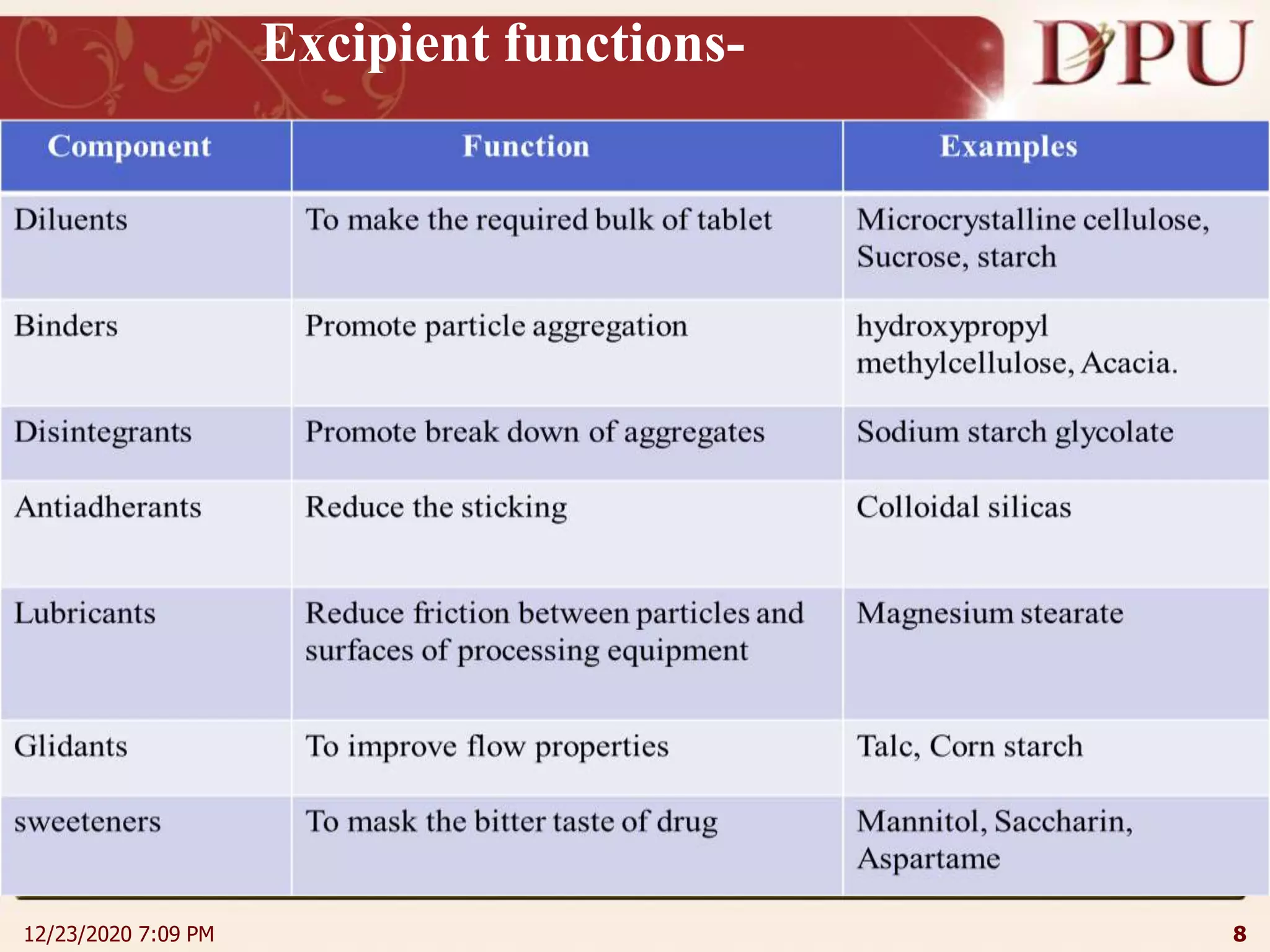
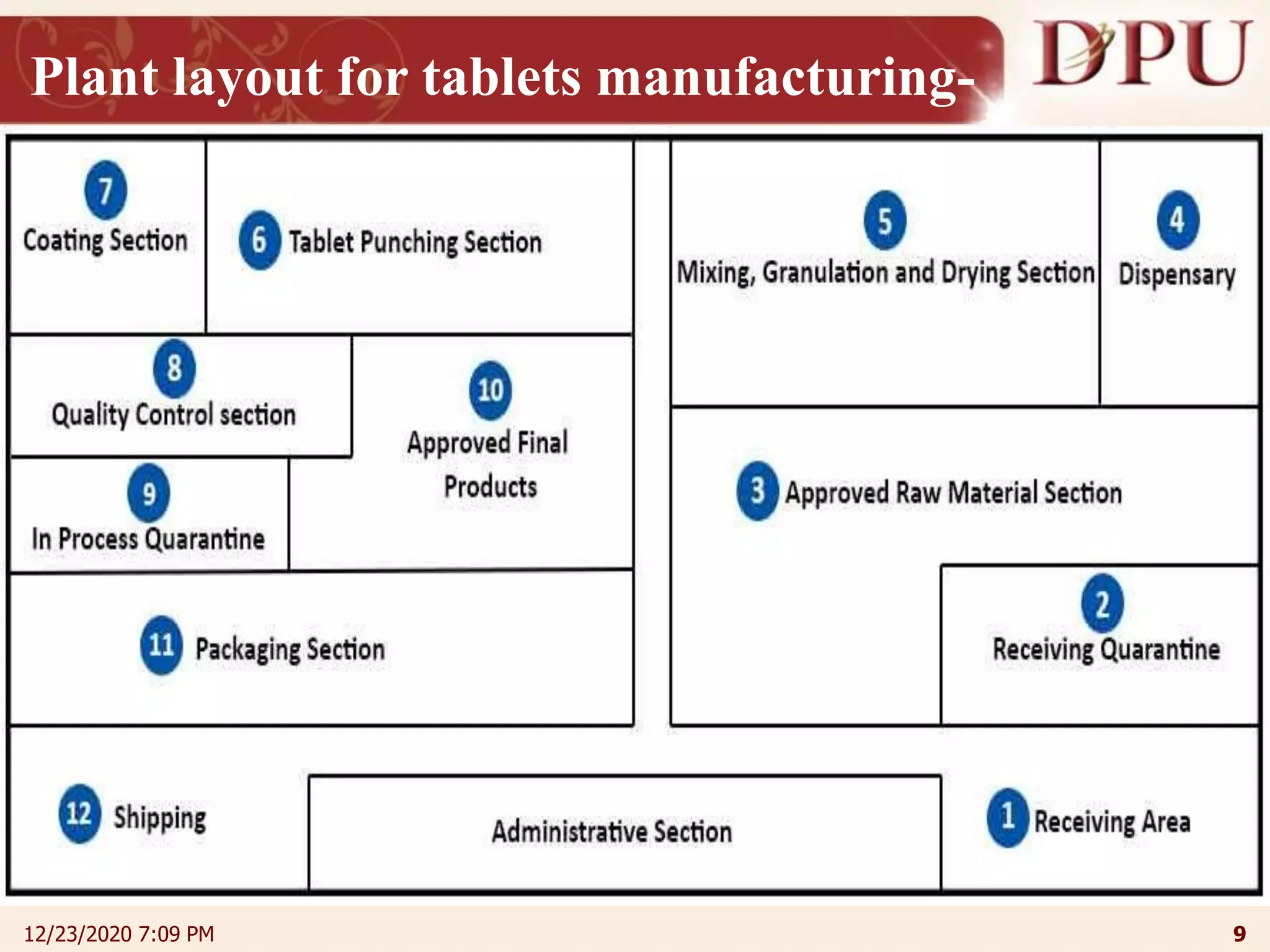
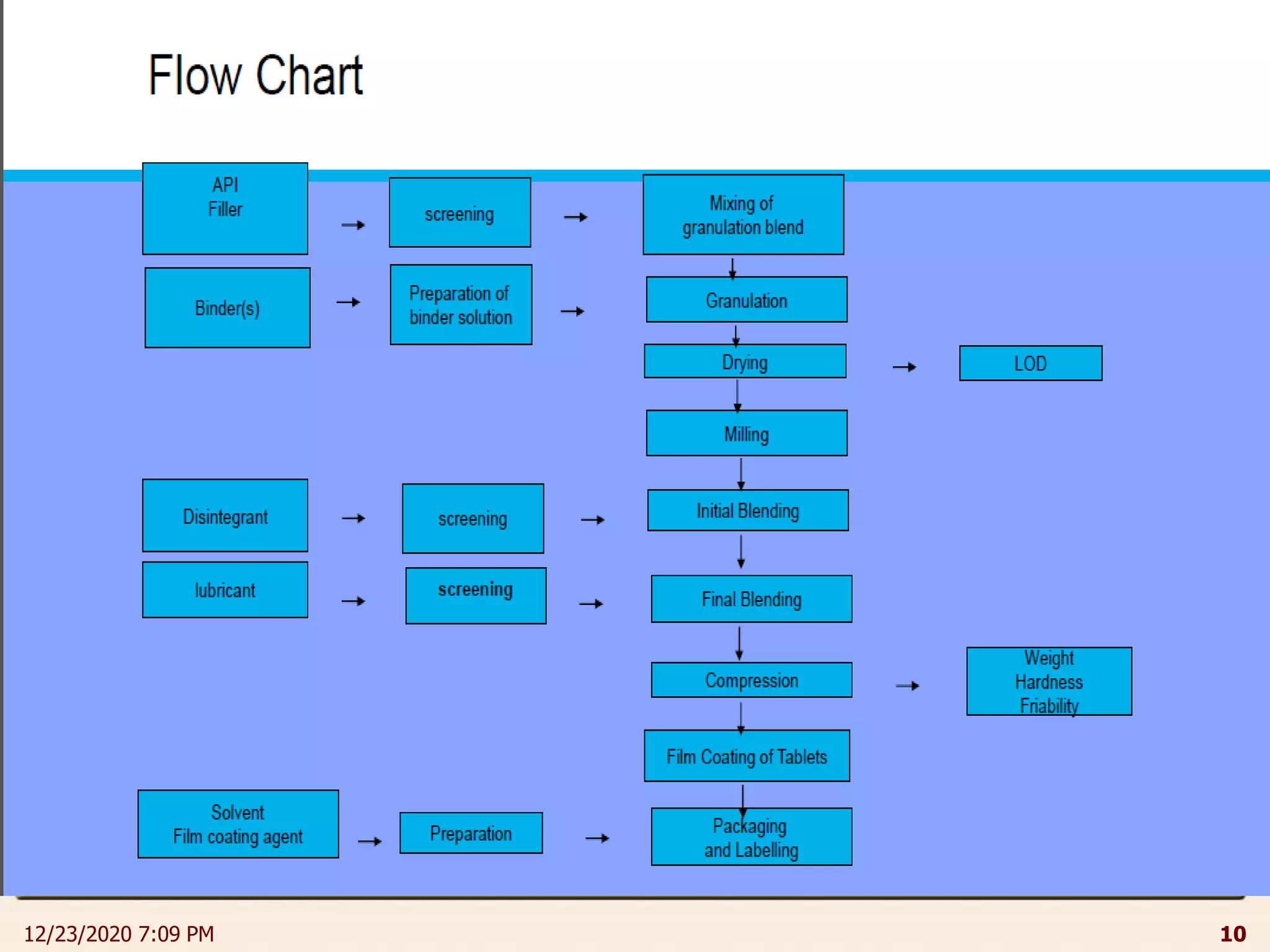
