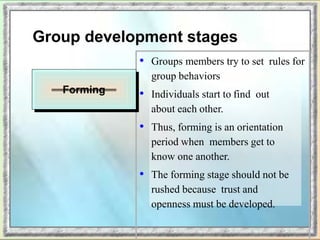
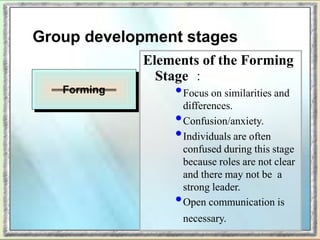
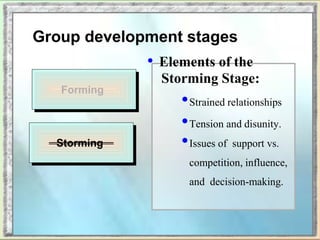
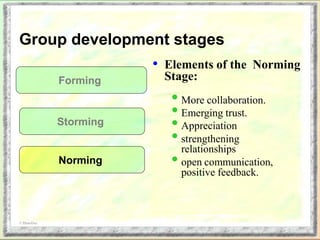
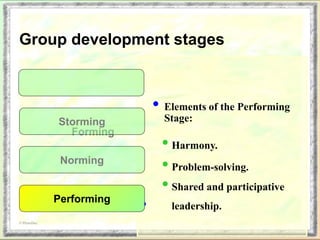
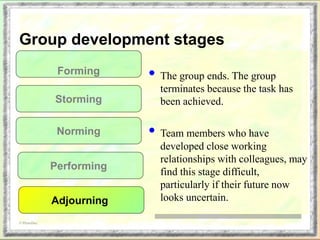
The document discusses group dynamics and the stages of group development. It describes how groups form when individuals come together for a common purpose or task. Group dynamics refers to the interactions and relationships between members. There are typically five stages of group development: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. In the forming stage, members orient themselves to the group and each other. Storming involves conflicts as members struggle for power and leadership. During norming, trust and cohesion develop as roles and processes are established. In performing, the group works cooperatively and is productive. Finally, adjourning occurs when the group disbands after completing its task. The nurse manager's role involves understanding group dynamics to facilitate discussions