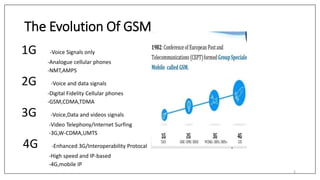
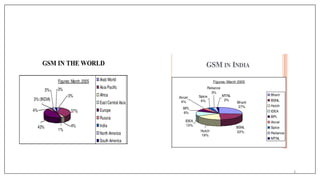
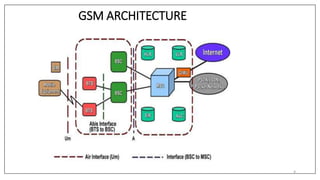
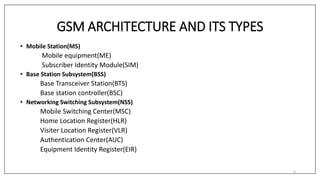
GSM was developed in the 1980s by the Conference of European Posts and Telecommunications (CEPT) to standardize pan-European mobile networks. The first GSM specifications were published in 1990. Phase 2 in 1995 extended coverage to rural areas. GSM introduced digital cellular technology and allowed for improved voice quality and expanded data communication services compared to earlier analog networks. The core network components include the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), Home Location Register (HLR), Visitor Location Register (VLR), and Authentication Center (AUC).