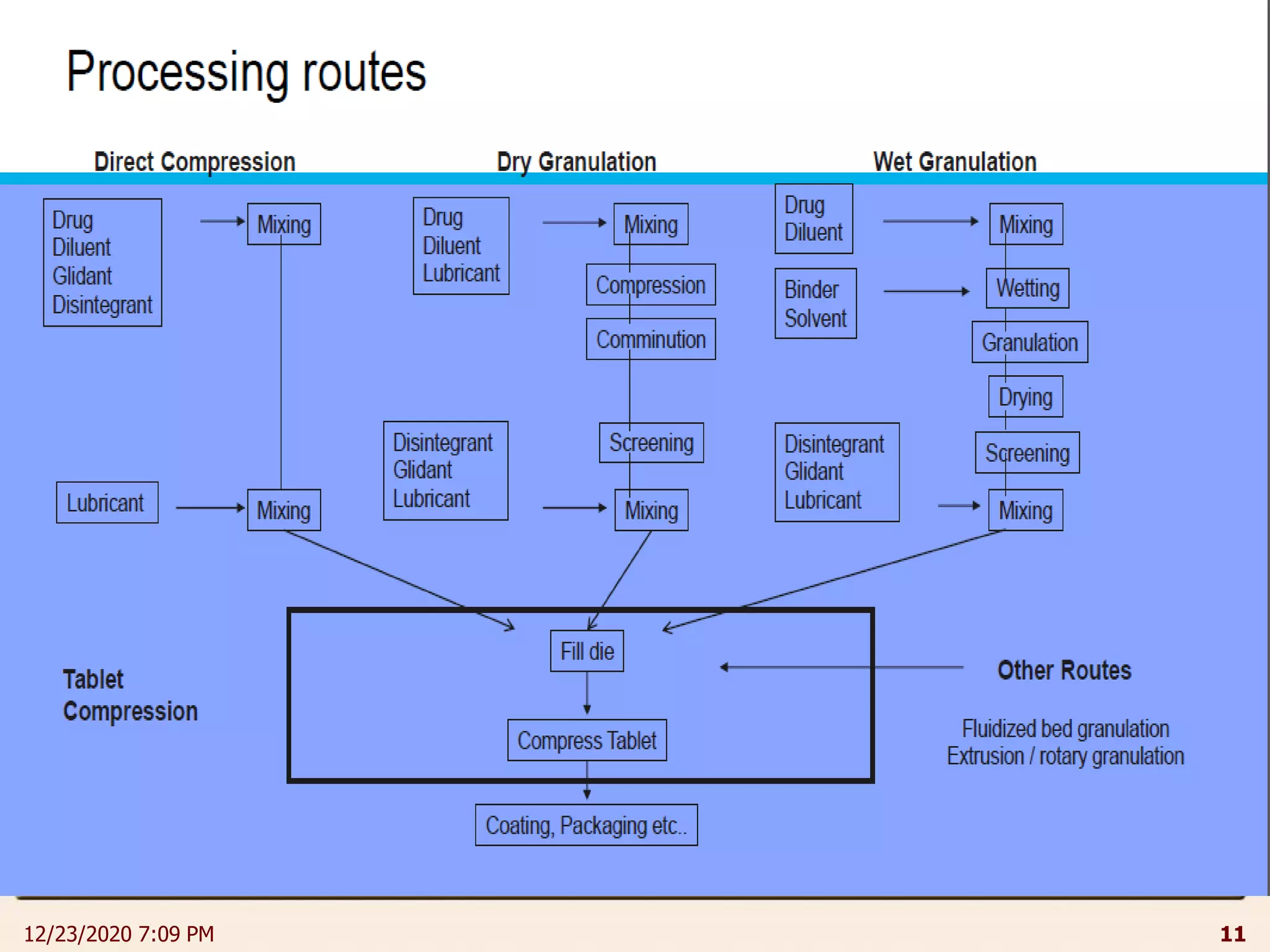
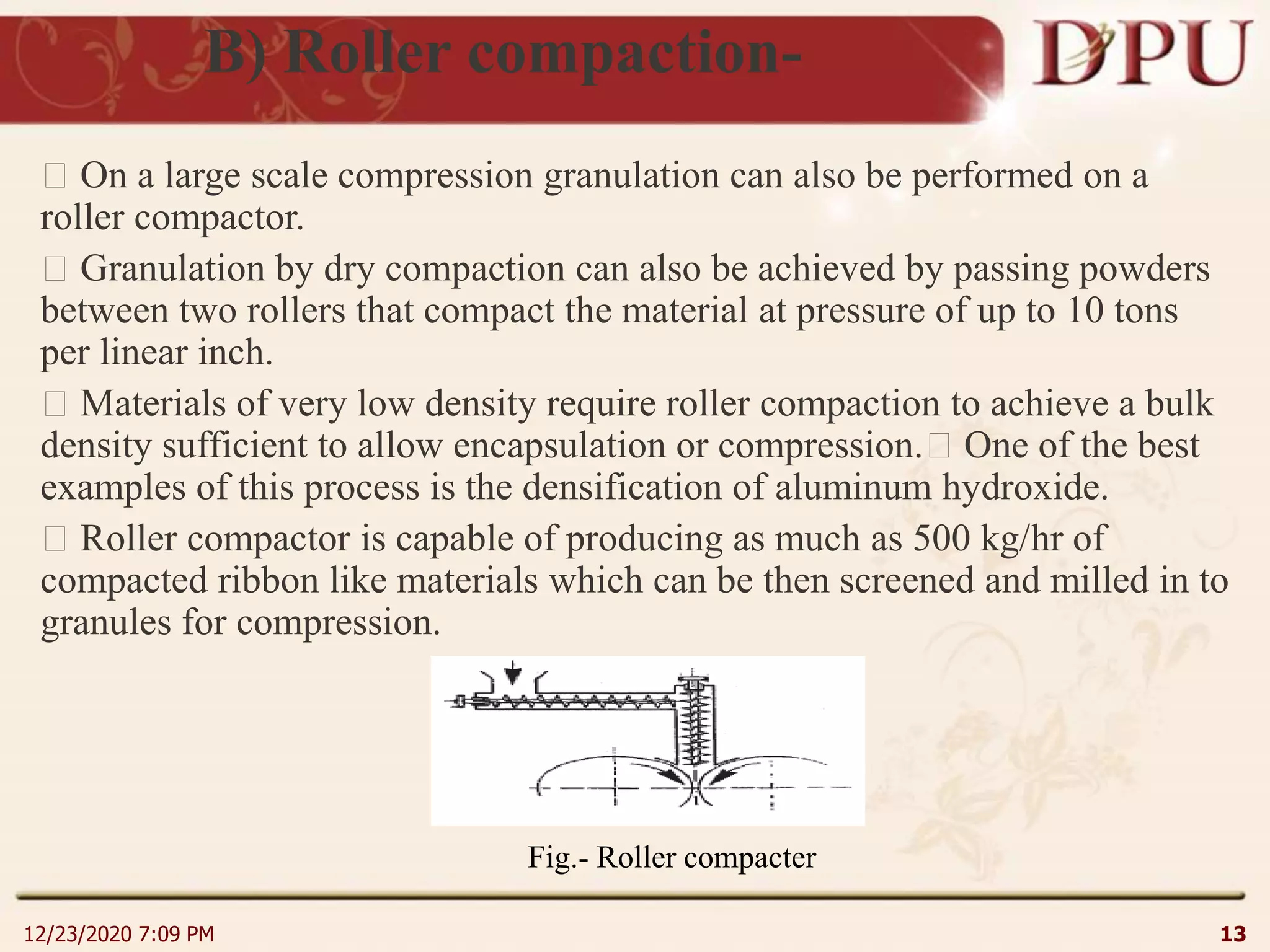
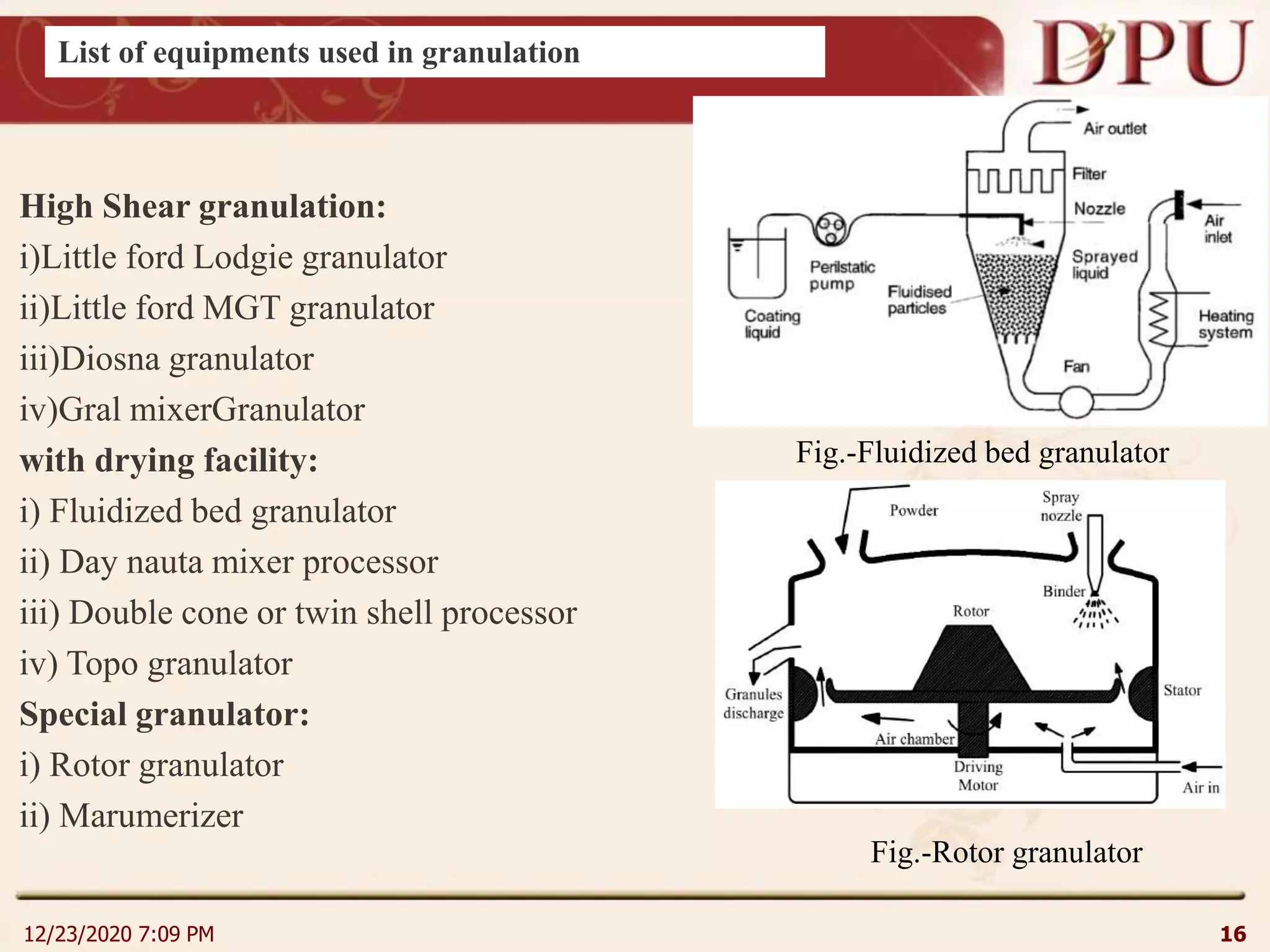
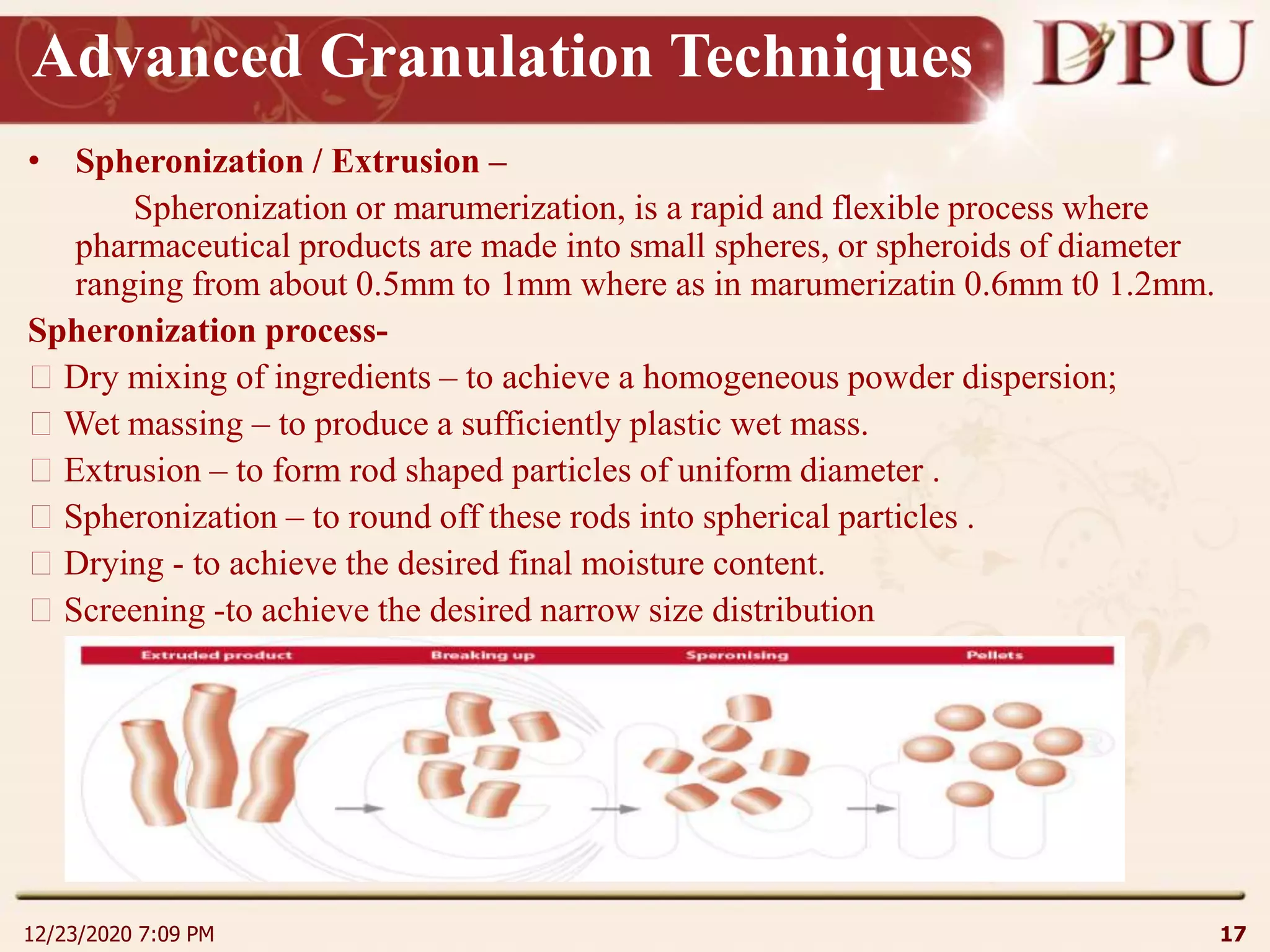
