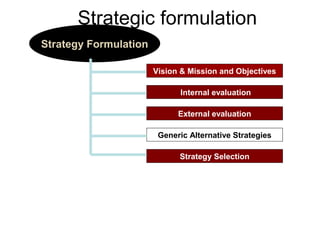
Here are brief descriptions of 3 generic strategies with examples of when they should be adopted:
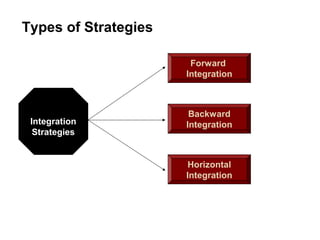
Integration strategies: Forward integration involves gaining control over distributors and retailers. It should be adopted when current distributors are expensive/unreliable or availability is limited. Backward integration controls suppliers and is effective when current suppliers are expensive/unreliable or have few options. Horizontal integration controls competitors and works when competing in a growing industry allows economies of scale.
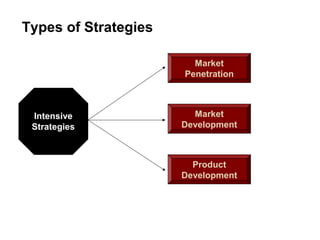
Intensive strategies: Market penetration increases market share of current products/markets through increased sales to present customers. It works when markets are not saturated. Product development increases sales through improving or developing new products, as when products reach maturity or technology rapidly changes.
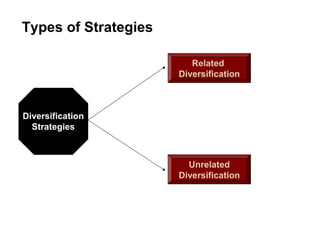
Diversification strategies: