Embed presentation
Downloaded 18 times

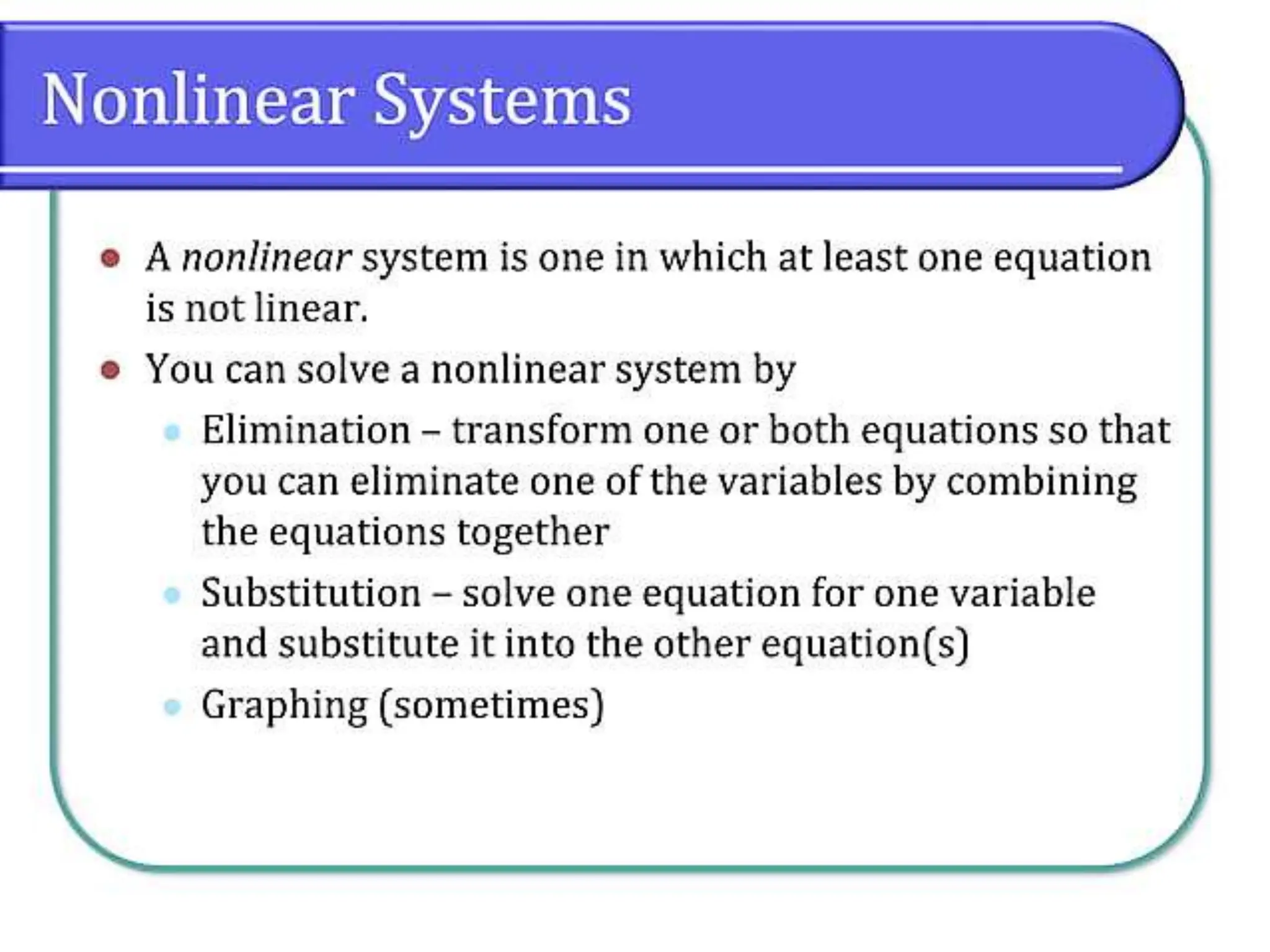




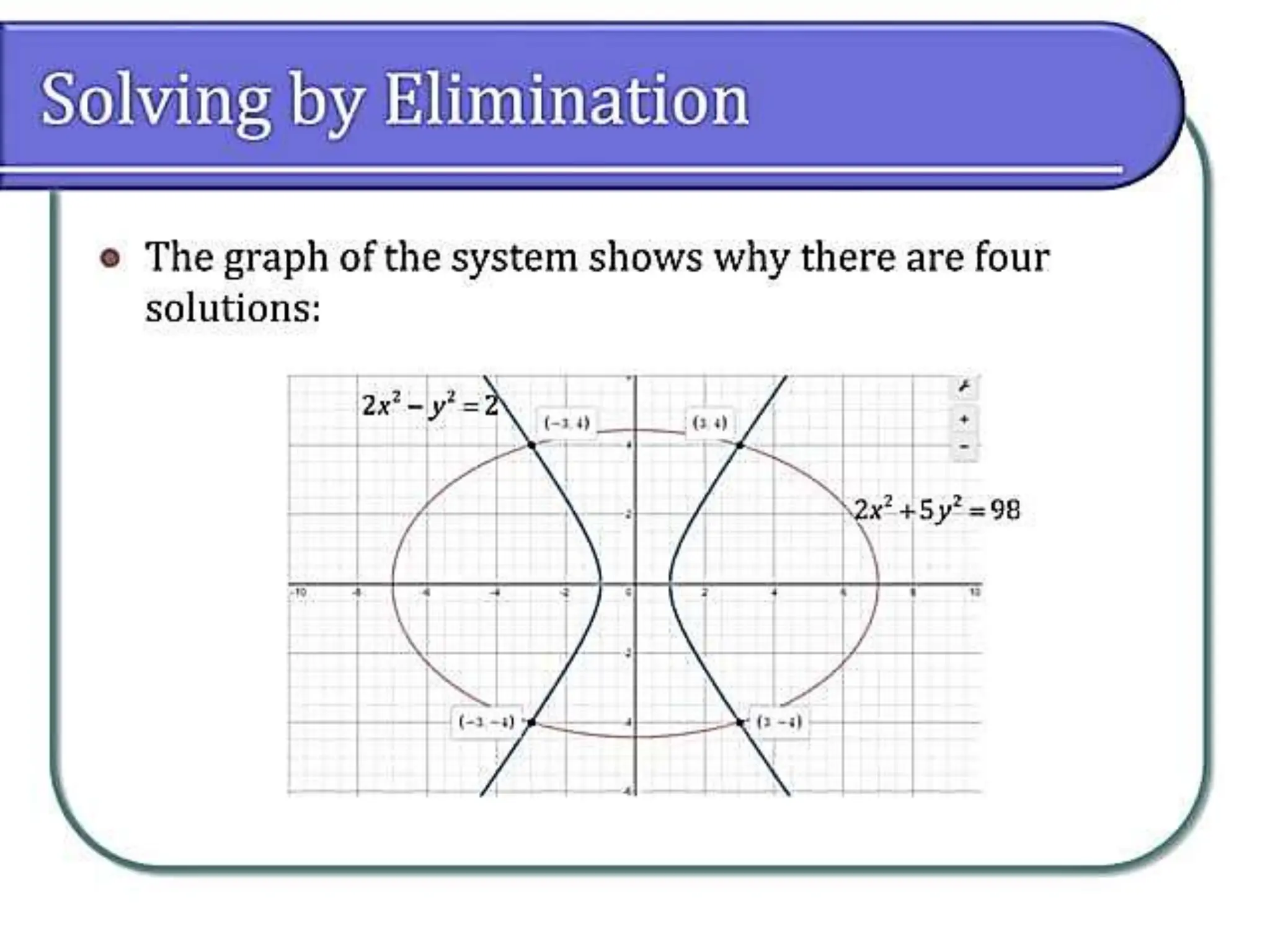

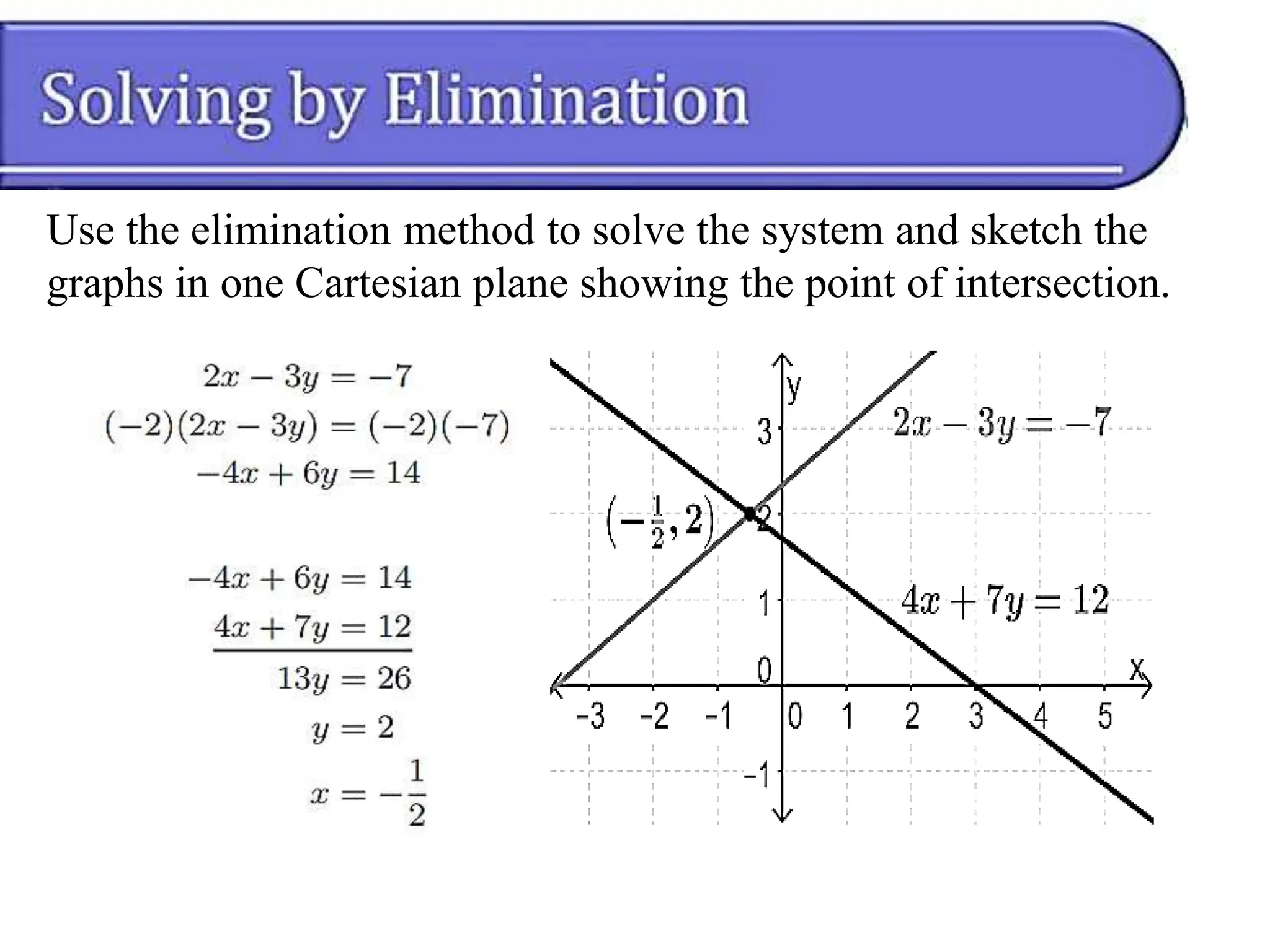








