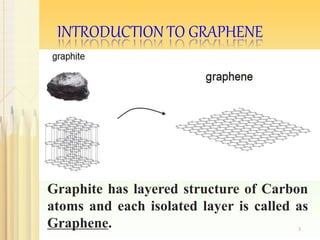
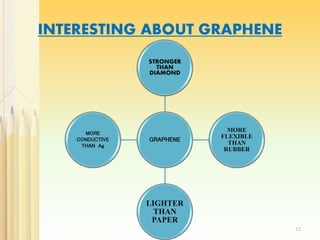
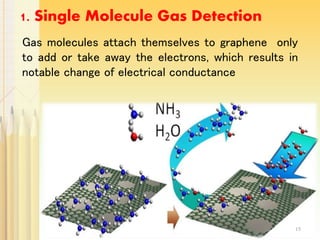
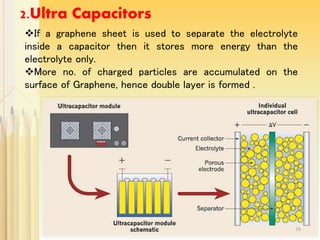
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice, is known for its remarkable properties, including high electrical, thermal, and mechanical strength, making it a significant material for future technologies. While it holds potential applications in various fields, such as ultra-capacitors and transparent electrodes, challenges remain in its commercial synthesis and safety concerns. Ongoing advancements in graphene production methods may enhance its integration into modern devices and replace existing materials.