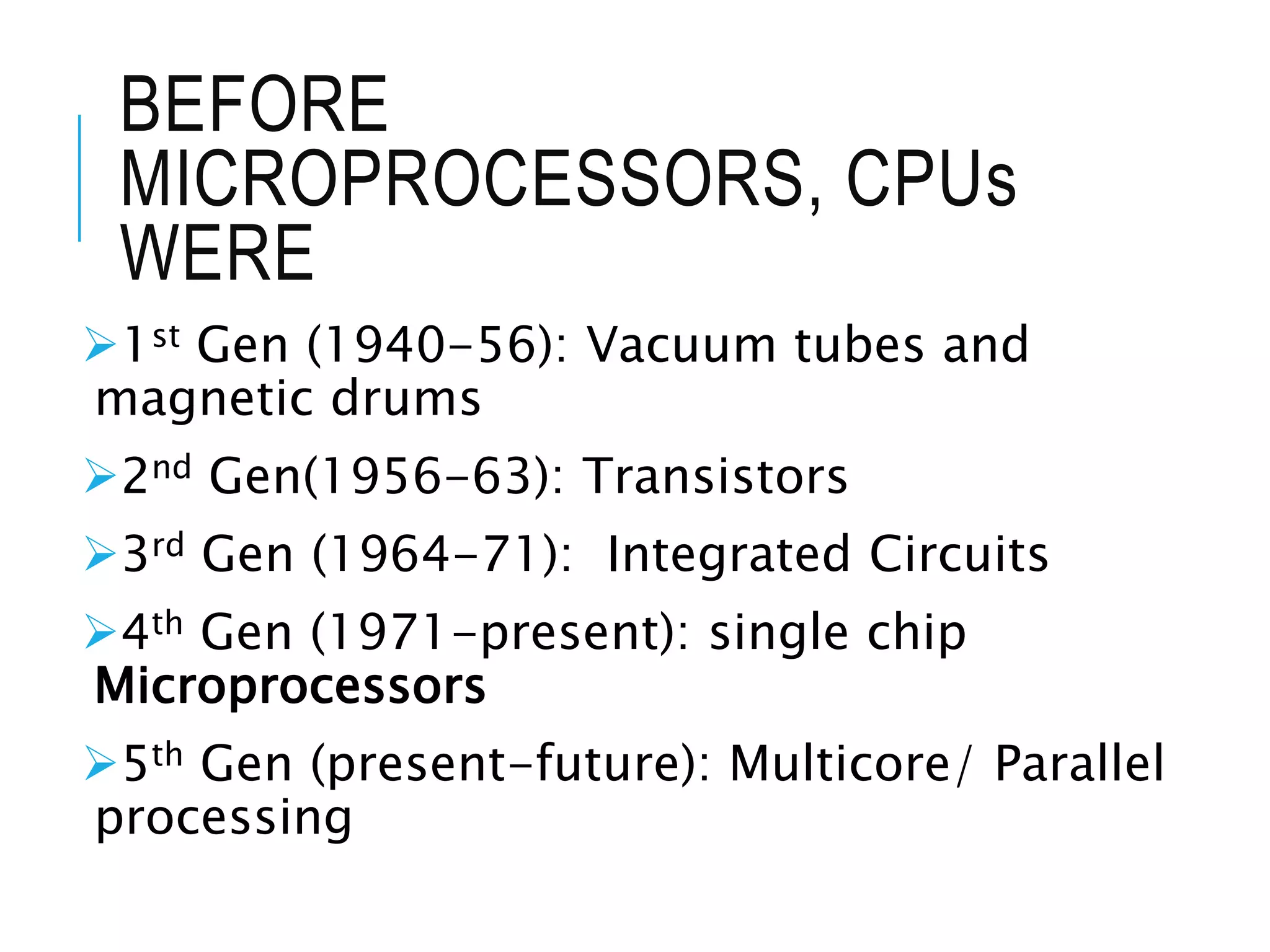
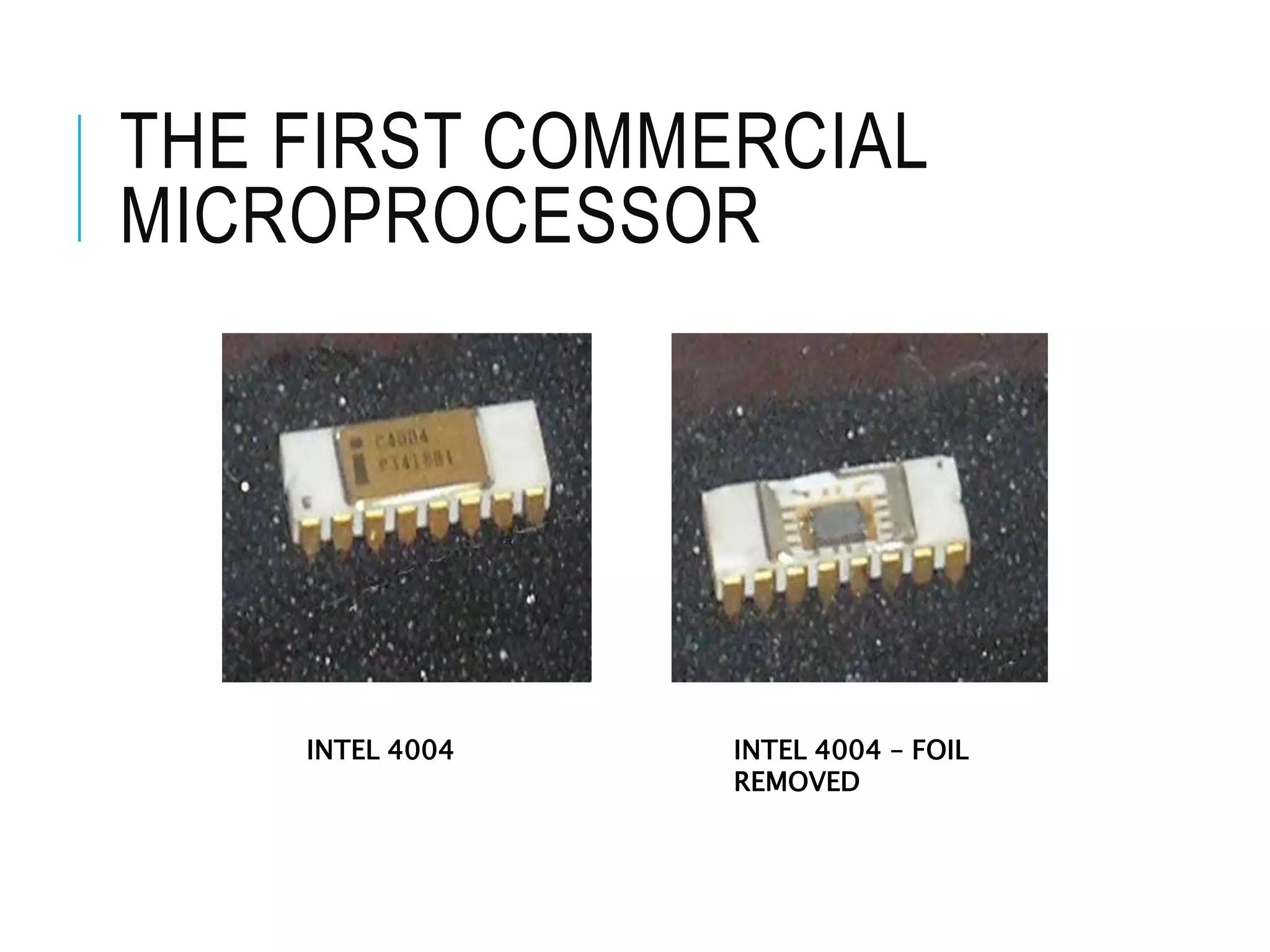
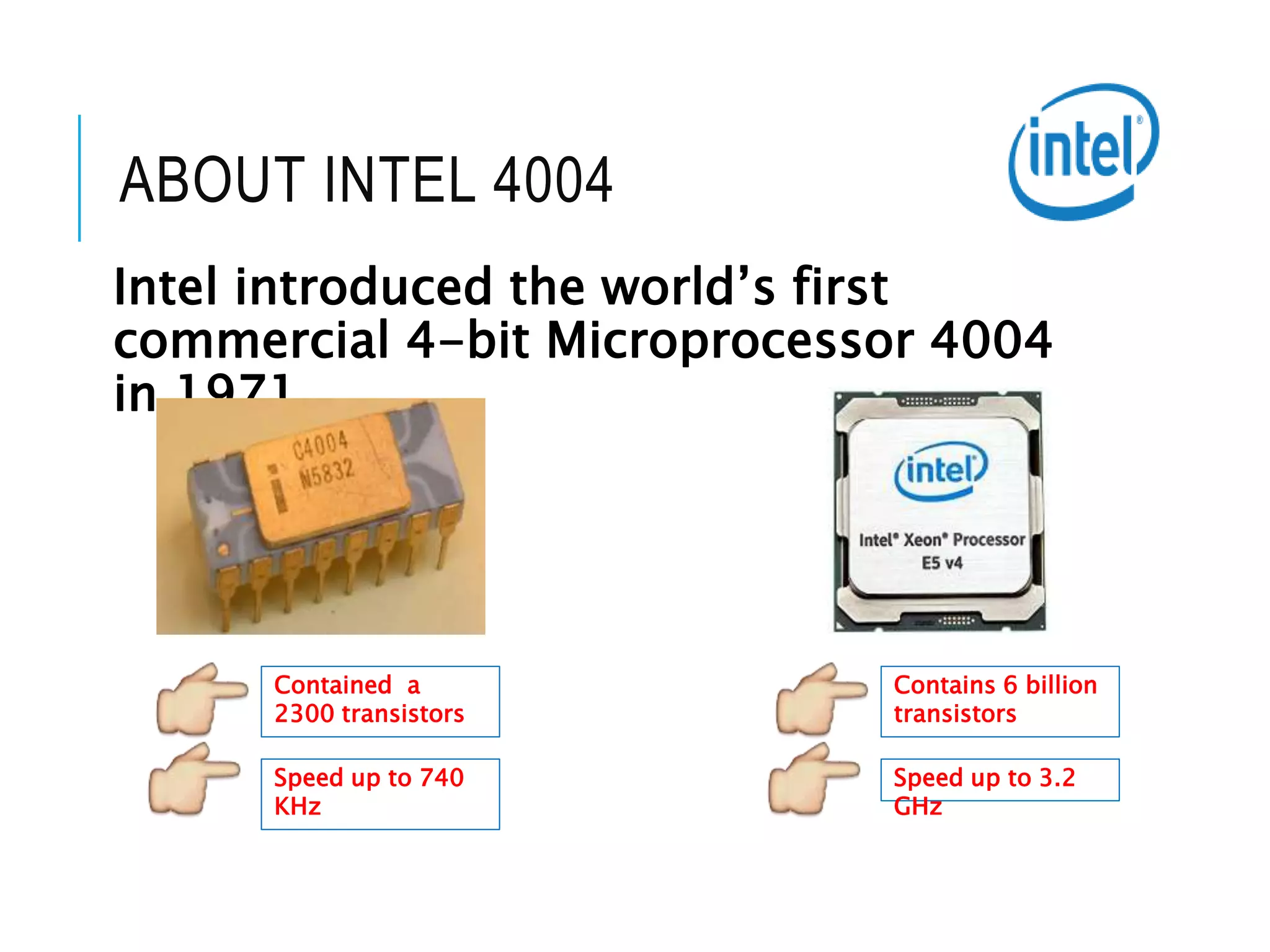
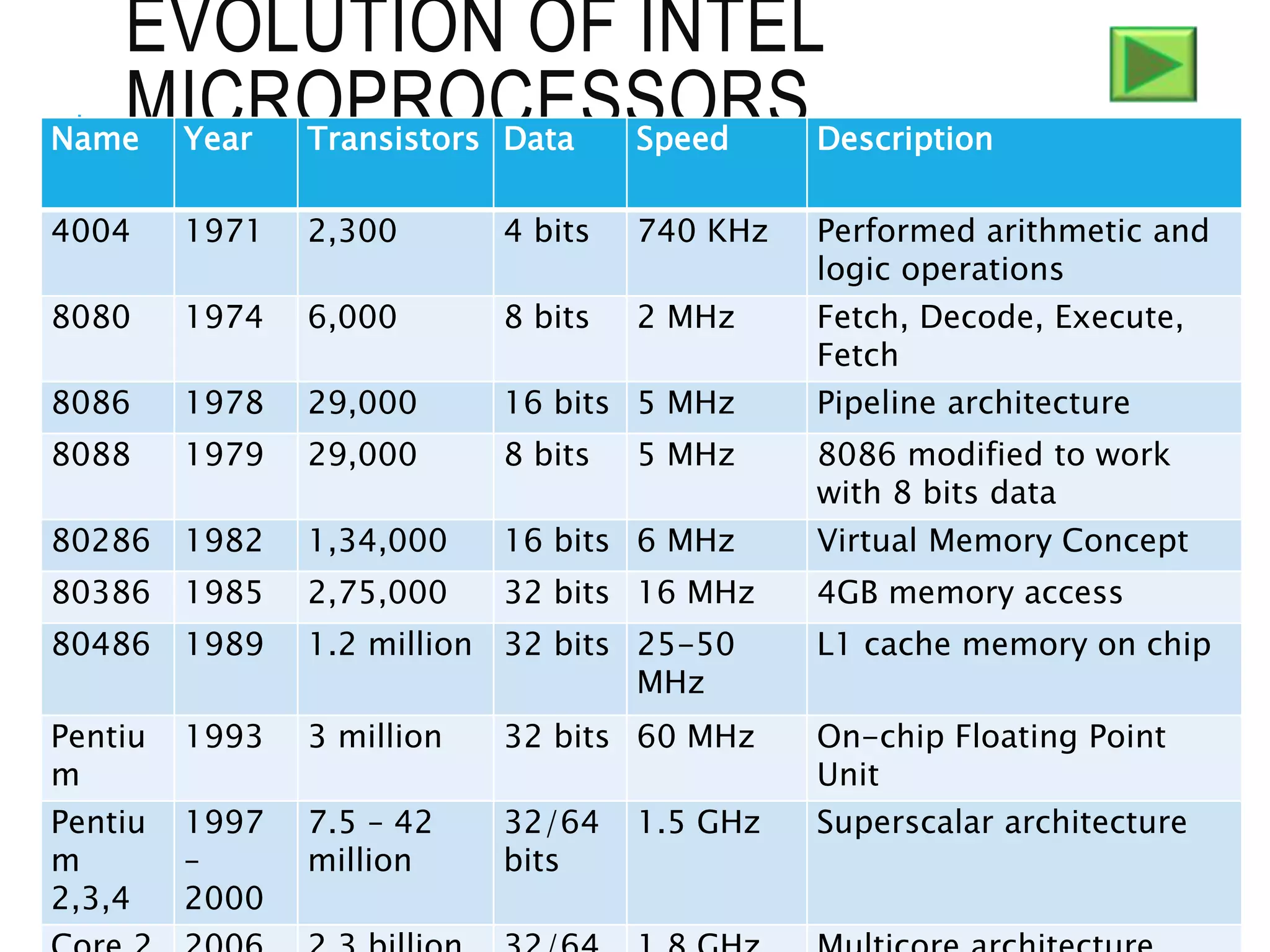
