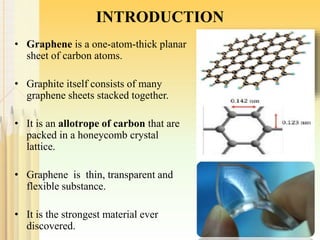
The document discusses graphene, a one-atom-thick carbon material known for its exceptional properties such as high tensile strength and electrical conductivity, and its potential applications in technology. It outlines various synthesis methods, advantages, and disadvantages of graphene, along with a list of companies operating in the graphene sector. The conclusion emphasizes the ongoing improvement in the quality and availability of synthetic graphene, advocating for its integration into modern technology.