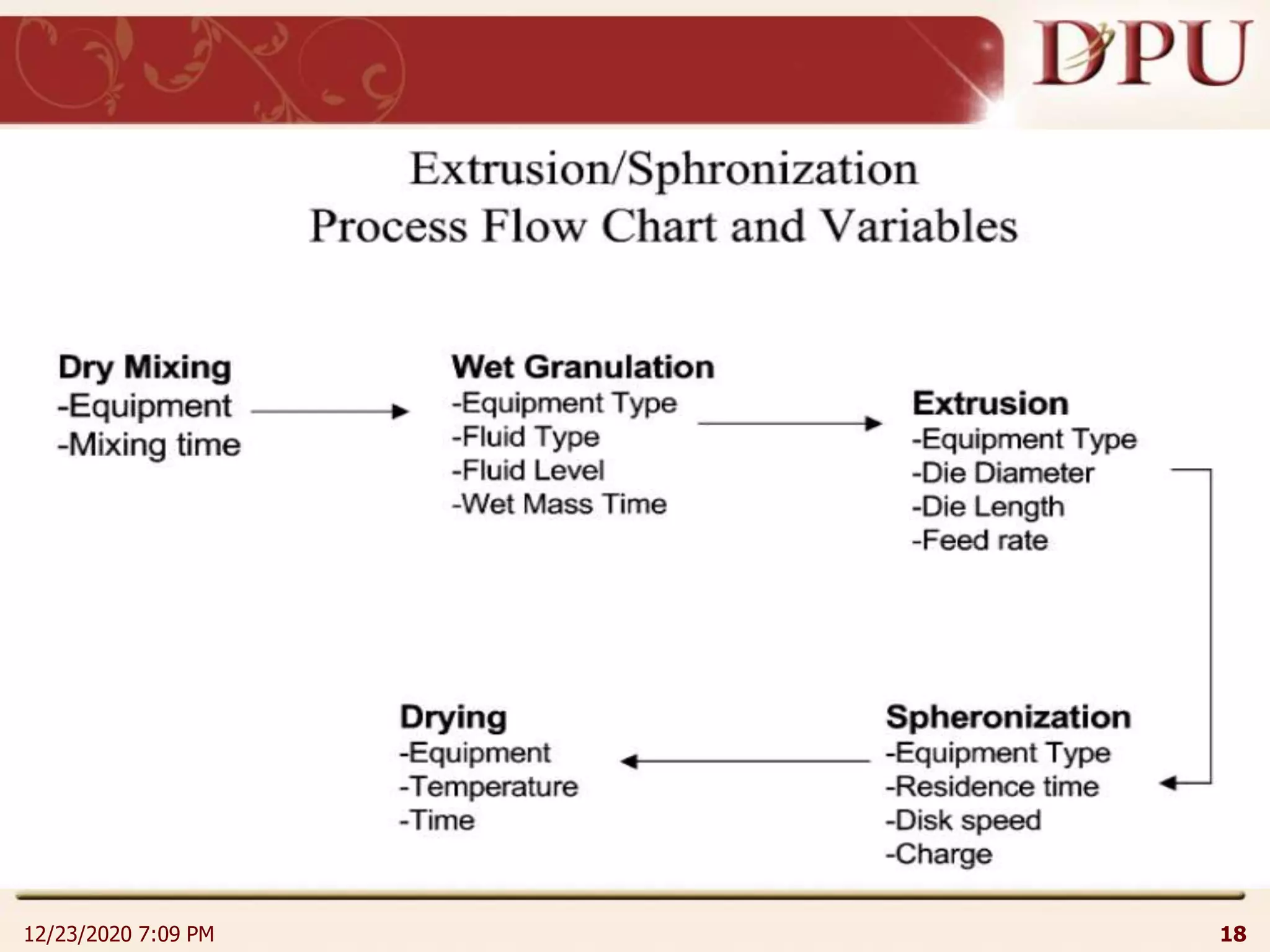
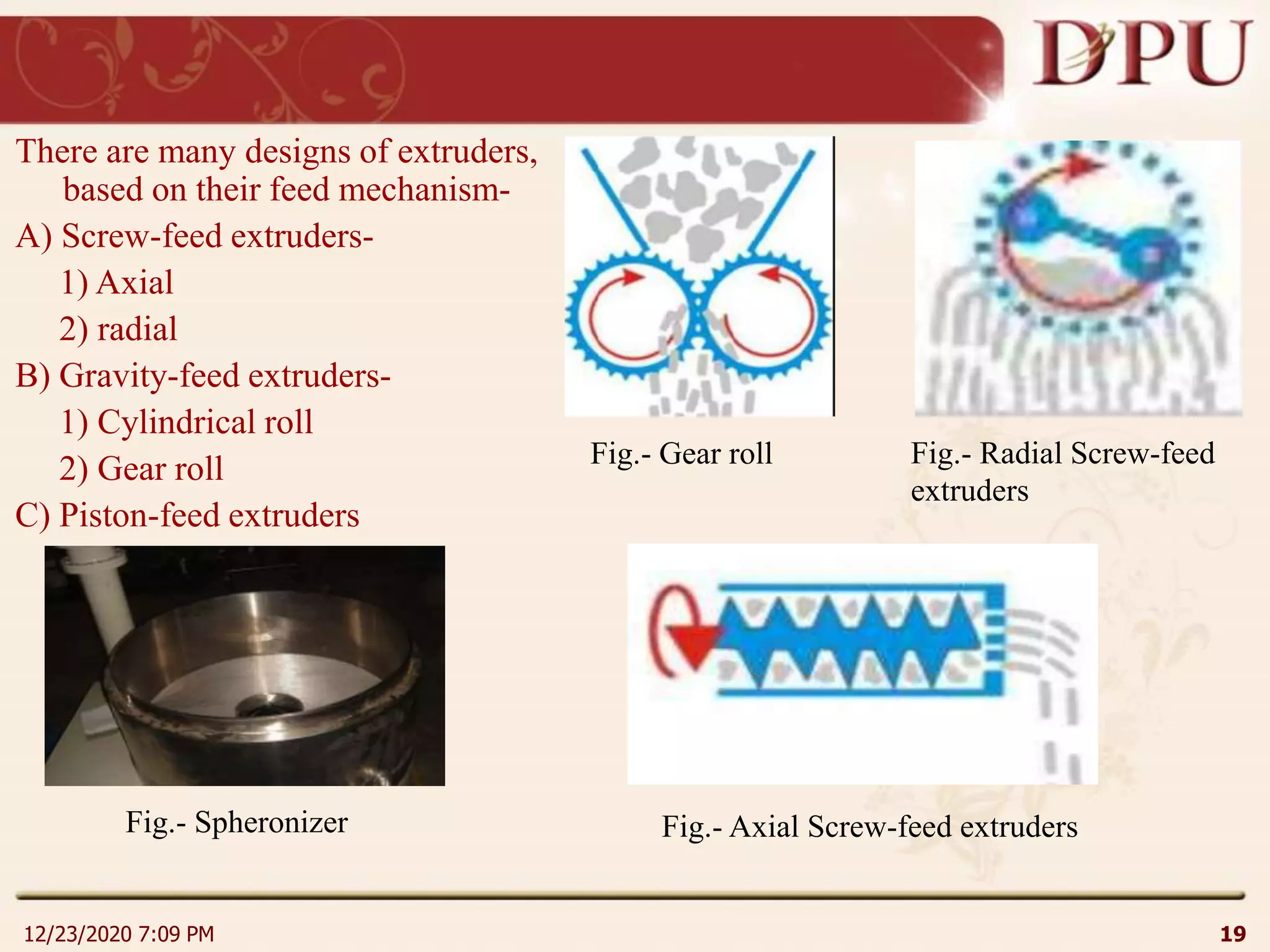
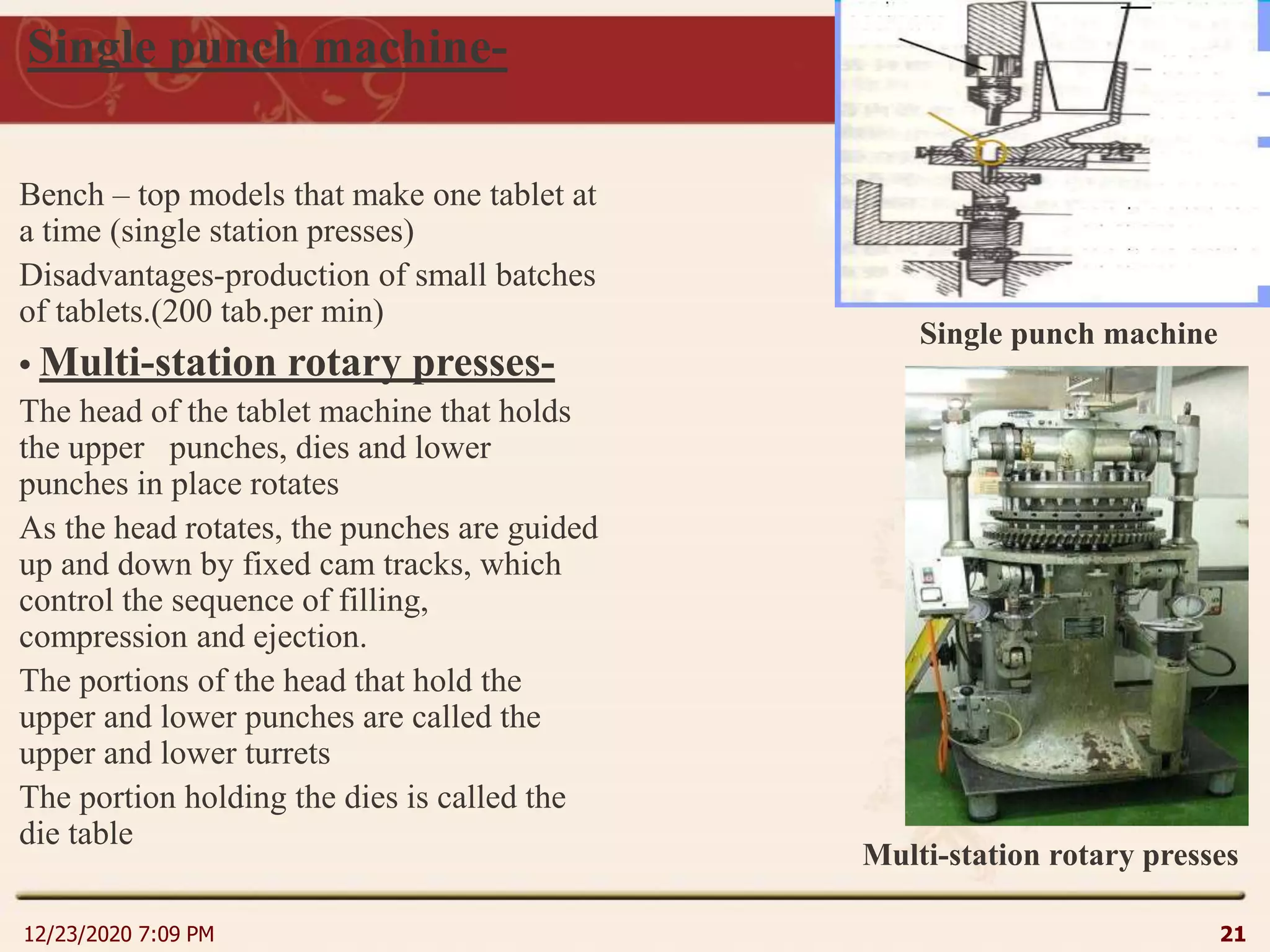
