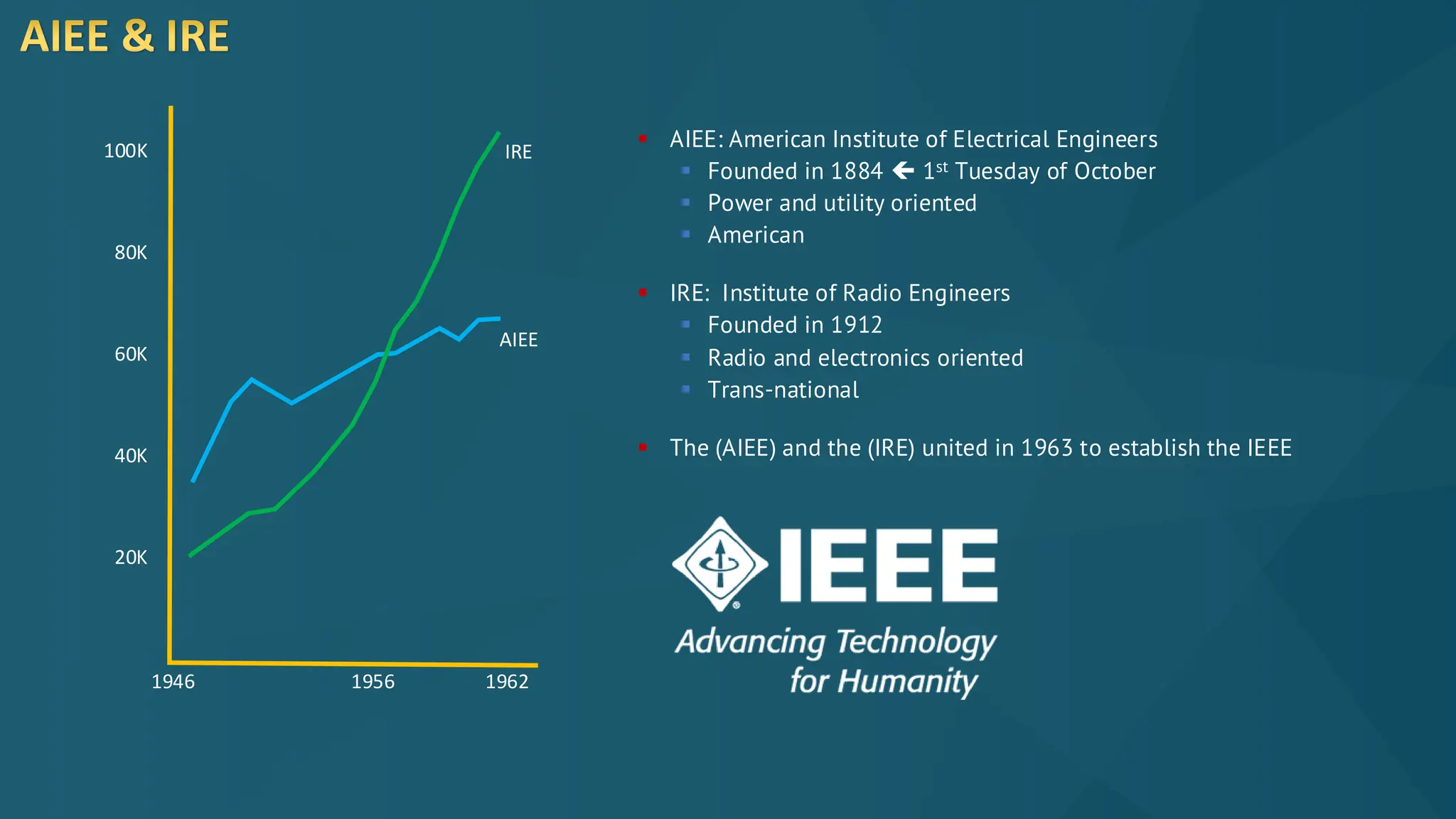
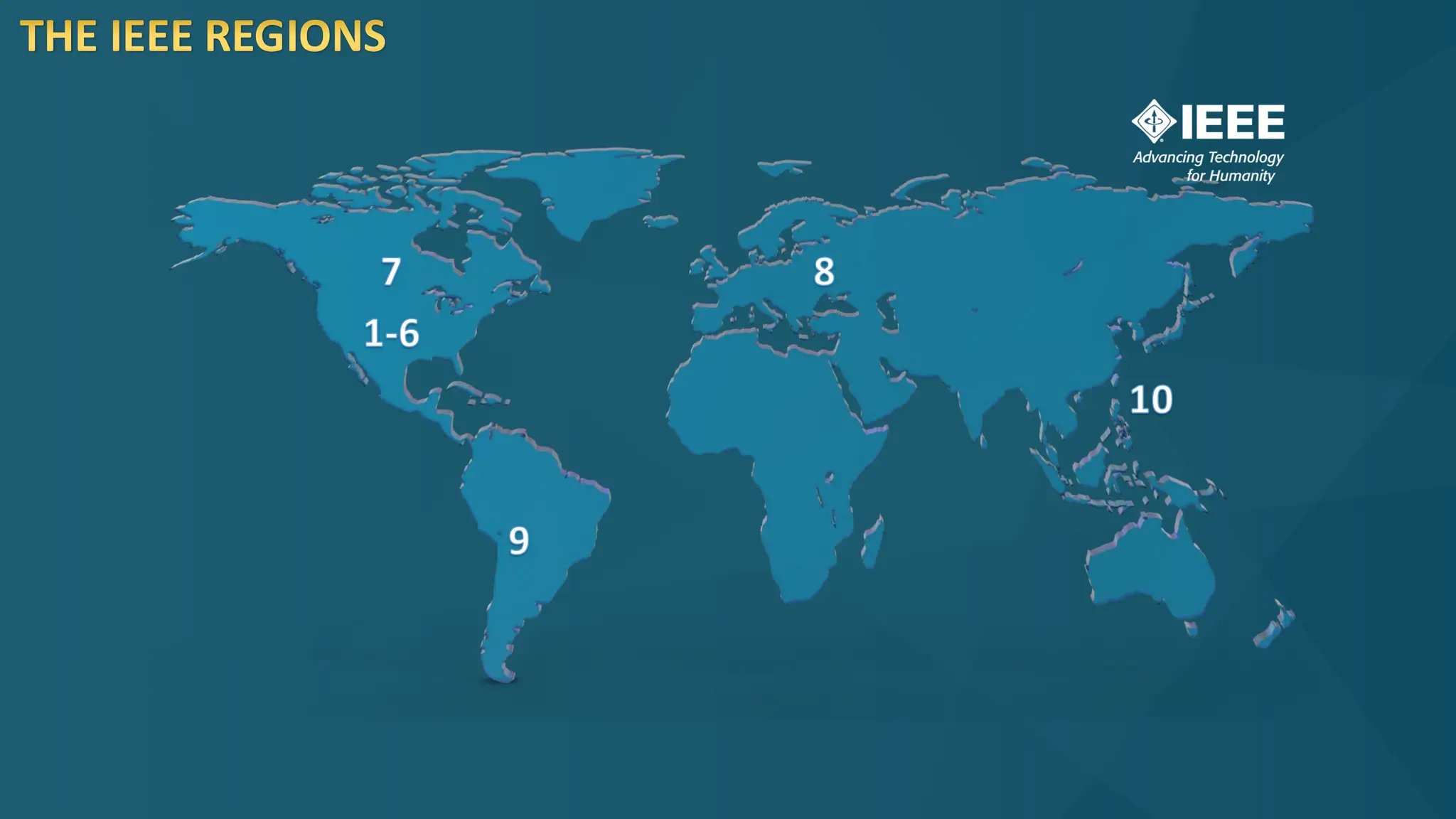
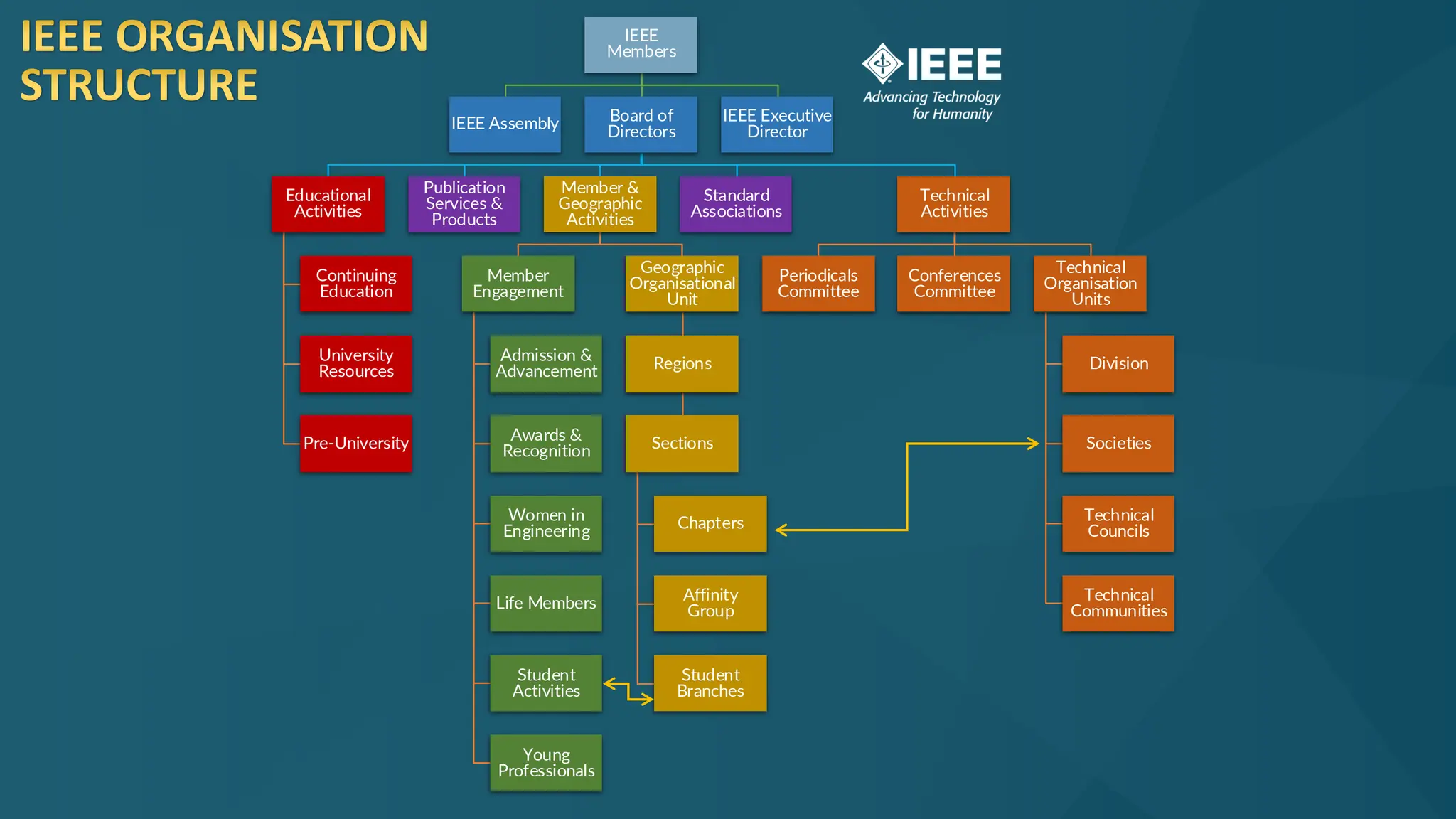
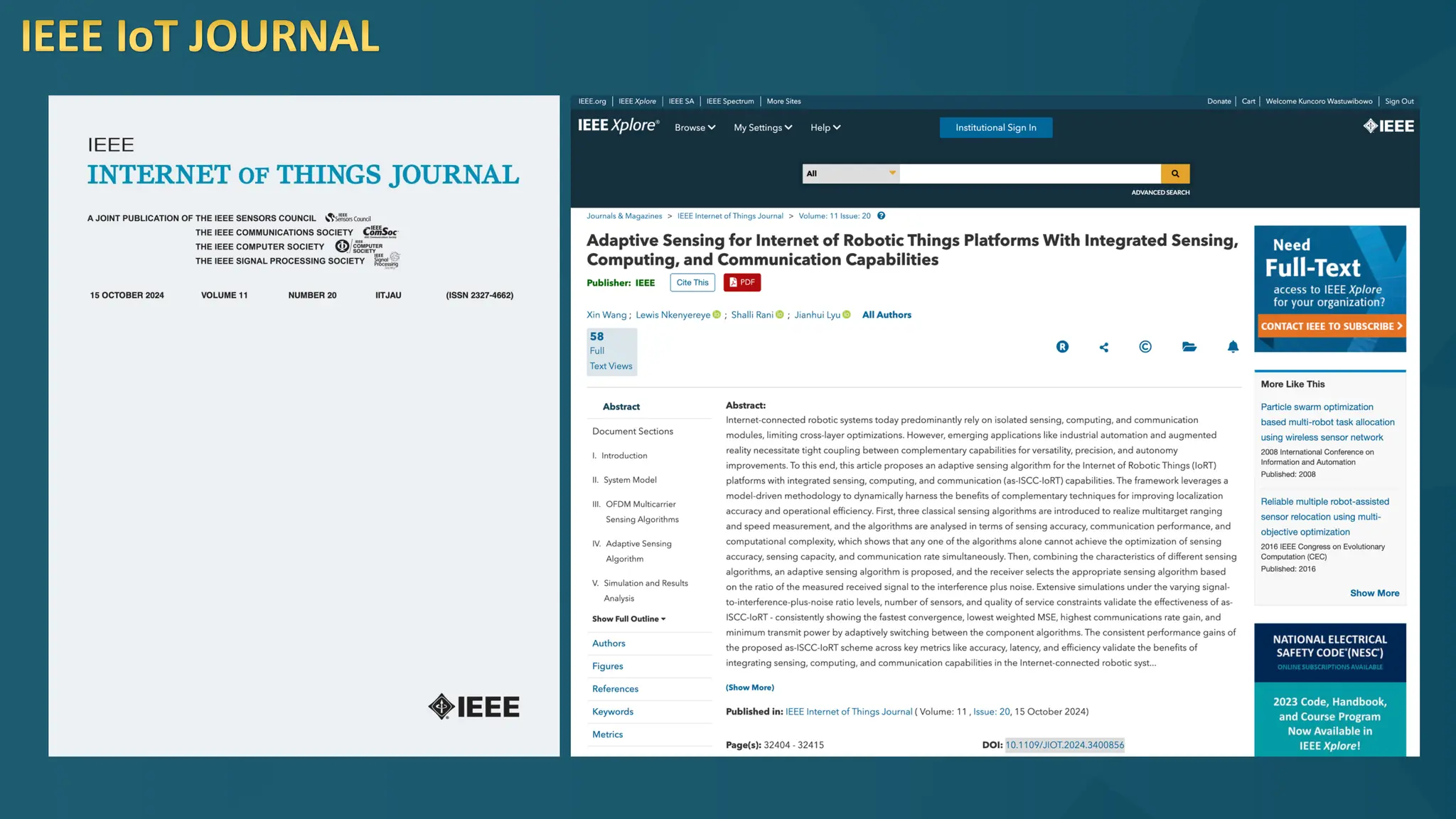
