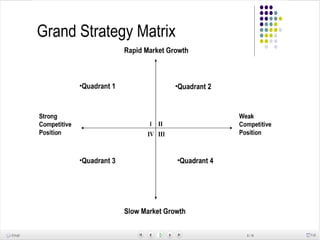
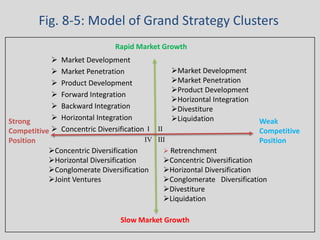
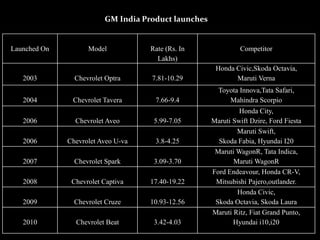
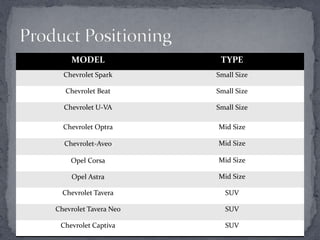
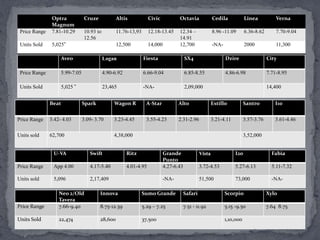
General Motors presented a grand strategy for the company that included four main alternatives: stability, growth, combination, and retrenchment. The strategies were mapped based on market growth and competitive position. Growth strategies included market penetration, market development, product development, and integration approaches like backward, forward, and horizontal integration. Diversification could be concentric, horizontal, or conglomerate. The presentation analyzed GM India's product lineup, branding, and proposed a three pillar marketing strategy focusing on integration, partnerships and sustaining efforts.