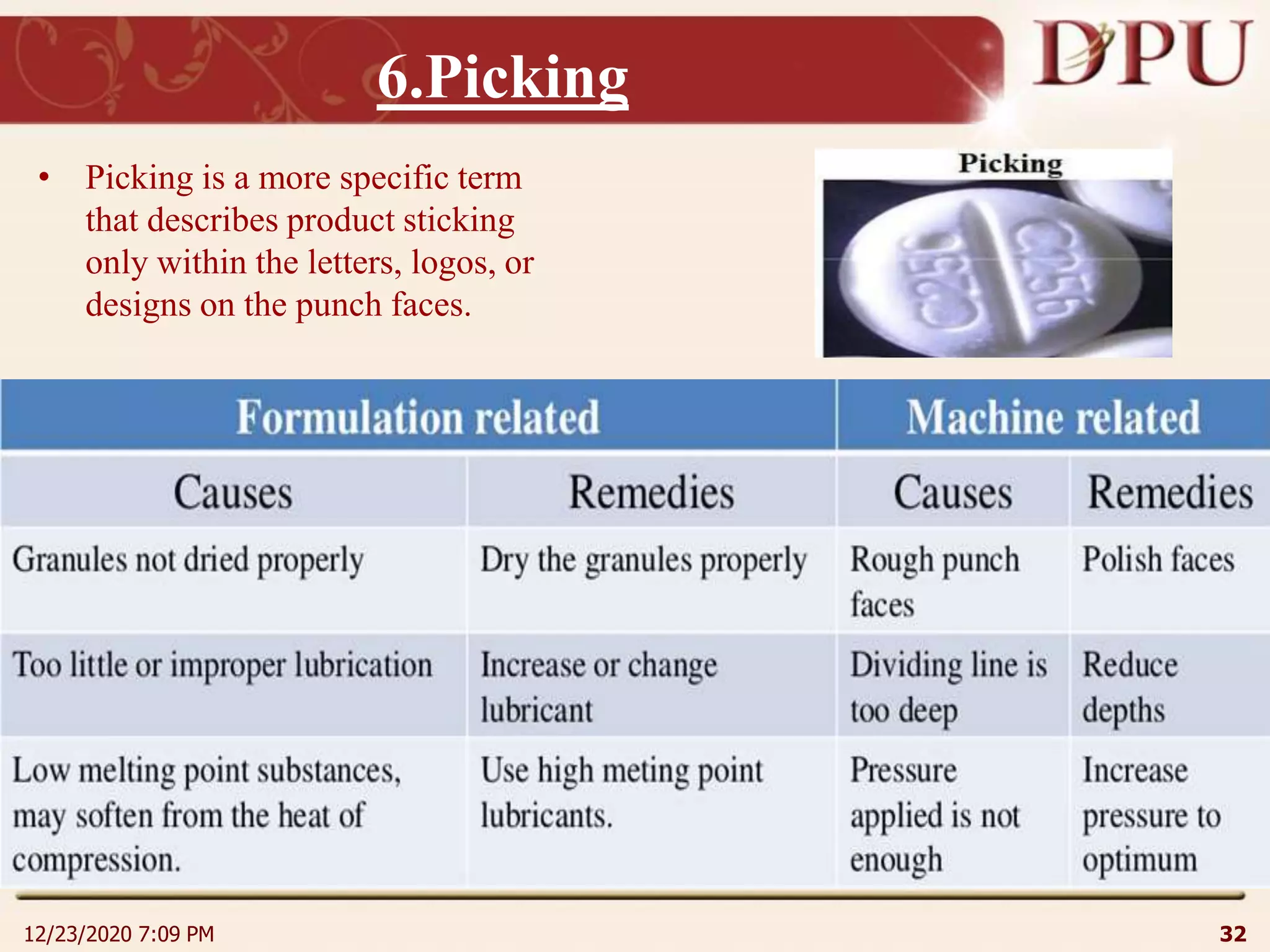
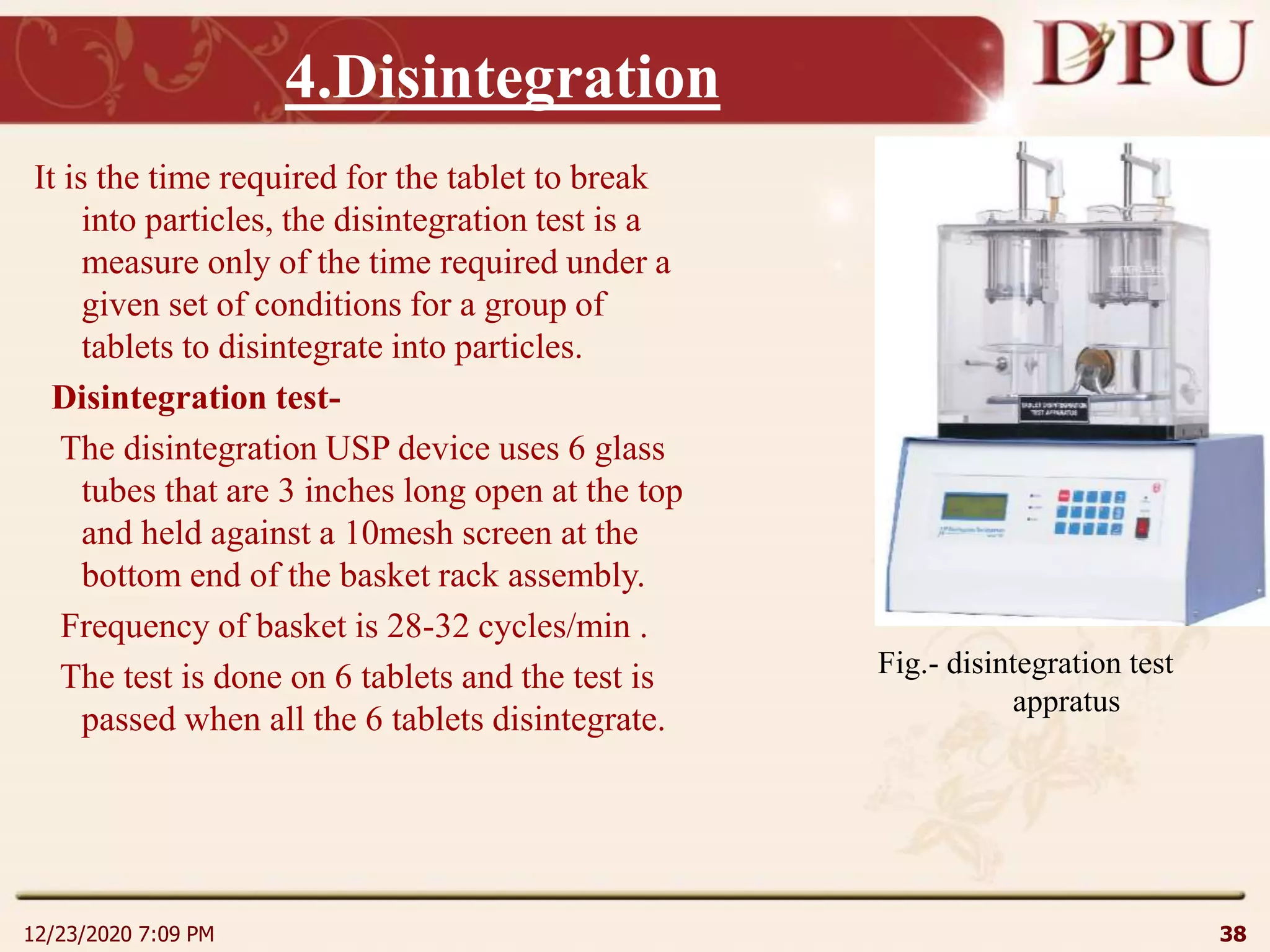
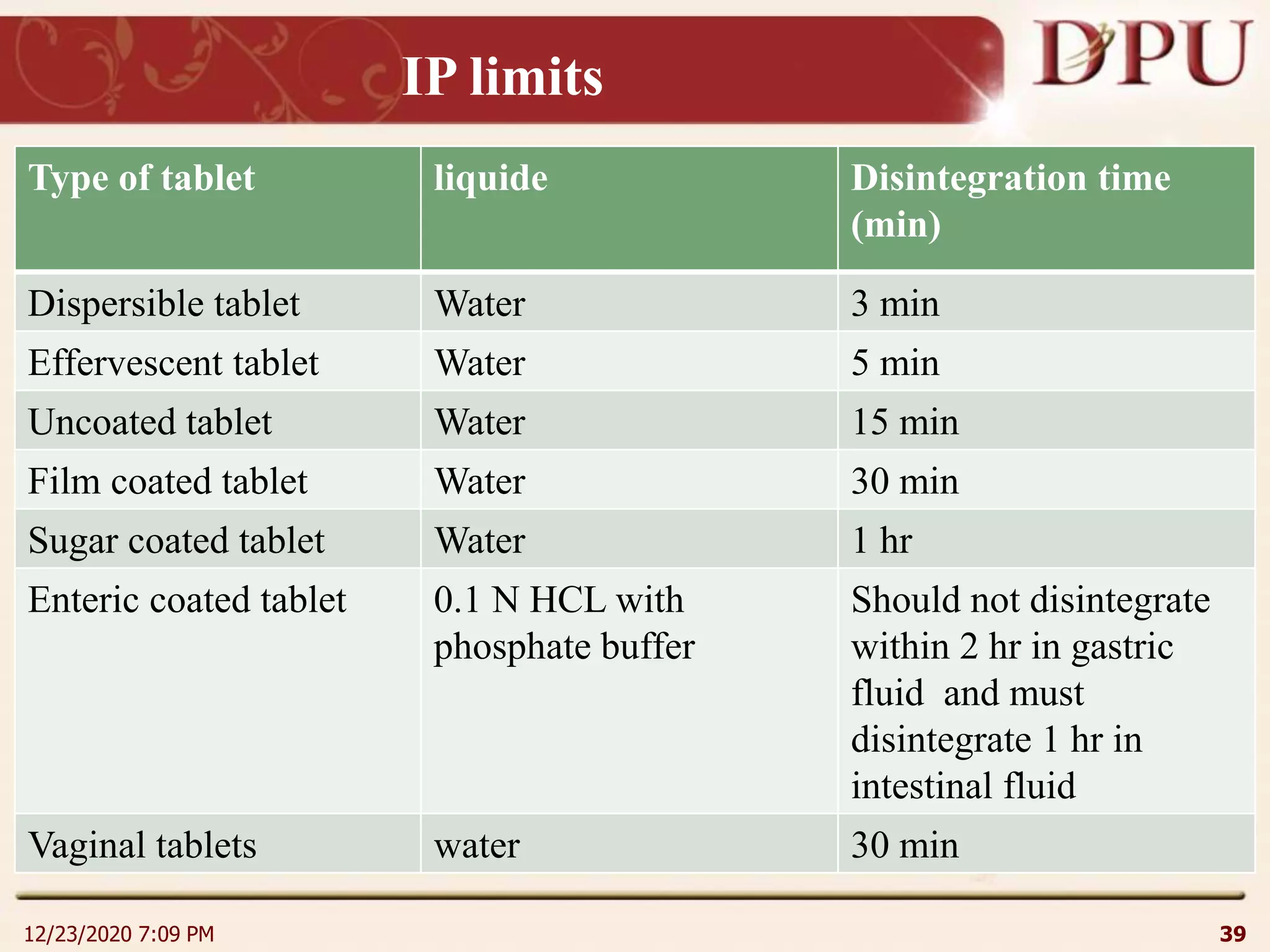
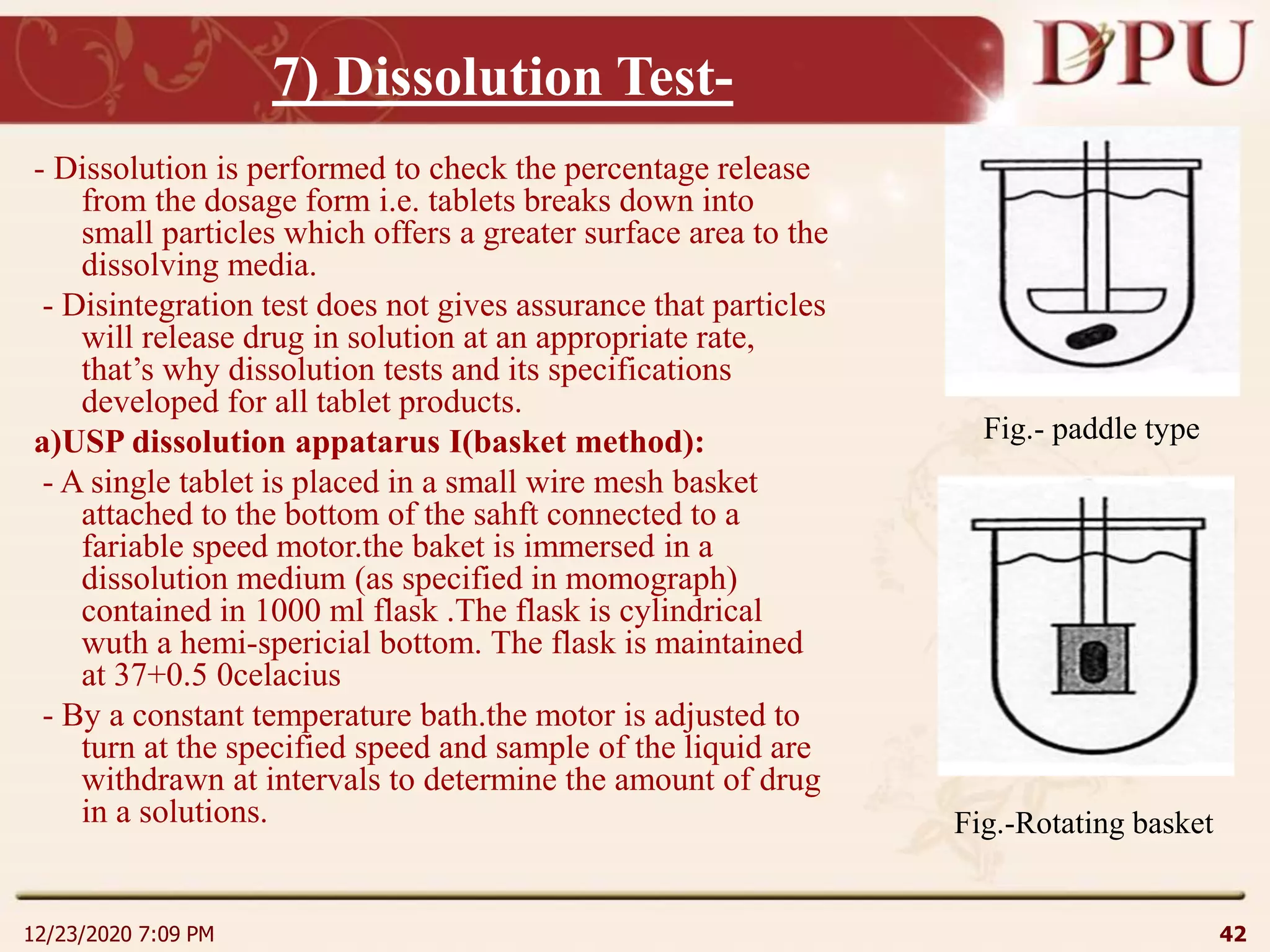
