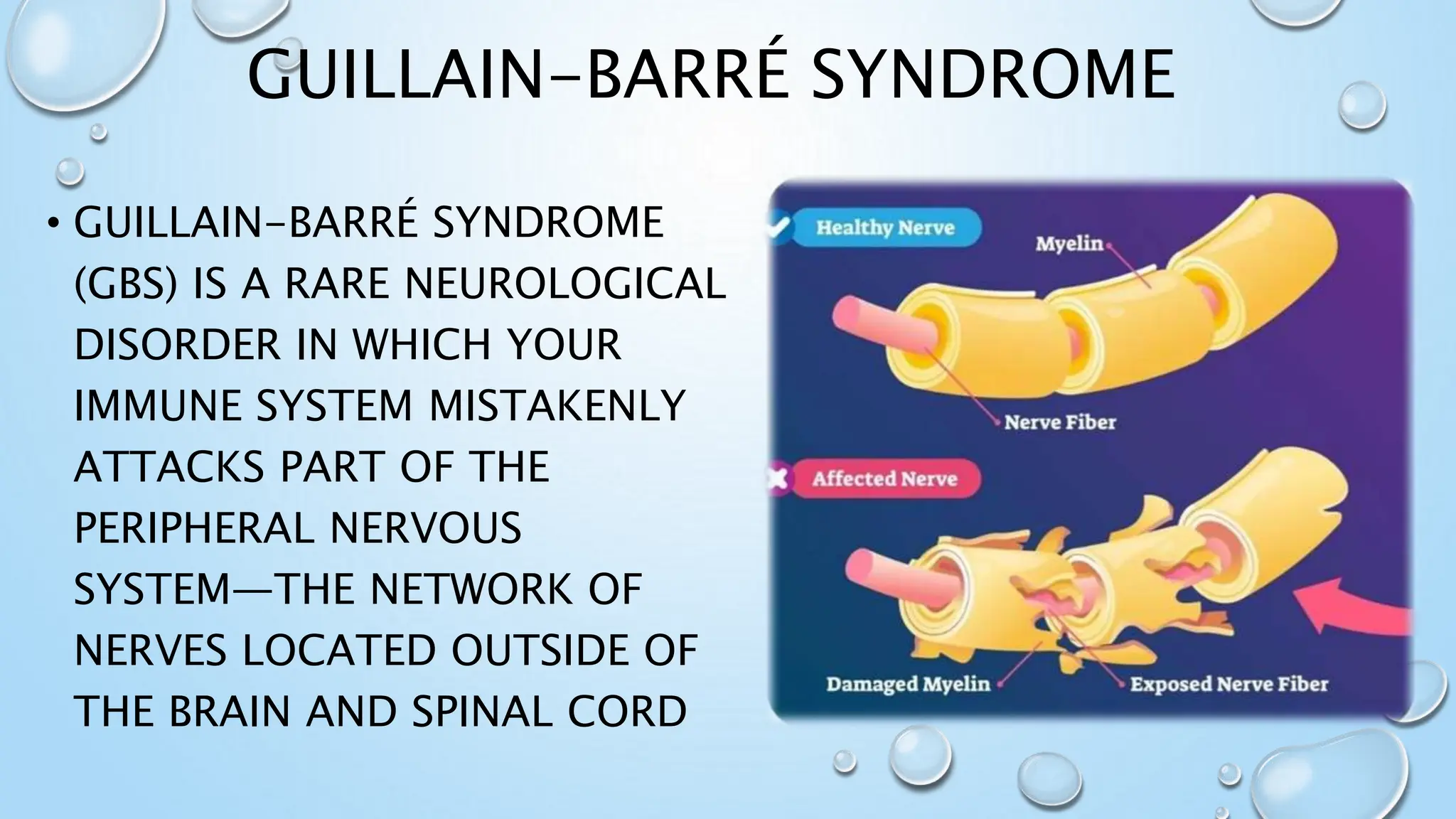
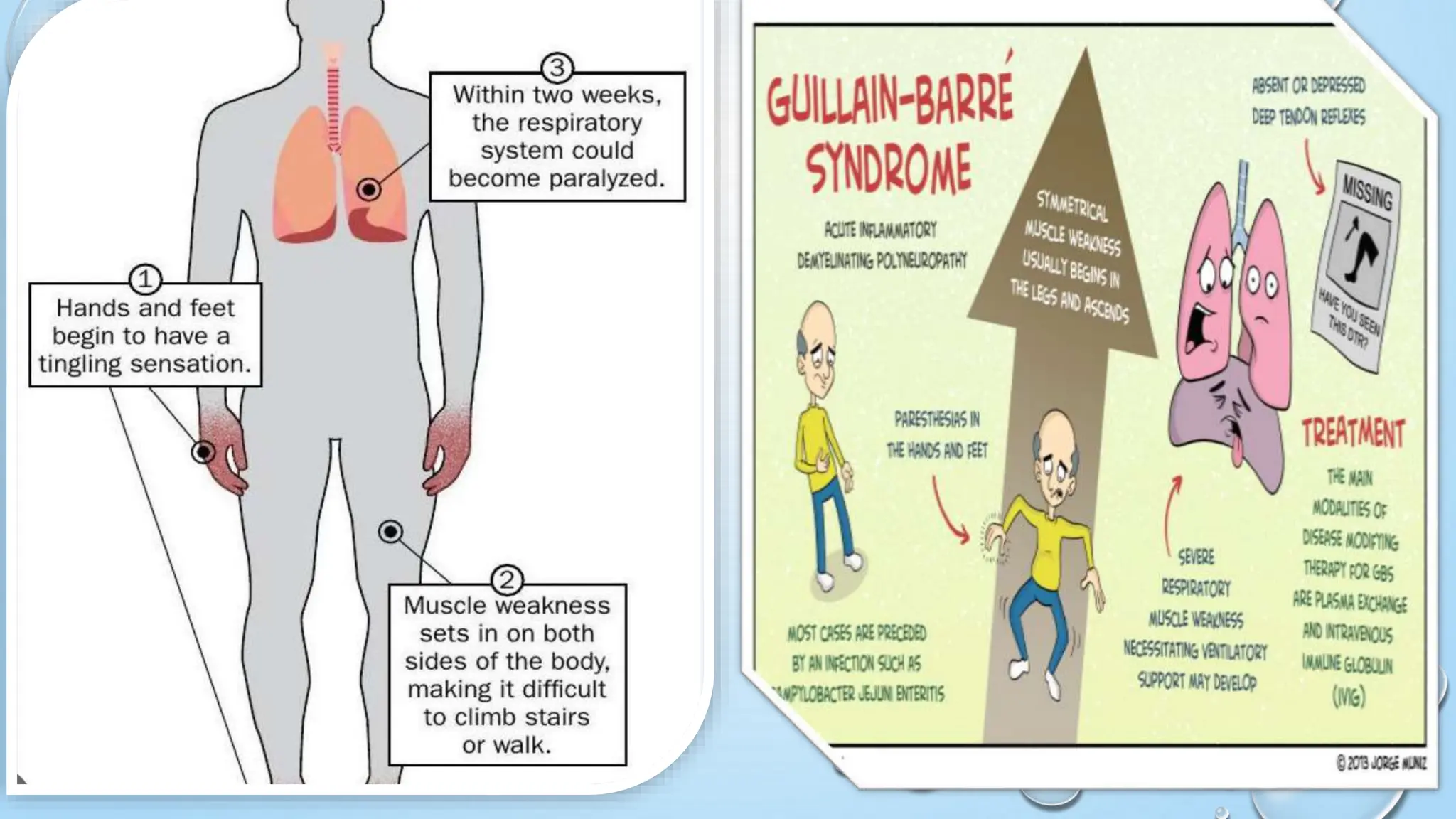
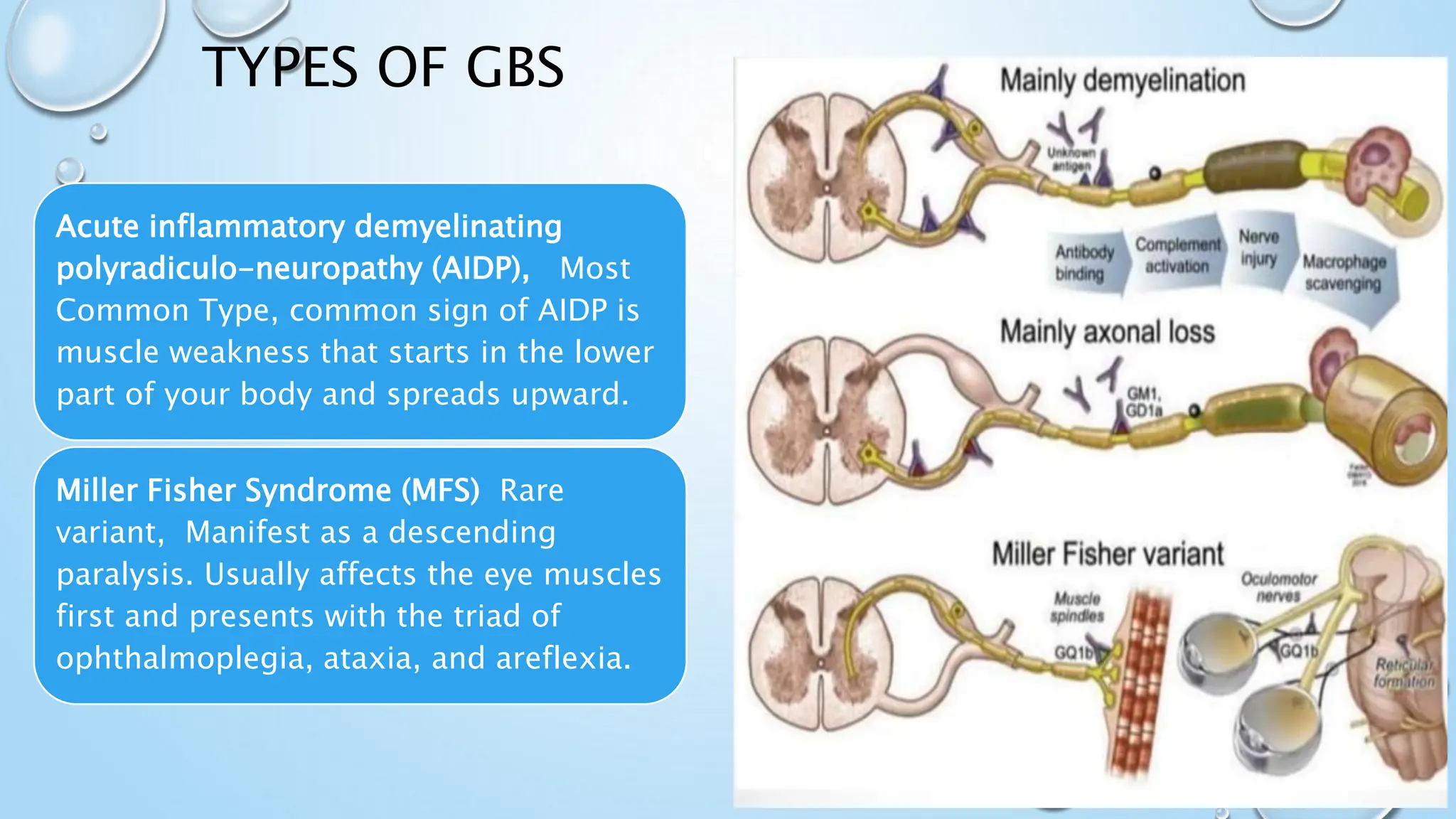
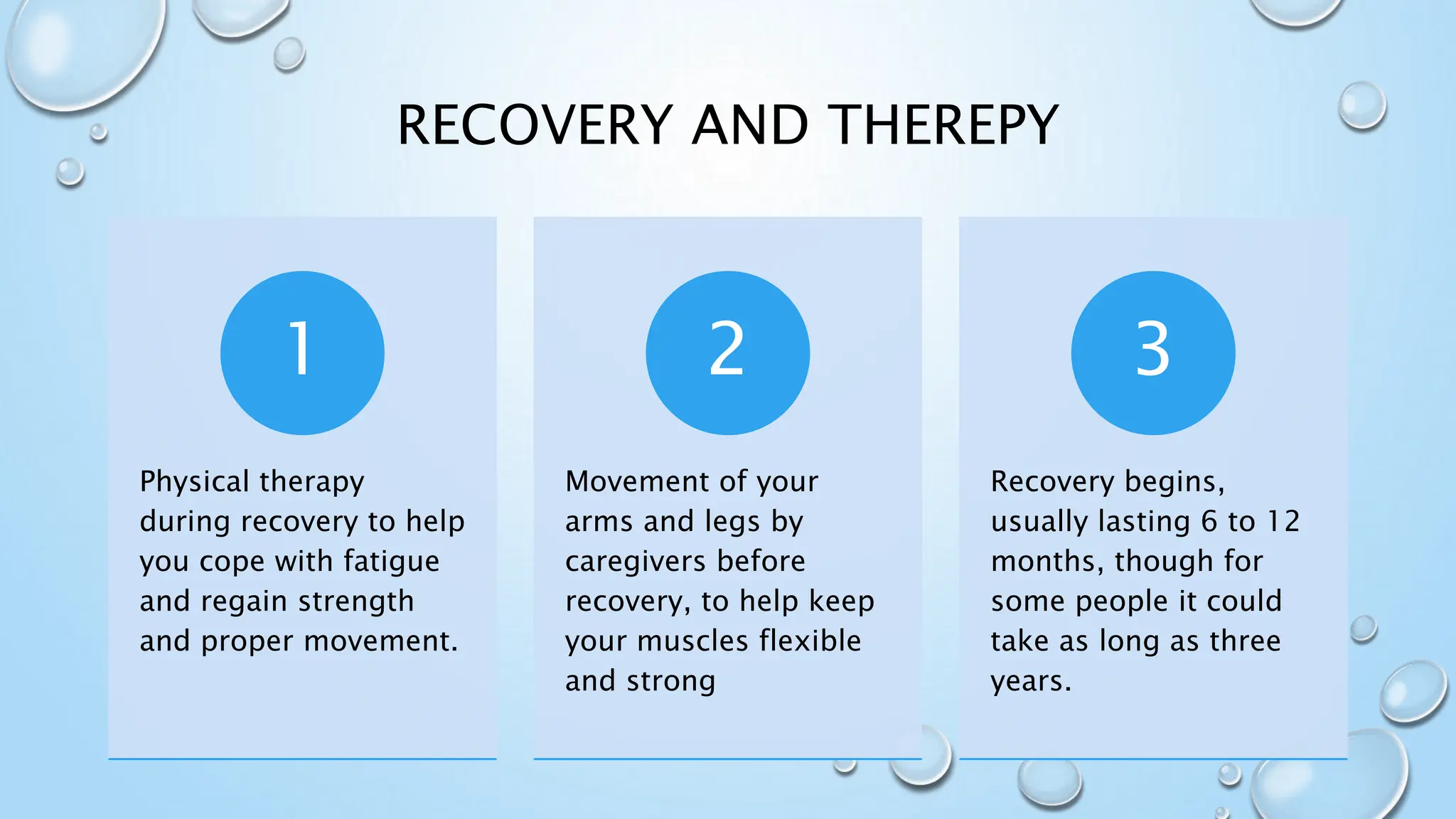
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder where the immune system attacks the peripheral nervous system, causing symptoms such as muscle weakness, difficulty walking, and facial movement issues. The most common causes include infections (particularly with Campylobacter) and can develop into different forms like AIDP and MFS. Diagnosis involves nerve conduction studies, spinal taps, and electromyography, while treatment options include plasmapheresis and immunoglobulin therapy, with recovery often taking several months to years.