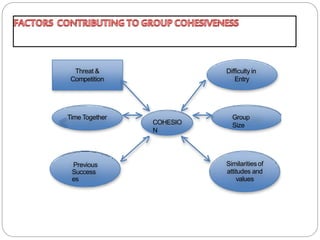
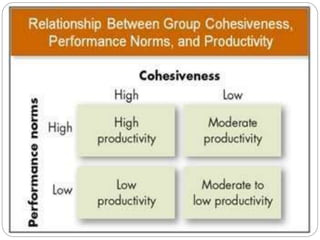
Group cohesiveness refers to the bonding of group members to one another and the degree to which members are motivated to stay in the group. It develops through communication, shared interests, and a sense of "we-ness". Dimensions of cohesiveness include group unity, attraction between members, and commitment to working together towards shared goals. Factors that increase cohesiveness are threats from outside the group, difficulty entering the group, time spent together, previous successes, and similarities between members. Benefits include higher morale and productivity, while disadvantages can be personality clashes and struggles for power. Cohesiveness is strengthened by smaller groups, agreement on goals, and interdependence, and weakened by larger groups and individual rewards.