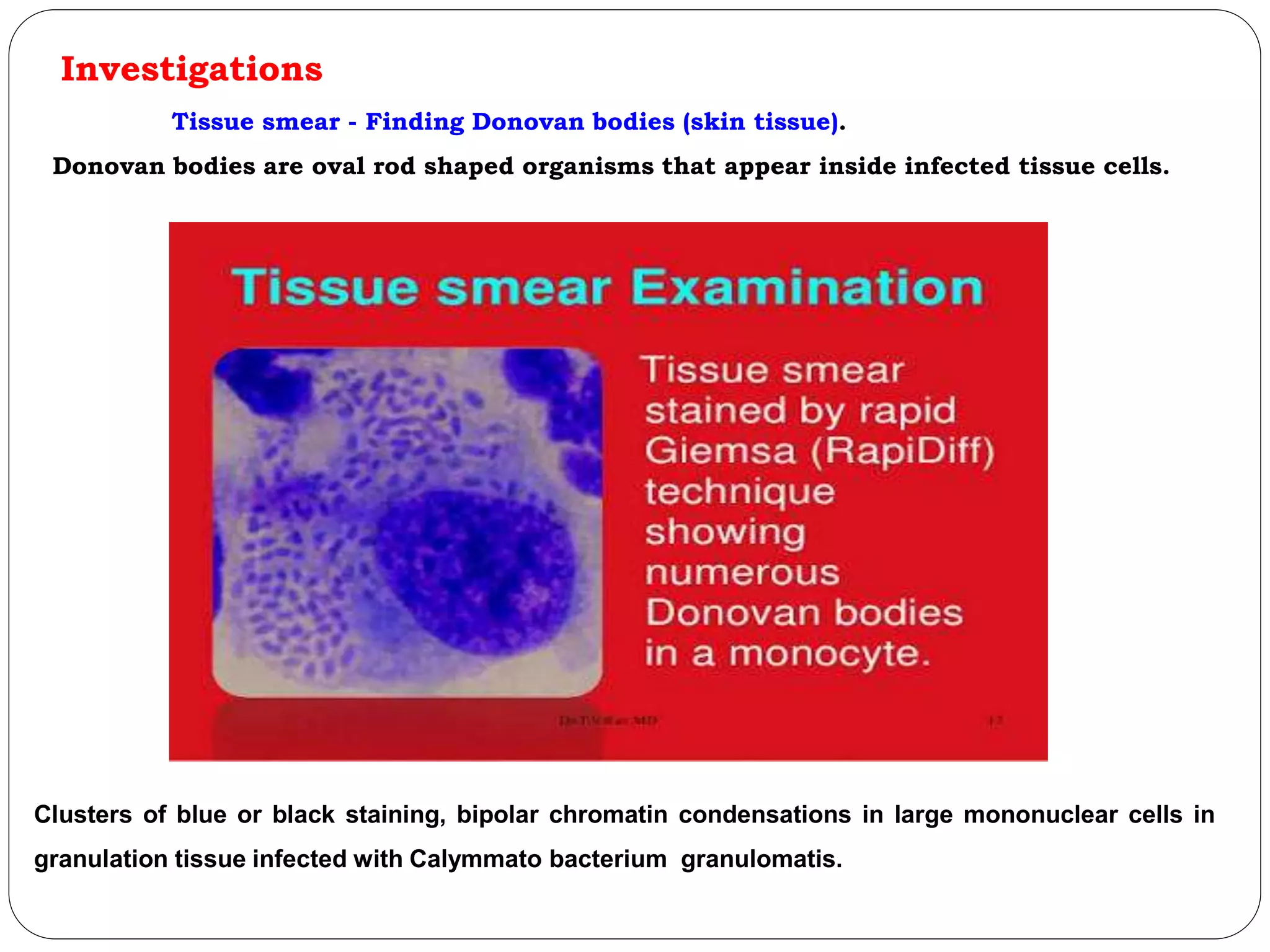
Granuloma inguinale, also known as Donovanosis, is a bacterial infection caused by Klebsiella granulomatis that is transmitted sexually or through contact with infected feces. It initially presents as a painless papule or nodule on the genitals that progresses to form ulcers with granulation tissue edges. If left untreated, it can spread and cause complications like scarring or infection of other organs. Diagnosis involves finding Donovan bodies in tissue smears under microscopy. Treatment is with oral antibiotics like azithromycin or doxycycline for at least 3 weeks after lesions have fully healed to prevent relapse.