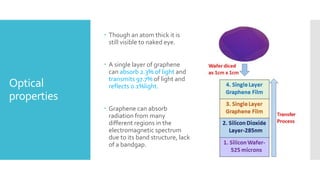
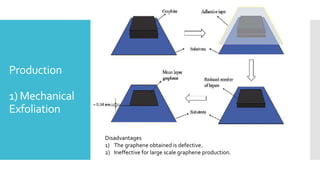
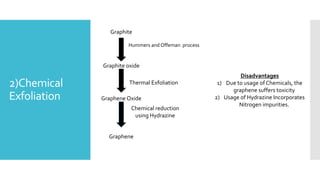
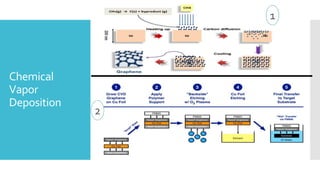
Graphene is a lightweight and strong allotrope of carbon, 200 times stronger than steel, consisting of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice. It has high electrical conductivity and impressive mechanical properties, making it suitable for various applications, such as in touch screens, batteries, and military equipment, but its production remains expensive and complex with potential toxicity issues. The material shows promise for revolutionizing electronic technology and offers environmental advantages, though challenges like lack of a bandgap and instability at small sizes persist.