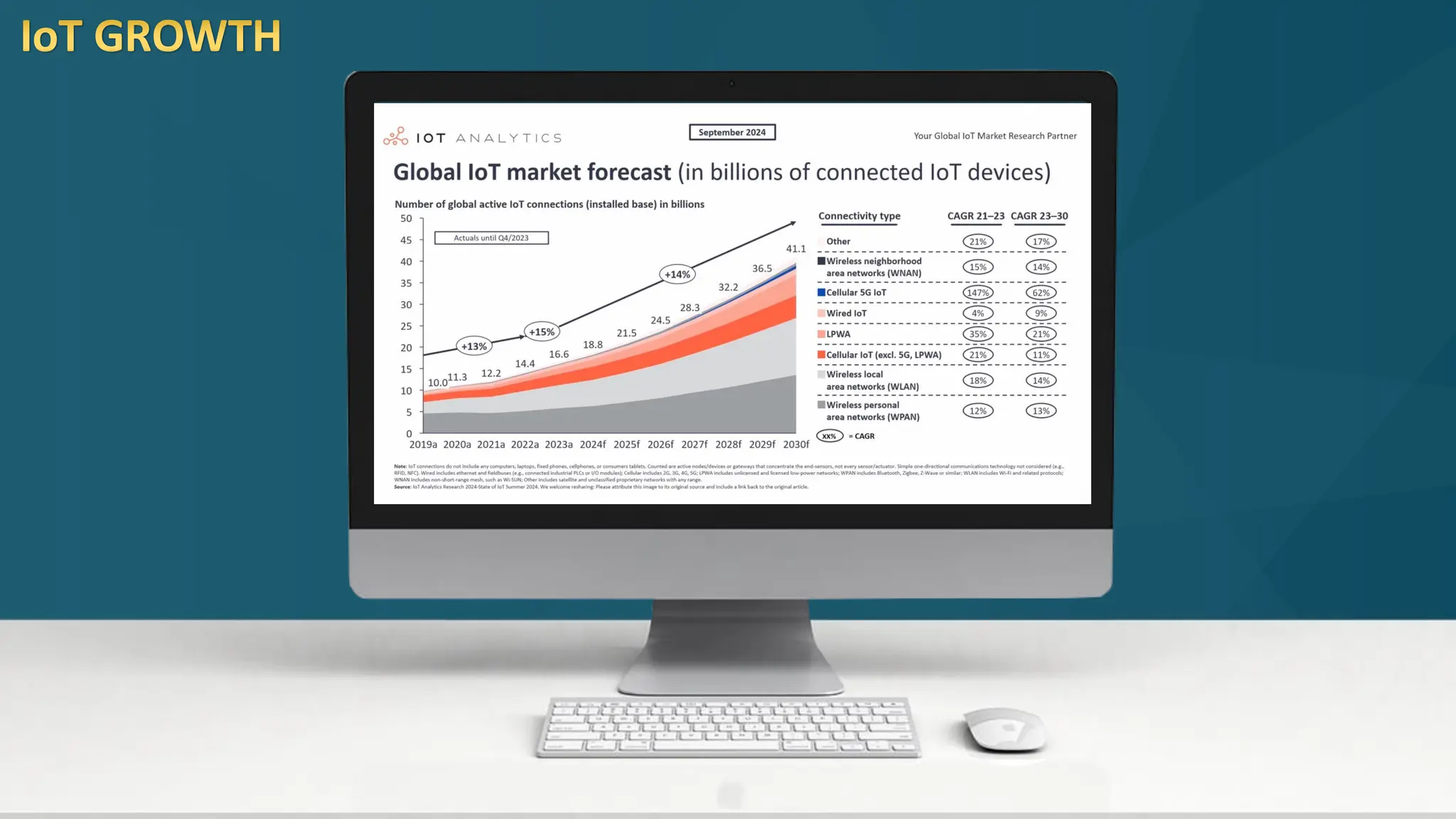
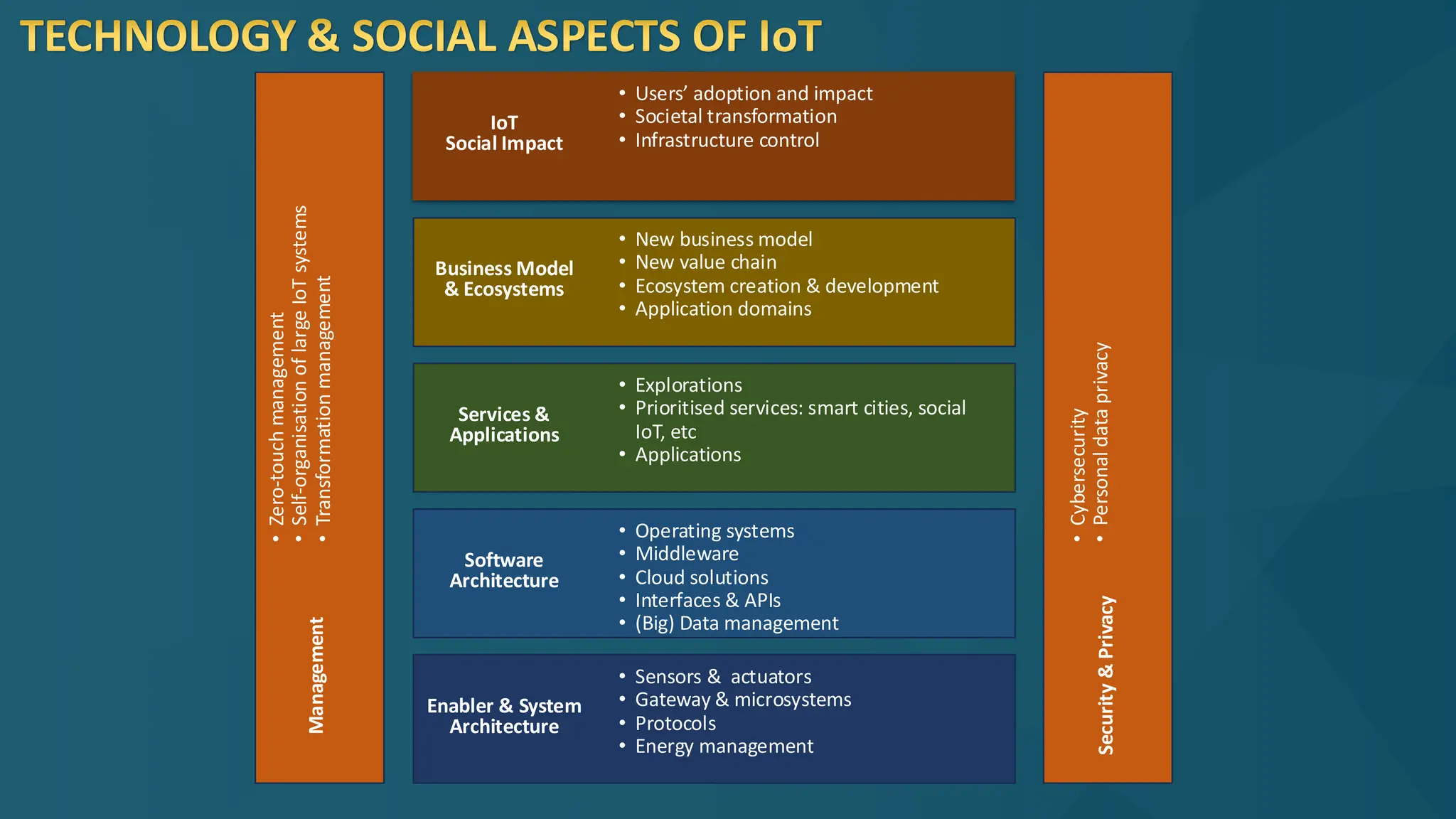
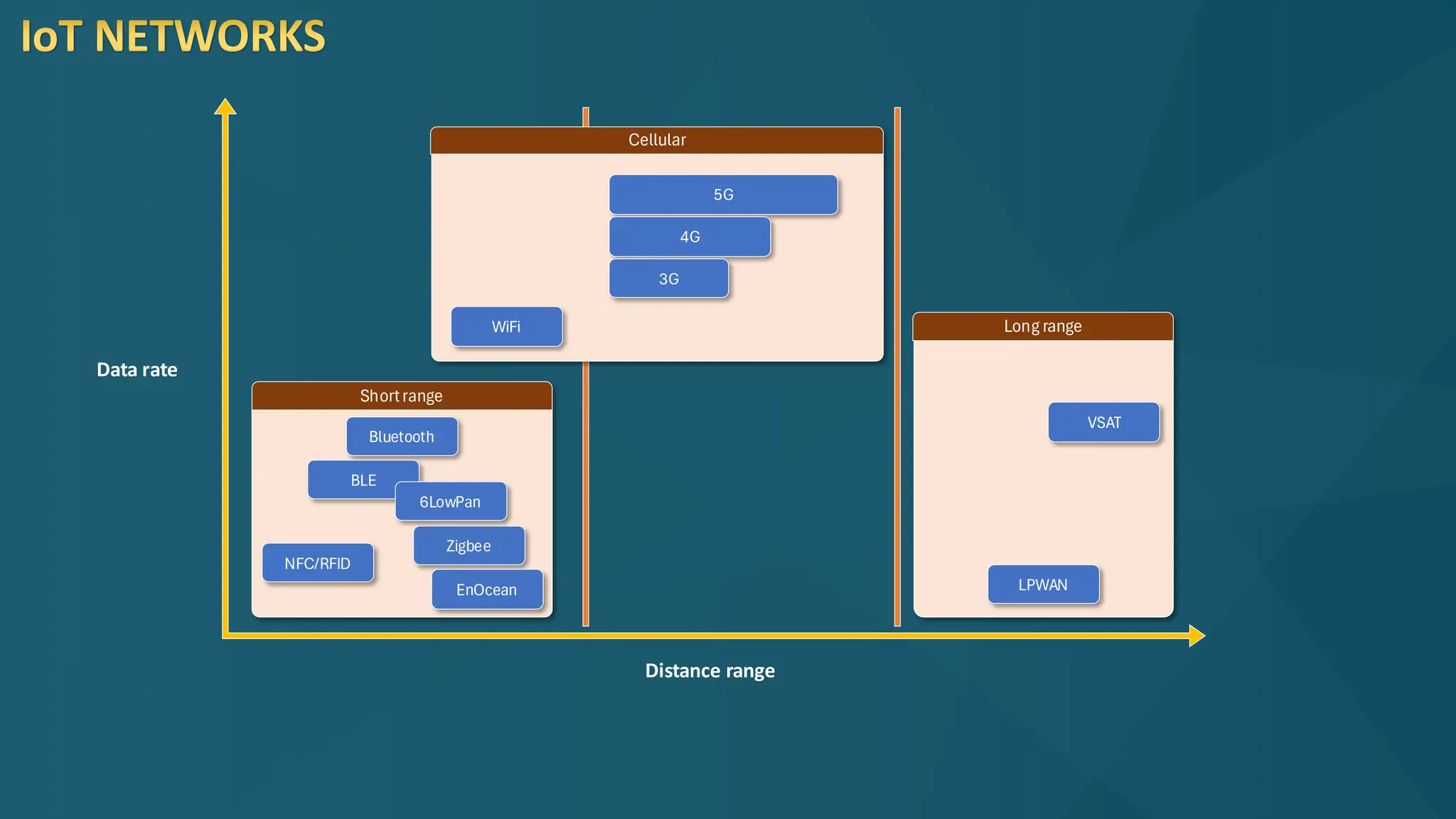
