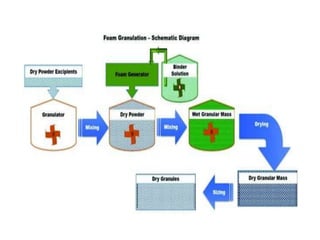
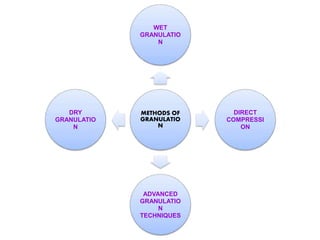
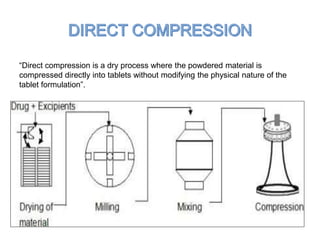
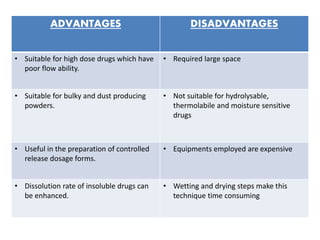
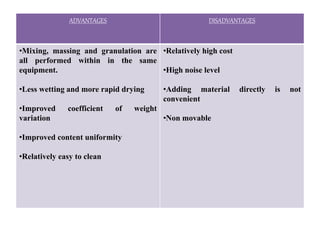
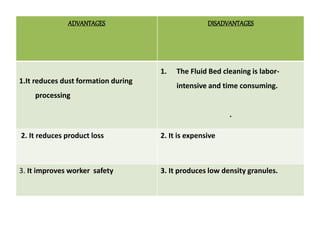
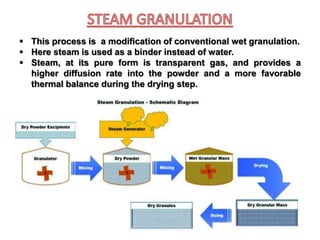
This seminar presentation summarized various granulation techniques used in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It began with an introduction defining granulation and its purposes in improving powder flow, uniformity, and eliminating dust. The main granulation methods discussed were wet, dry and direct compression granulation. Advanced techniques like steam, melt, and foam granulation were also covered. The presentation concluded that granulation technology allows for efficient production of drug delivery systems and can improve drug dissolution and bioavailability through formation of solid solutions.














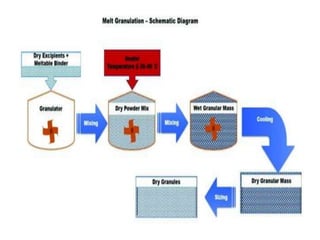
![ This granulation method is also know as theromplastic granulation.
Here granulation is achieved by the addition of meltable binder.
e.g:- Water soluble binders
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG - 2000 to 8000)
[40-60 0C]
Water insoluble binders
Stearic acid [46-59 0C]
Stearyl alcohol [56-60 0C]
Binder is in solid state at room temperature but melts in the temperature range of
50 – 90˚C.
Melted binder then acts like a binding liquid.
There is no need of drying phase since dried granules are obtained by cooling it to
room temperature.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarongranulationbypurnima-190104074619/85/Seminar-on-granulation-by-purnima-26-320.jpg)