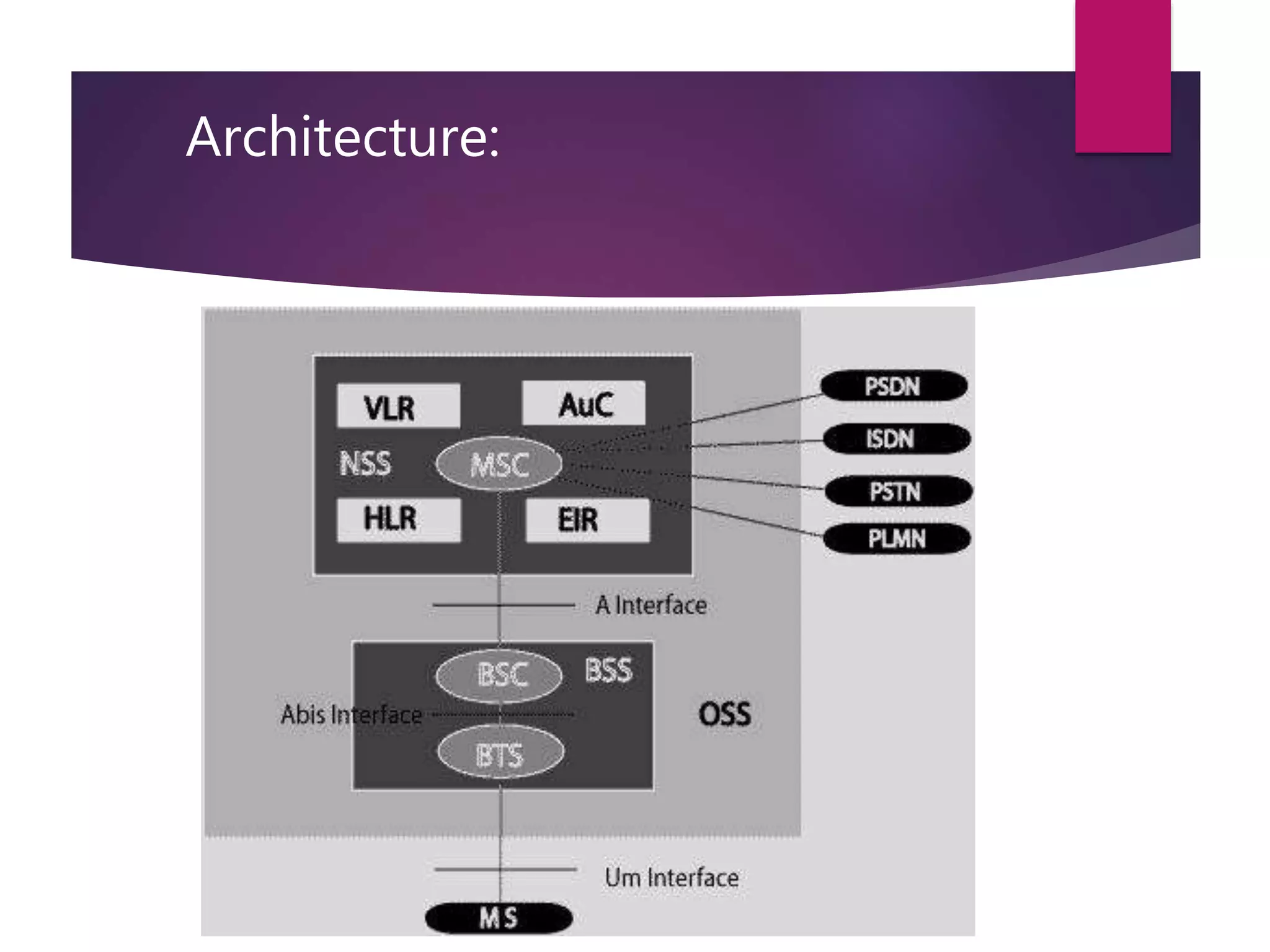
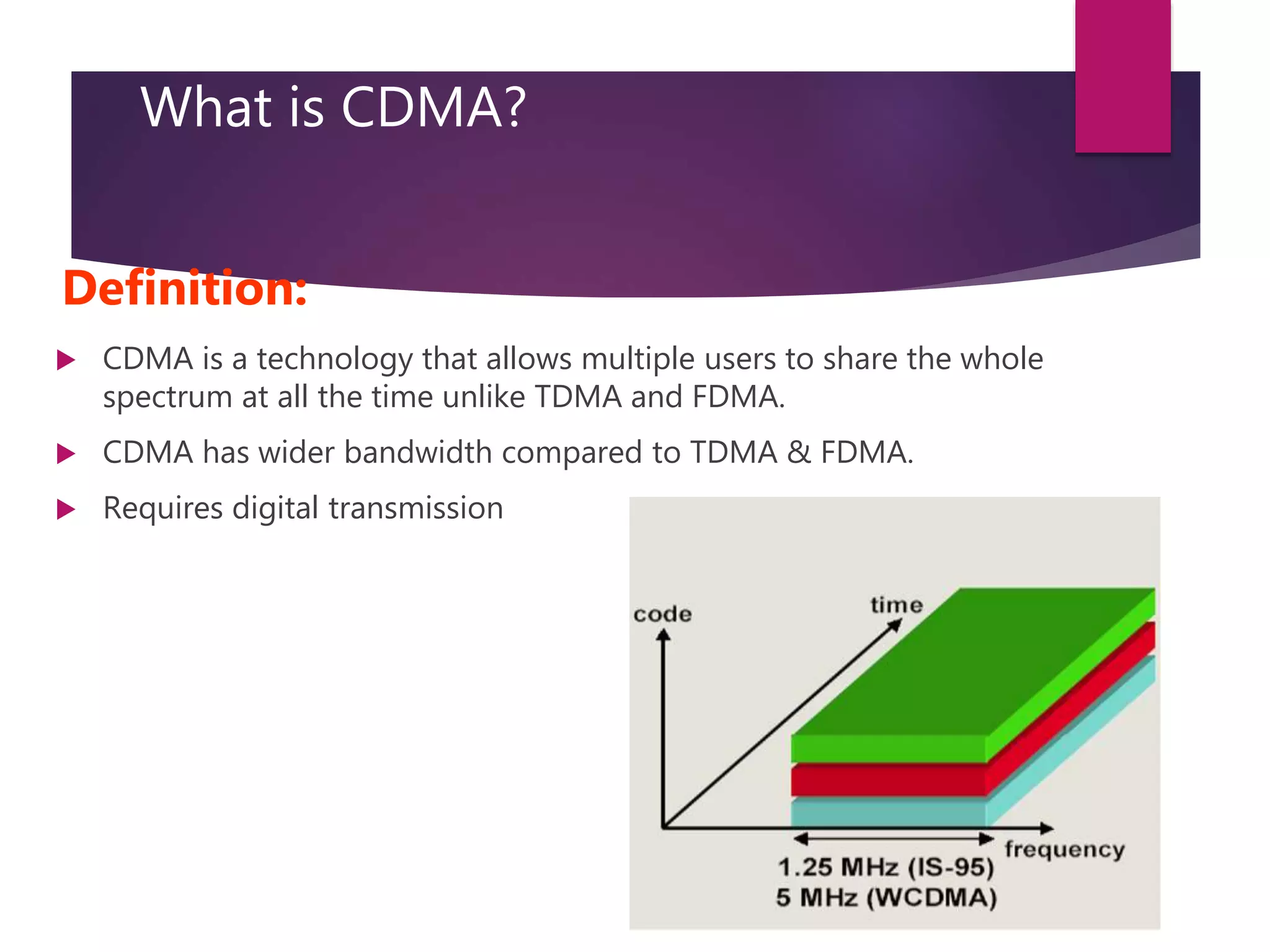
This document compares and contrasts three mobile communication technologies: GSM, TDMA, and CDMA. GSM is a digital cellular standard that uses TDMA and operates in the 900/1800MHz bands. TDMA allows multiple users to share the same frequency channel by dividing transmissions into time slots. CDMA differs in that it allows all users to transmit over the whole spectrum simultaneously by assigning each user a unique spreading code.