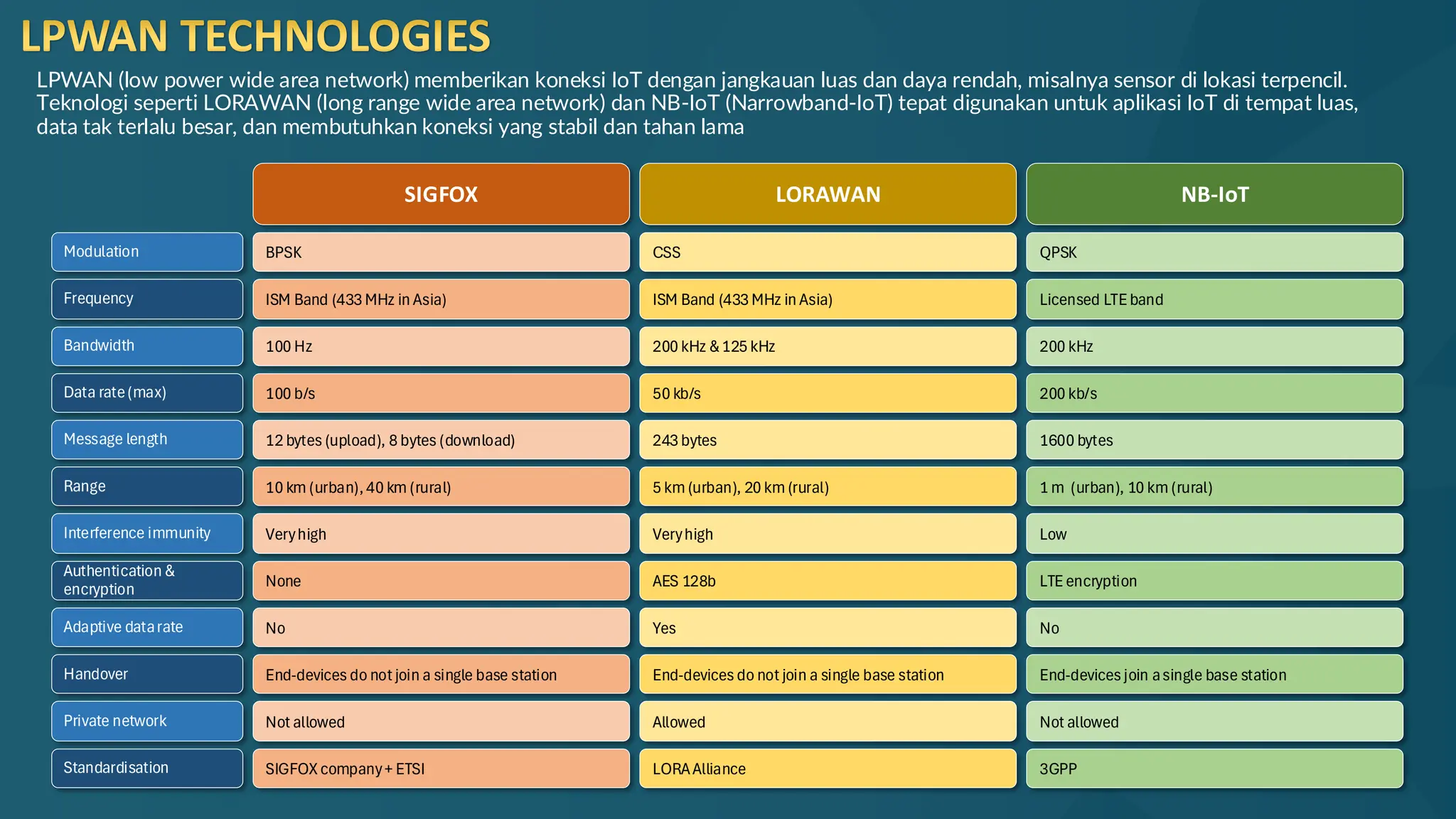
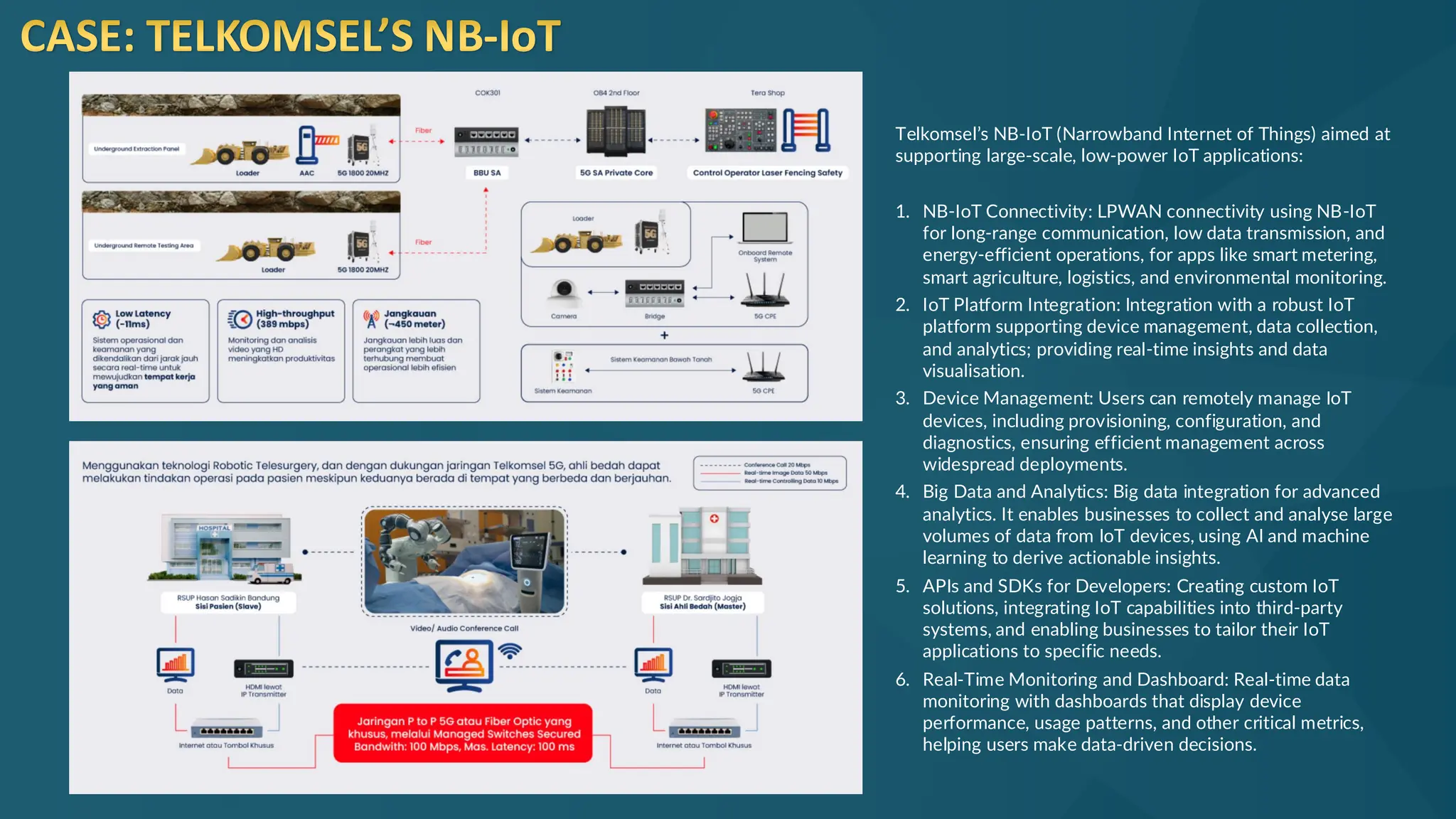
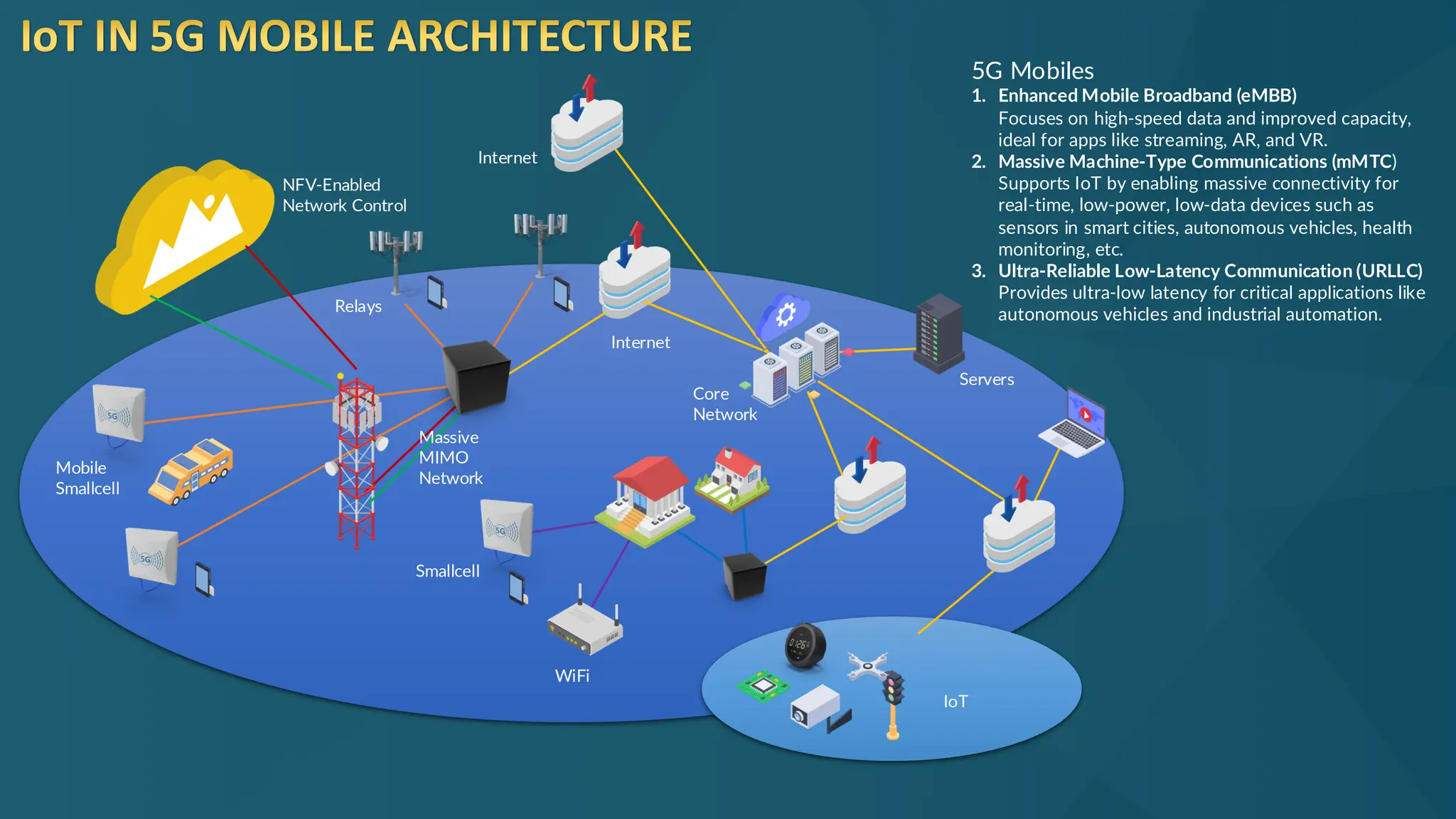
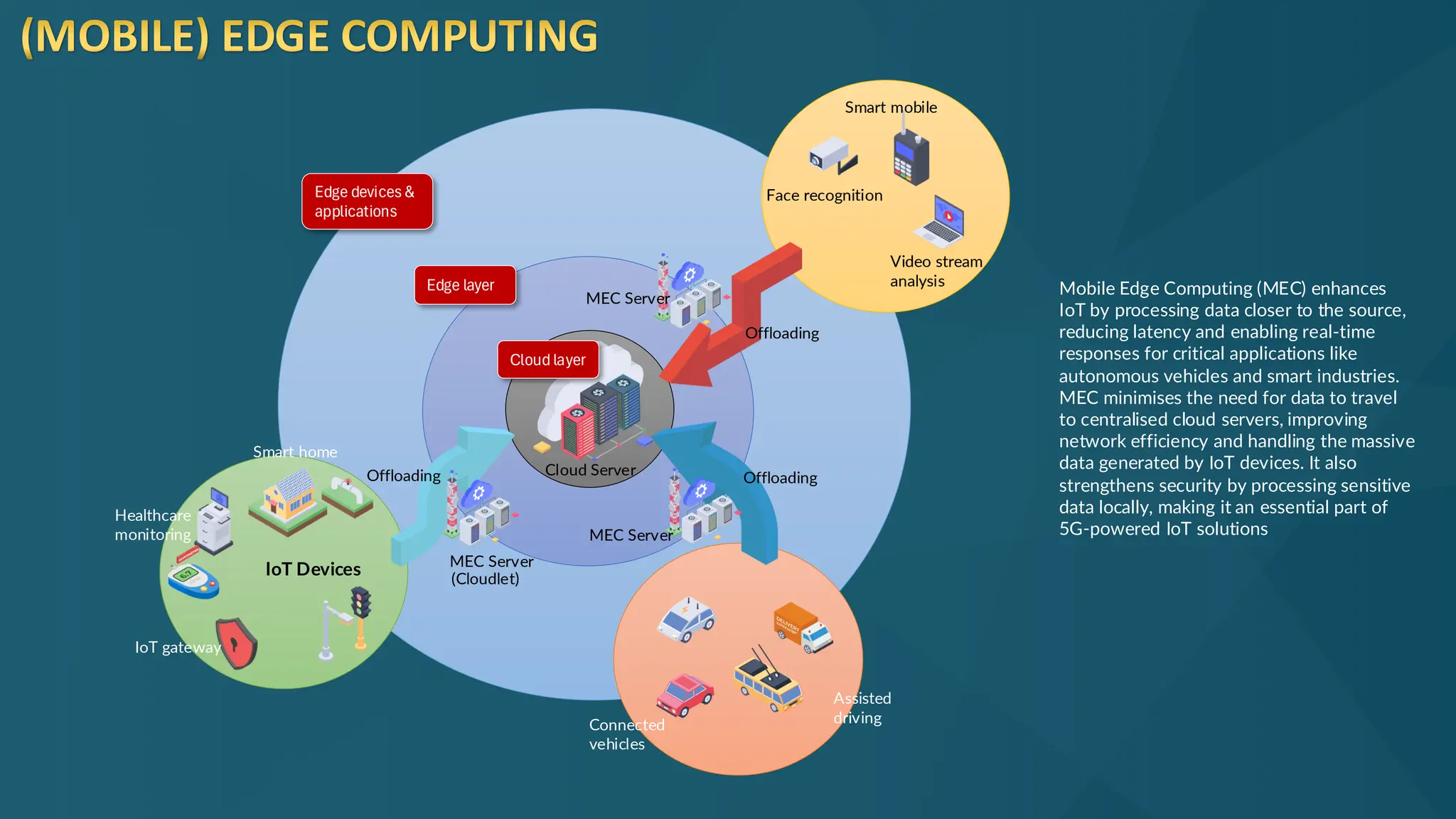
