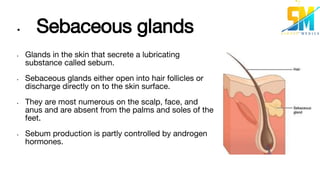
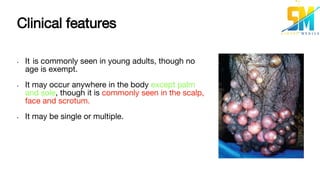
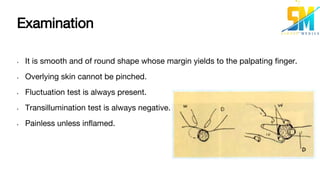
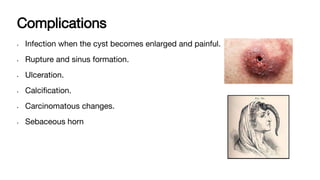
Sebaceous cysts are caused by blockage of the duct of the sebaceous gland, causing the gland to become distended by its own secretion of sebum. Clinically, sebaceous cysts present as movable, non-tender swellings under the skin, often with a visible punctum or opening. They are diagnosed through examination finding fluctuation and transillumination negativity. Treatment involves surgical removal by incising the cyst and expressing its contents. Complications can arise if the cyst becomes infected or ruptured.