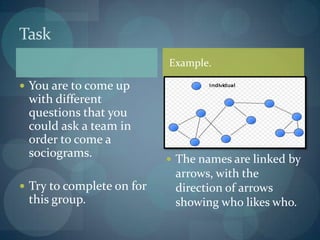
The document discusses cohesion in sports teams and the coach's role in creating an effective team climate. It defines cohesion as the forces that compel members to remain in a group. There are two types of cohesion - task cohesion, which is commitment to achieve common goals like winning, and social cohesion, which is the degree team members like each other. The coach assesses team climate through questionnaires and sociograms, which map members' relationships, and works to build an effective climate to improve performance.