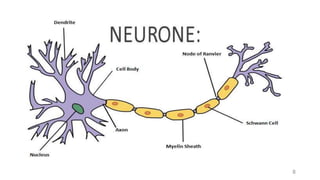
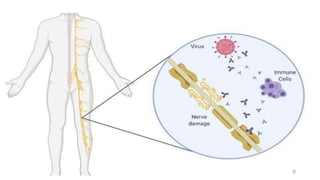
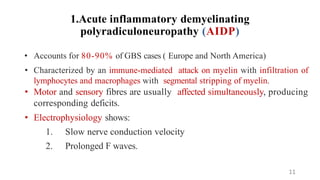
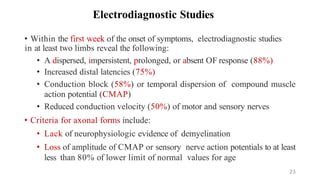
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is an acute inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy that causes weakness and diminished reflexes as the immune system attacks the nerves. It is usually preceded by a viral or bacterial infection. There are different subtypes depending on whether the myelin sheath or axons are affected. Diagnosis involves physical exam, lumbar puncture showing elevated proteins, and electrodiagnostic studies. Treatment involves plasma exchange or IV immunoglobulin to modulate the immune system. Most patients require hospitalization but most make a full recovery, though some experience long-term weakness or paralysis.