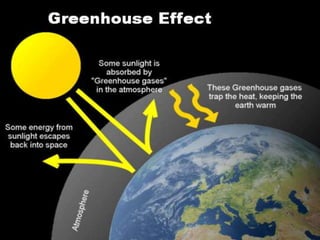
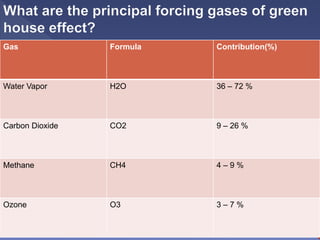
The document discusses greenhouse gases and their role in global warming. It defines key terms like greenhouse, greenhouse effect, greenhouse gases, and climate change. It explains that greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane and water vapor trap heat in the atmosphere and cause the greenhouse effect, which is responsible for rising global temperatures and climate change. Without some greenhouse effect, the Earth would be too cold to support life, but excess greenhouse gases are warming the planet to dangerous levels.