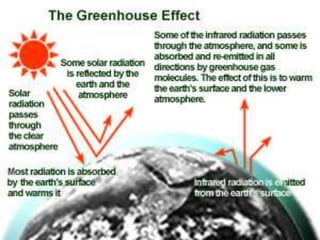
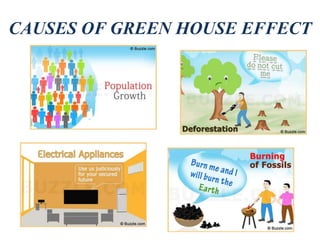
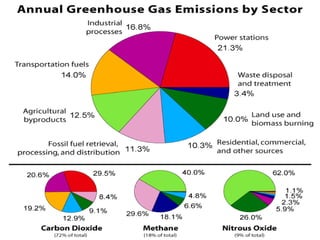
The document discusses the greenhouse effect and global warming. It defines the greenhouse effect as certain gases, like carbon dioxide and methane, trapping heat in the lower atmosphere and causing the surface temperature to increase. Global warming is defined as the long-term rise in the Earth's temperatures due to these increased gases. The document lists the major greenhouse gases and examines the causes of the greenhouse effect and global warming, both natural and human-made, as well as their effects. It concludes with recommendations for preventing further global warming through conservation efforts.