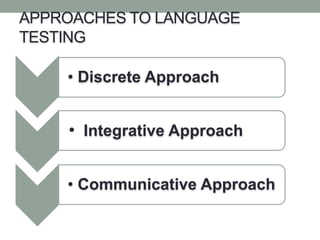
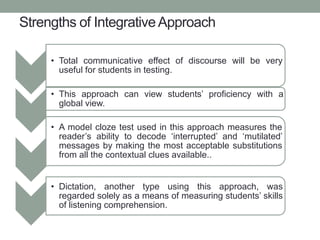
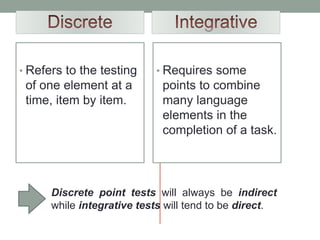
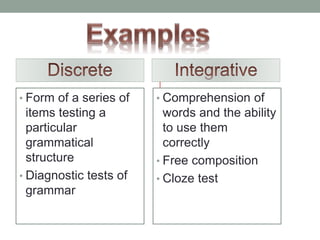
The document discusses various assessment approaches in education, highlighting the importance of validity, reliability, and practicality. It covers different testing methodologies including discrete, integrative, and communicative approaches, along with performance-based assessment, detailing their strengths and weaknesses. The conclusion emphasizes the significance of assessment in evaluating and improving teaching and learning outcomes.