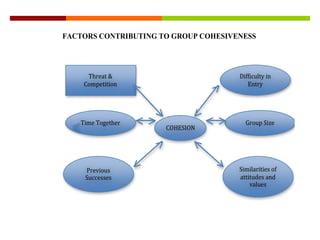
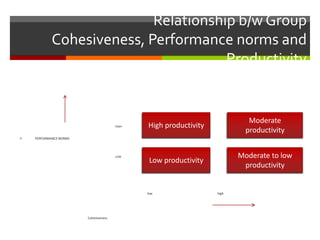
Group cohesiveness refers to the ability of group members to think and act as one, whether physically together or not. It develops from a sense of belonging, attraction to other members, and commitment to working together to achieve shared goals. Factors that contribute to cohesiveness include threats to the group, difficulty entering the group, time spent together, smaller group size, past successes, and similarity of attitudes and values among members. Higher cohesiveness is generally associated with higher performance and productivity up to a moderate level, beyond which it can decrease performance. Ways to increase cohesiveness include agreeing on goals, increasing homogeneity, interactions, competition, and rewarding the group, while decreasing it involves disagreeing on goals,