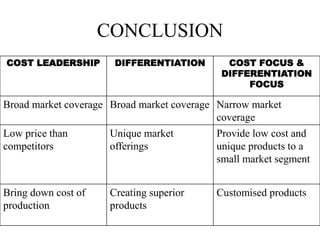
The document outlines Michael Porter's three generic competitive strategies: low cost leadership, differentiation, and focus strategies aimed at achieving competitive advantage. Examples include companies like Wal-Mart and Samsung, illustrating how these strategies can be effectively employed to address various market demands. The conclusion reinforces the advantages of each strategy for broad or narrow market coverage.