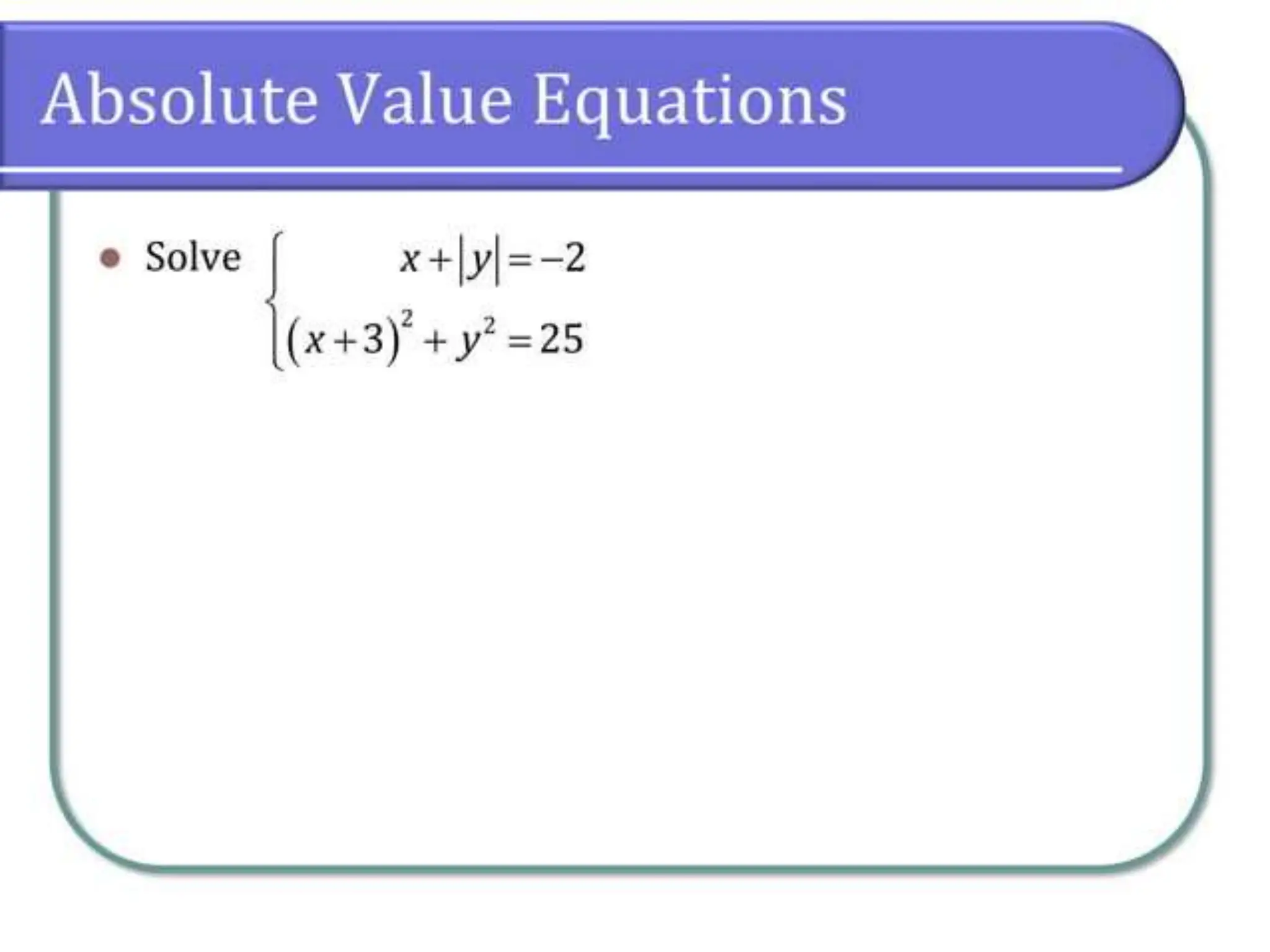


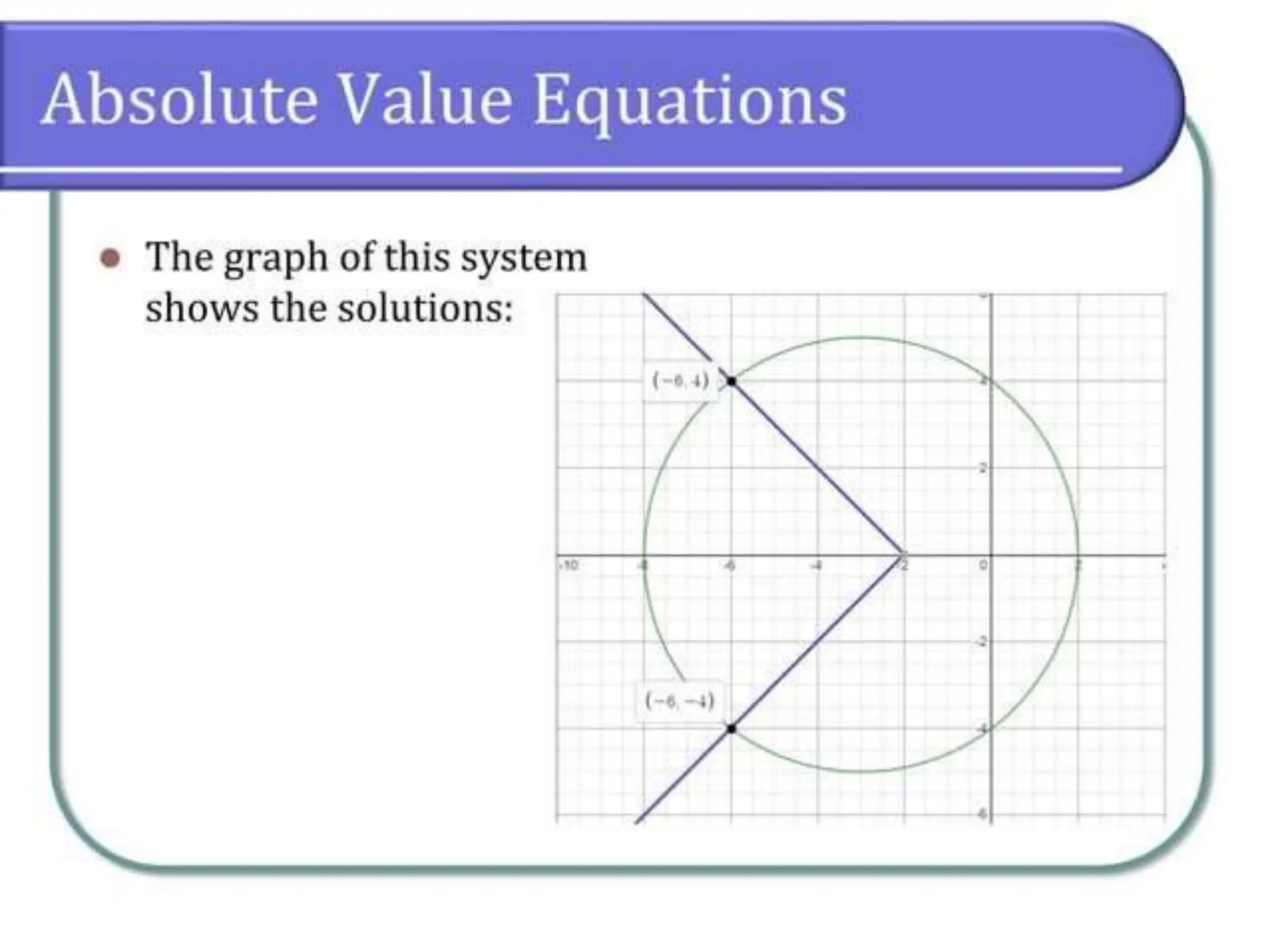


This document discusses methods for solving systems of nonlinear equations, including elimination, substitution, and graphing. It provides examples of using elimination and substitution to solve specific systems. Elimination involves rewriting equations and adding them to eliminate a variable, while substitution isolates a variable in one equation and substitutes it into the other equation. The examples find the point of intersection by solving the systems algebraically and graphing the equations on the same plane.























