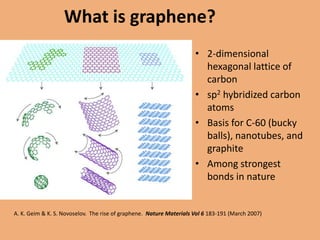
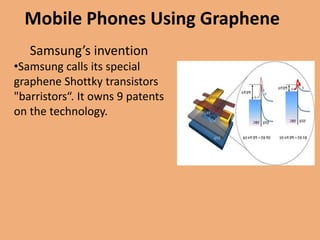
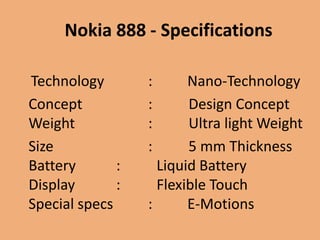
Graphene is a one-atom thick sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice. It is the strongest material known and a highly efficient conductor of electricity and heat. Researchers are developing graphene-based transistors and circuits that could enable faster, more efficient mobile phones. Major companies like Samsung and Nokia plan to launch graphene-based phones in the near future that are predicted to be very thin, flexible, durable and fast-charging due to graphene's properties. However, graphene phone technology still faces challenges regarding energy efficiency and compatibility with existing technologies.