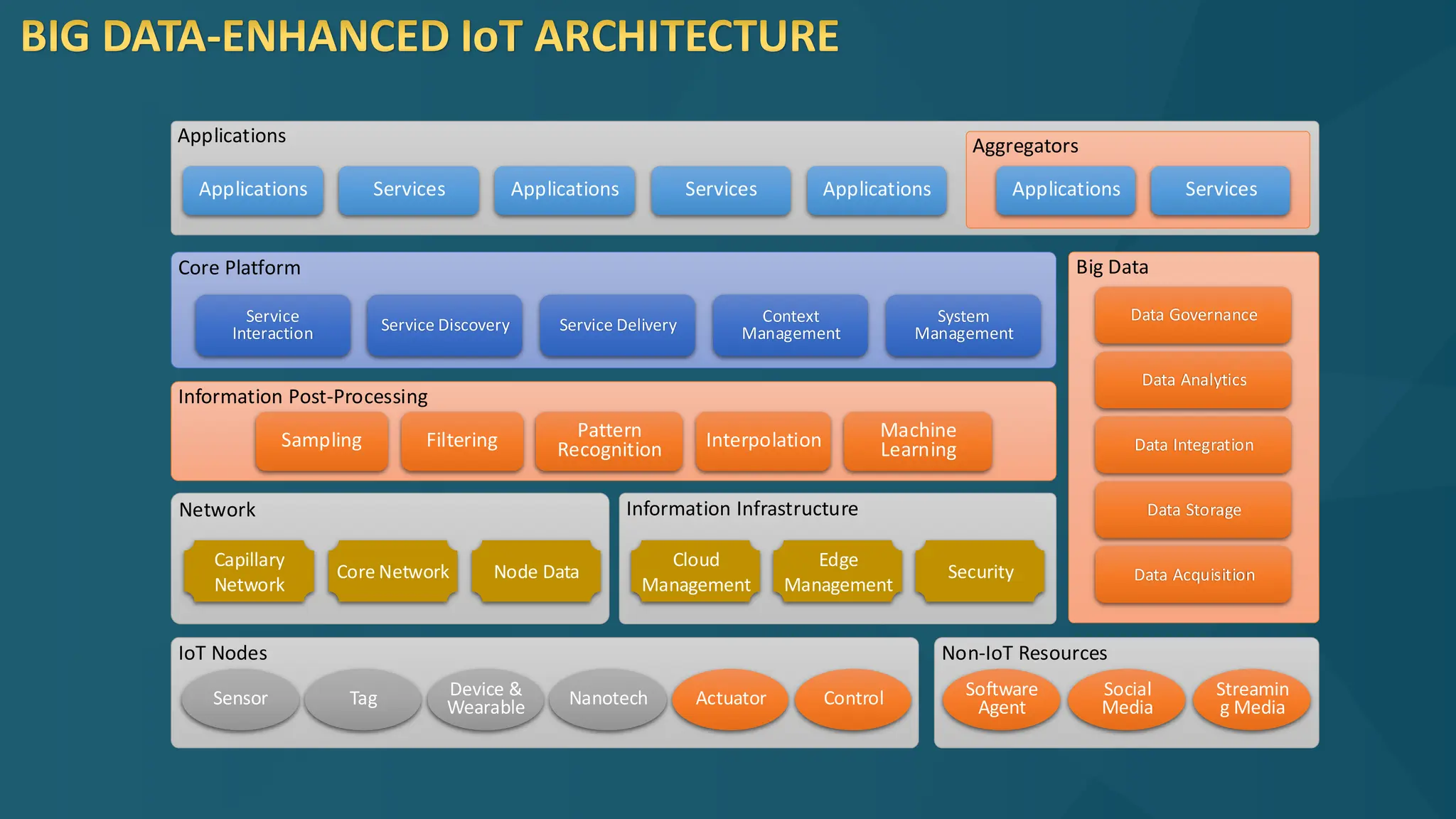
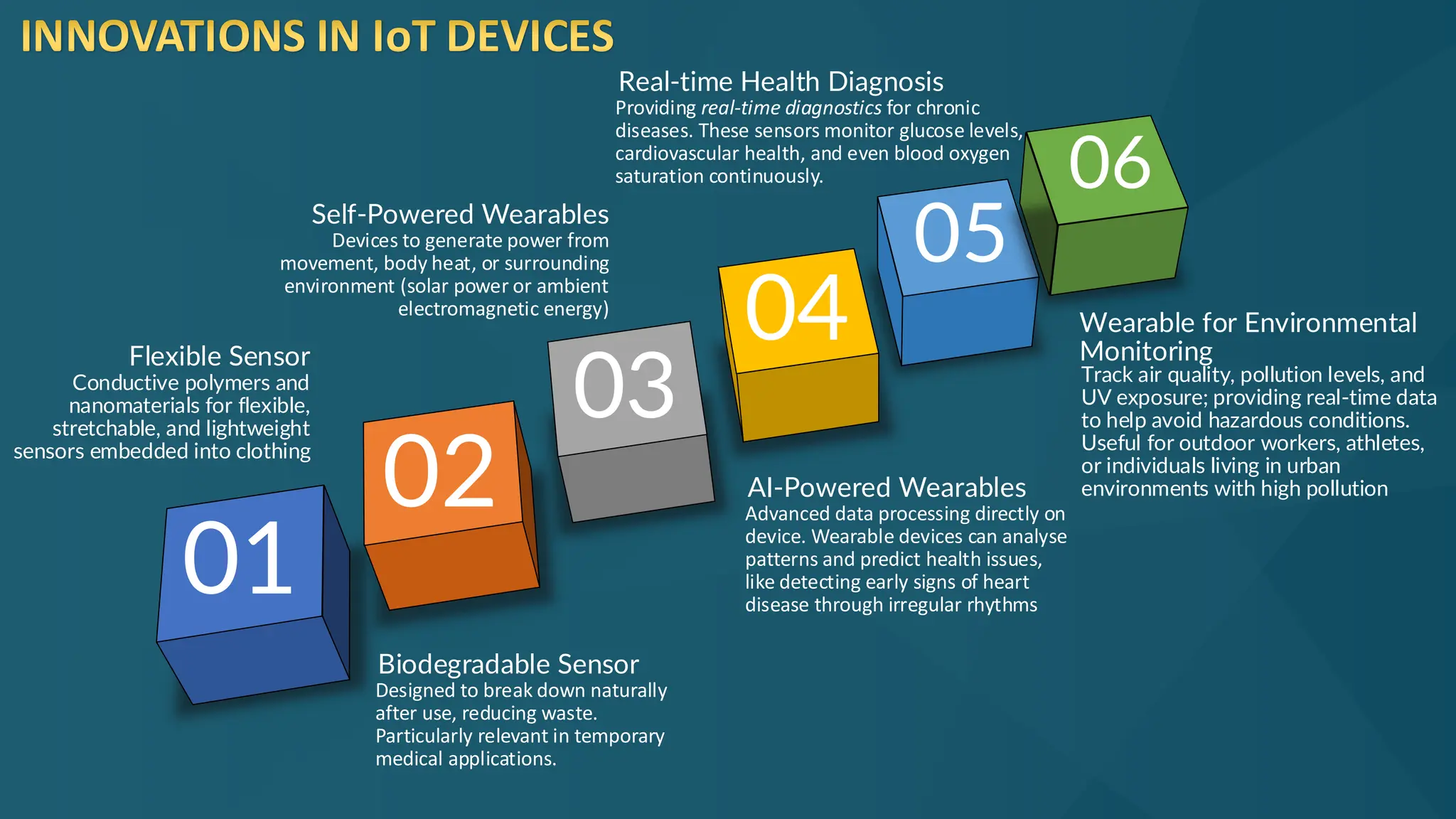
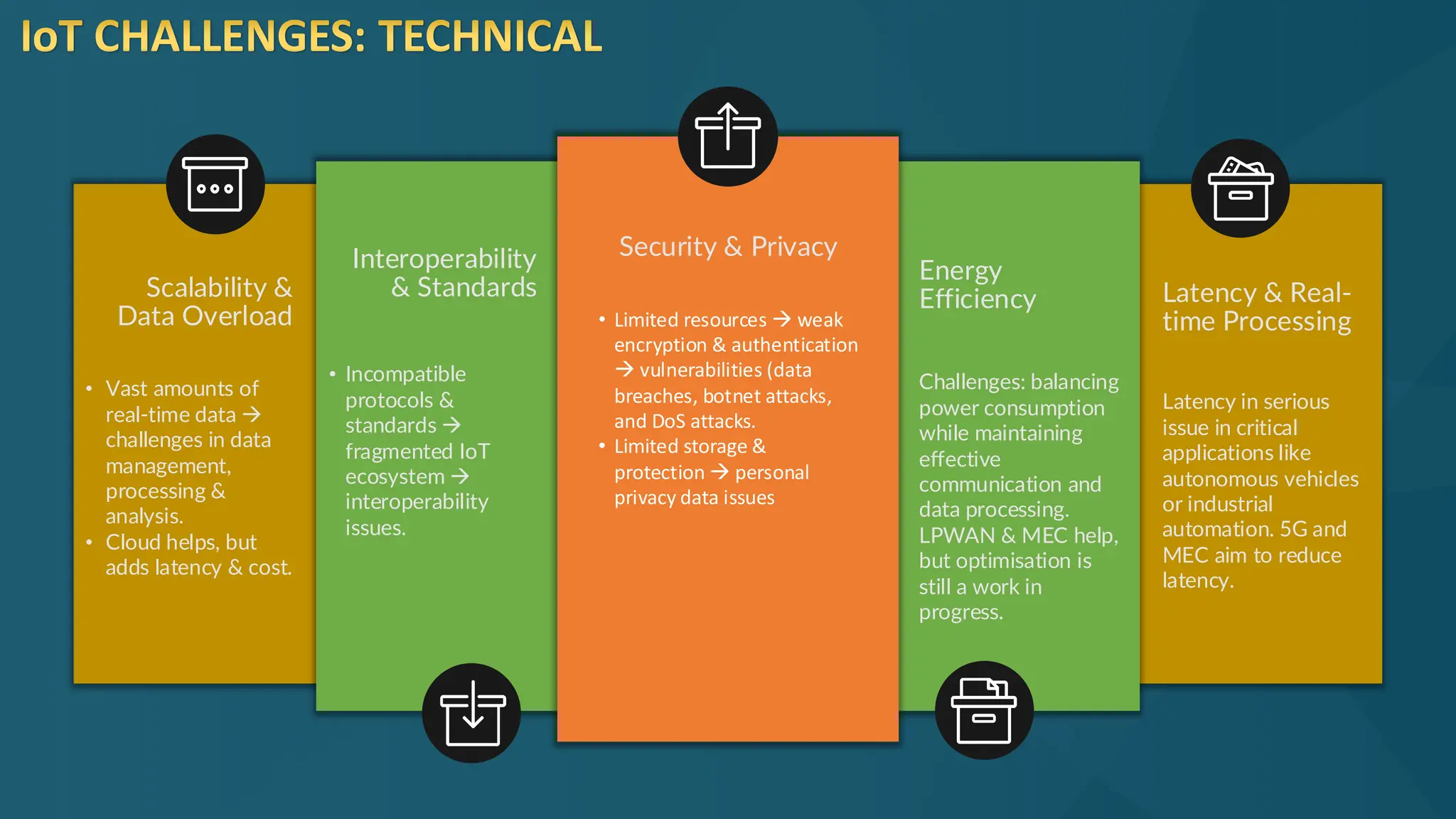
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT) and its potential to enhance connectivity for sustainable development, highlighting various technological advancements, platforms, and applications in this field. It also examines opportunities and challenges associated with IoT, including security issues, energy efficiency, and the need for interoperability among systems. Furthermore, specific cases of IoT implementations in sectors like agriculture, healthcare, smart cities, and industrial automation are presented, alongside the role of IEEE in driving innovation and collaboration in IoT developments.