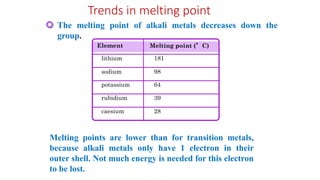
The document summarizes the properties and reactivity of alkali metals. It discusses their physical properties including softness, low density, and good heat and electricity conductivity. It describes their chemical reactivity including reactions with oxygen, halogens, nitrogen, carbon, and water. Alkali metals readily lose their outer shell electron to form +1 ions. Their reactivity increases down the group as atomic size increases. Common compounds include oxides, hydroxides, peroxides, and superoxides. Sodium and potassium are the most abundant in nature while lithium, rubidium, and cesium are rarer.



![Electron structure
All alkali metals have 1 electron in their outer shell.
H: 1s1
[He]2s1
[Ne]3s1
[Ar]4s1
⚫ They can easily obtain a full outer shell by losing 1 electron.
⚫ They lose their outer shell electron in reactions to form positive
ions with a +1 charge.
⚫ They have similar physical and chemical properties.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupia-230103154546-5d417bbf/85/Group-IA-pdf-4-320.jpg)







![These metals are very active metals, so they do not
present as free metals, but present at compounds in
nature.
+ Na and K are popular metals on earth:
the compounds contain Na and K are sea water,
rock salt xinvinit NaCl.KCl, carnallite
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O, Na2CO3, KNO3, NaNO3.
+ Li, Rb, Cs are rare metals, they present at
alumosilicate M2[Al2Si4O12].H2O: Li+, Rb+, Cs+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupia-230103154546-5d417bbf/85/Group-IA-pdf-13-320.jpg)