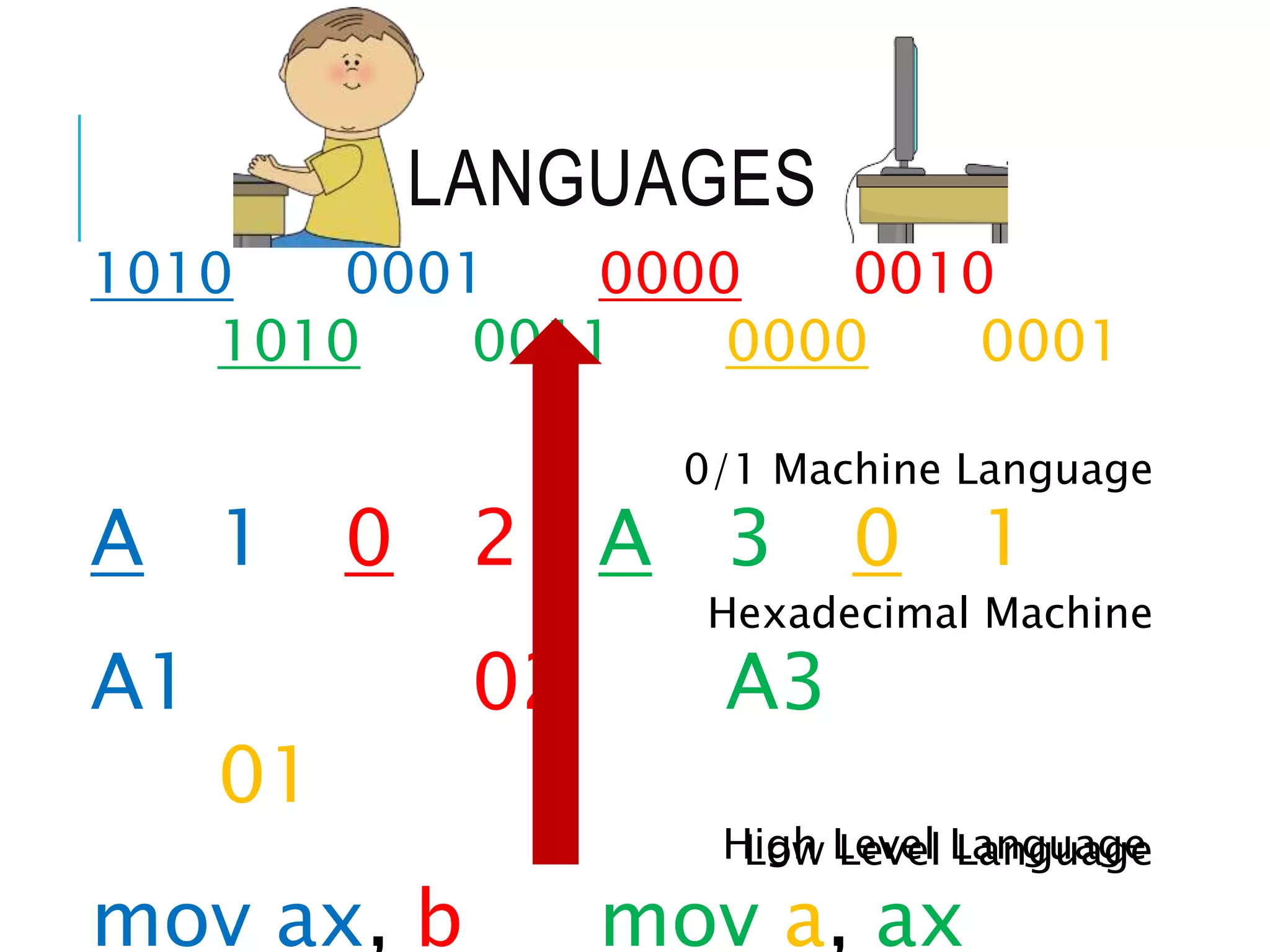
This document provides information about microprocessors and their evolution. It discusses how millions of transistors on a single chip can perform arithmetic and logical operations. The world's first microprocessor was developed in 1968-70 for use in military aircraft. Intel later launched the first commercial microprocessor, the Intel 4004, in 1971. The document traces the evolution of Intel microprocessors from the 4004 through various generations and models. It describes how microprocessors are used in a wide range of devices and outlines the key topics to be covered in a course on microprocessors.