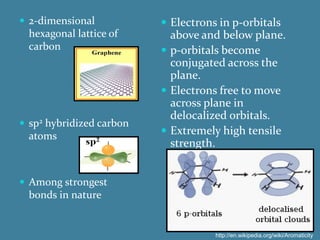
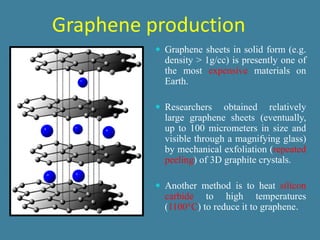
The document summarizes the properties and potential applications of graphene. Graphene is a one-atom thick sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice. It is the strongest material known, more conductive than silver, and highly transparent. Researchers at the University of Manchester were awarded the Nobel Prize for first isolating graphene sheets. Graphene's unique properties make it promising for applications like faster electronics, stronger and lighter composite materials, better solar cells and displays. However, challenges remain in controlling its conductivity for transistors.