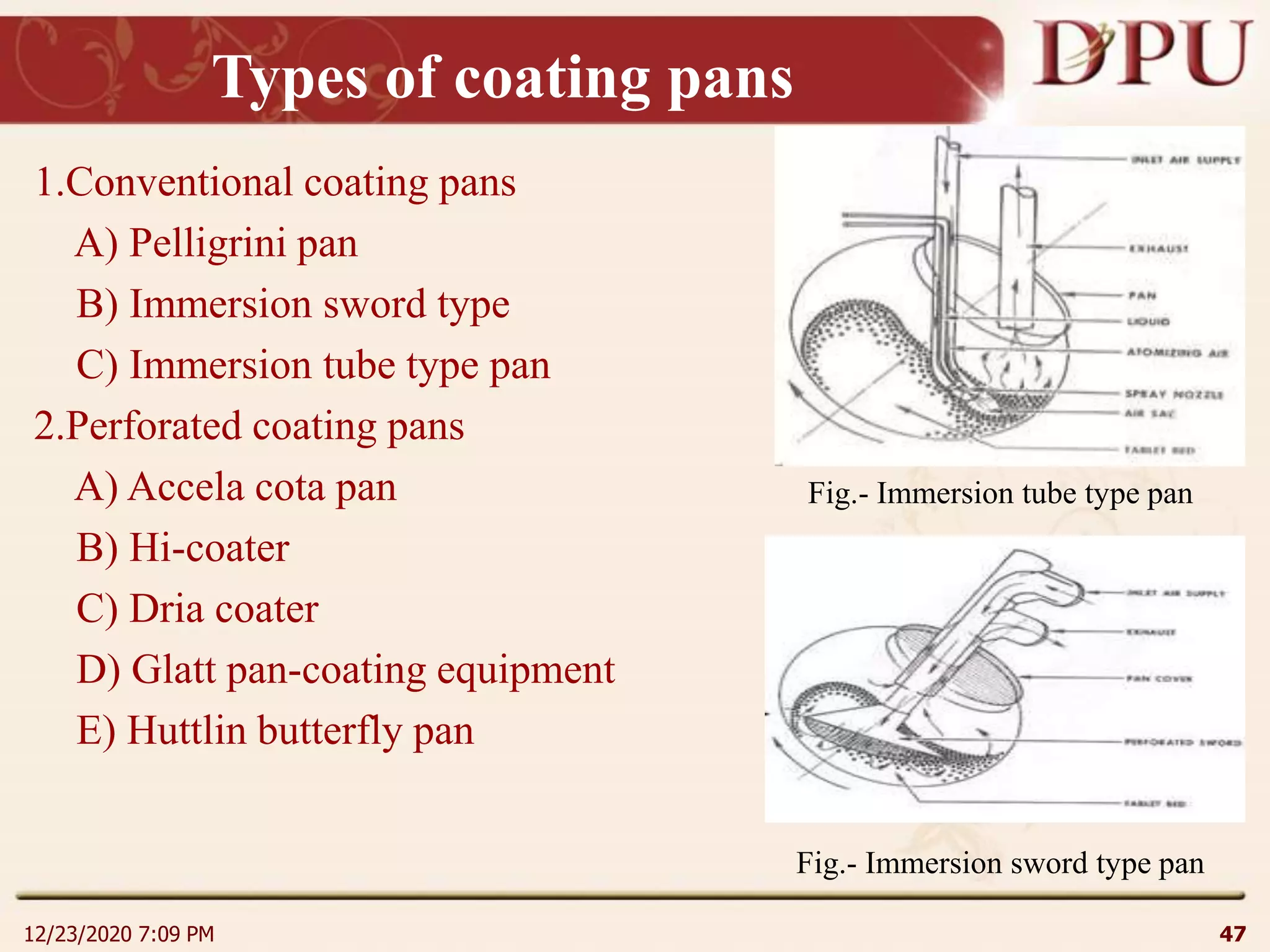
This document provides an overview of non-sterile tablet manufacturing processes. It begins with definitions of non-sterile dosage forms including tablets, capsules, ointments, suspensions and emulsions. It then discusses various aspects of tablet manufacturing including formulation, equipment used, granulation techniques, compression, and quality control tests. The document focuses on tablet manufacturing processes and quality checks to ensure consistent and quality tablets are produced.