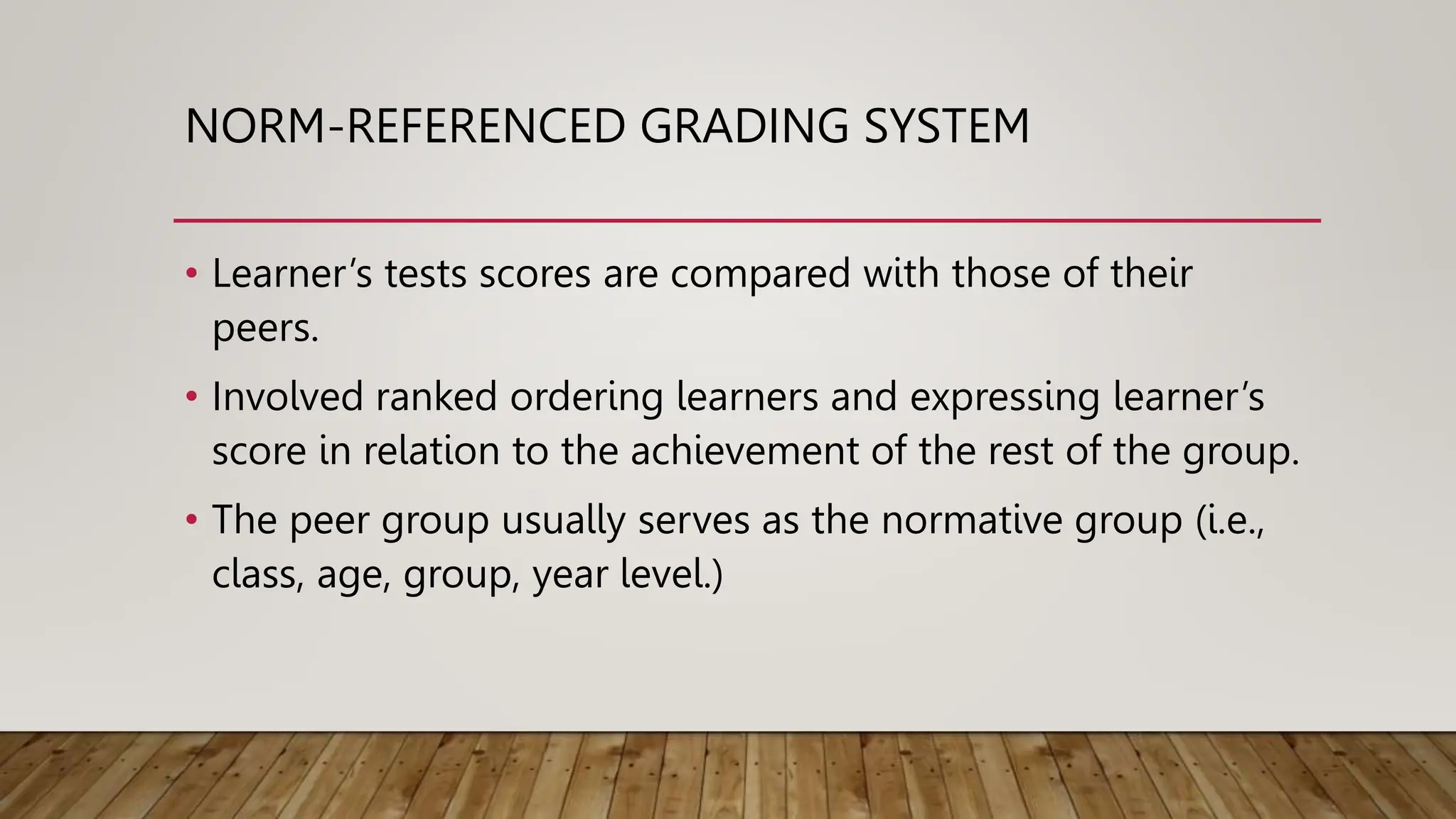
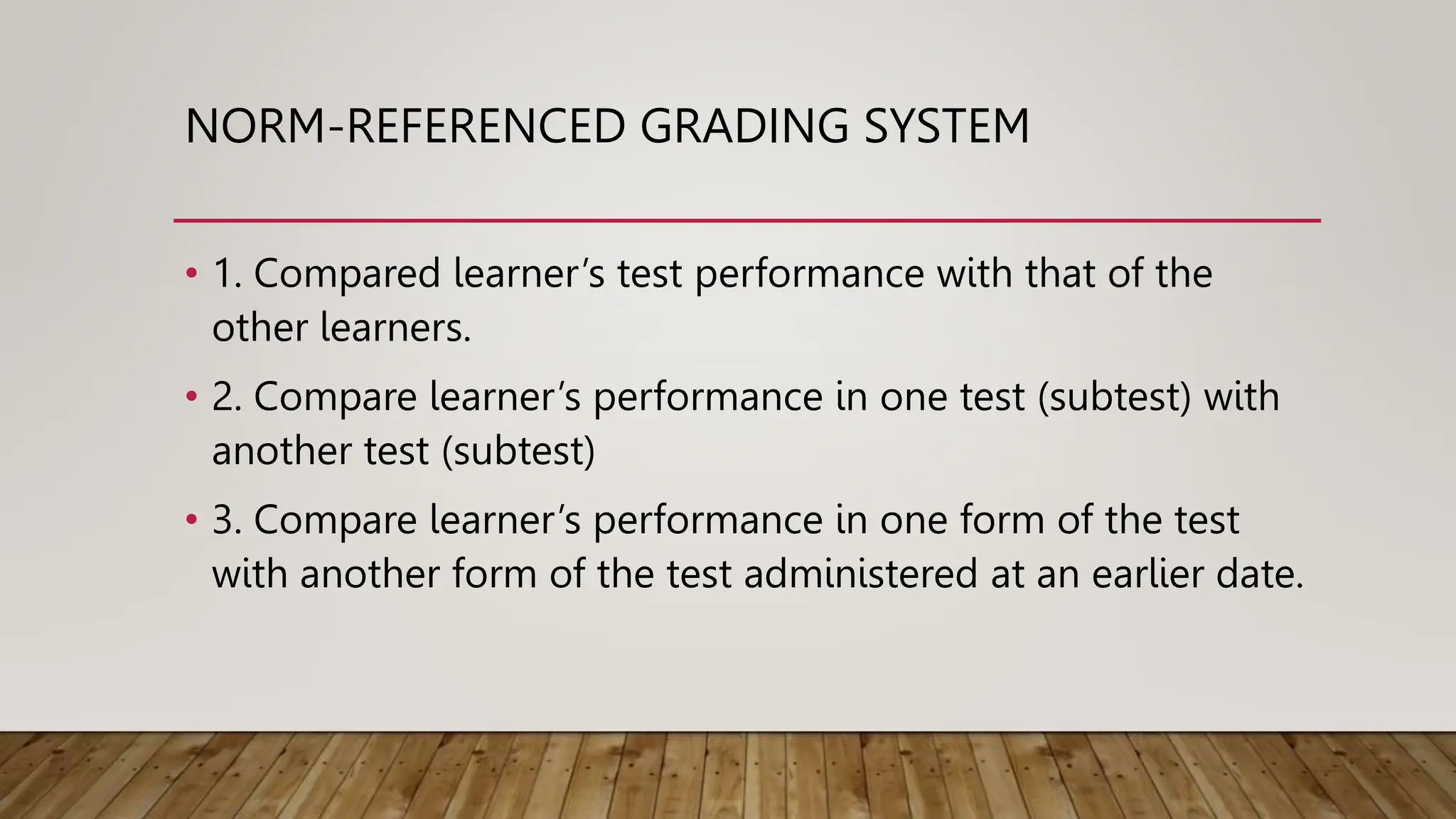
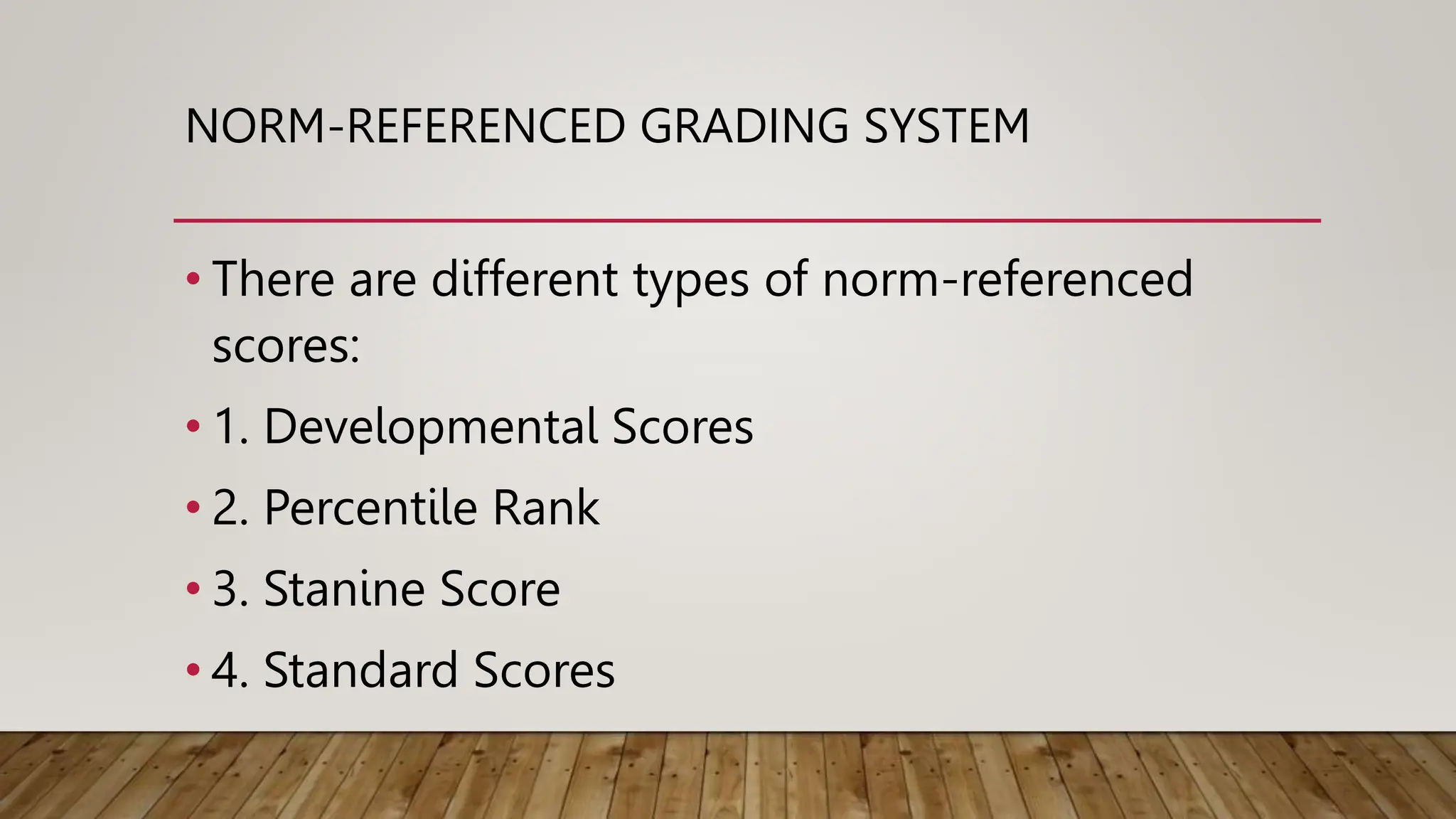
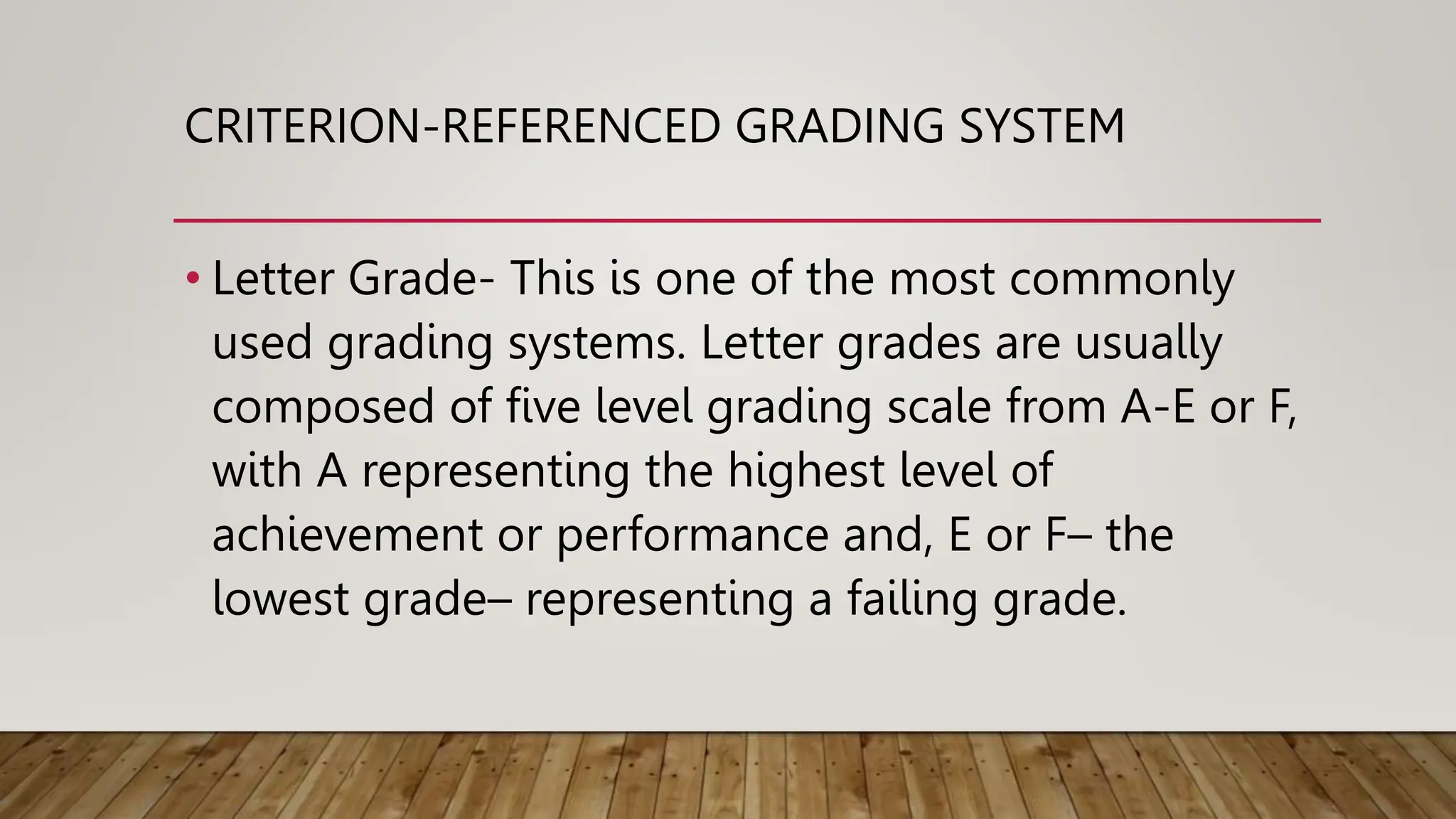
The document discusses grading systems, highlighting the importance of grading and reporting learner performance in education. It outlines two primary approaches: norm-referenced grading, which compares learner performance against peers, and criterion-referenced grading, which assesses performance based on specific learning goals. Additionally, it details various types of scores and grades used in these systems, including developmental, percentile, stanine, and letter grades.