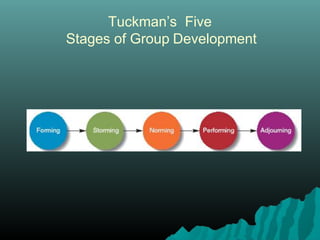
Group dynamics involves how people interact in groups and is influenced by personality, power, and behavior. It helps groups work effectively. There are advantages and disadvantages to both small and large groups. Tuckman's model of group development includes five stages: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. Group norms and cohesiveness impact group dynamics. Social loafing, where people put in less effort in a group, can be reduced through accountability, interdependence, and group identity.