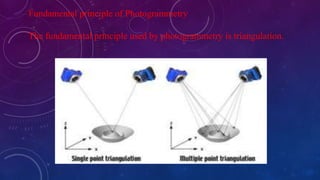
Photogrammetry is the science of making measurements from photographs. It involves deriving metric information about an object through measurements made on photographs. The fundamental principle of photogrammetry is triangulation. There are three main branches - aerial photogrammetry which uses cameras on aircraft, terrestrial photogrammetry which uses ground-based cameras, and space photogrammetry which uses cameras in space. Photogrammetry has various applications including topographic mapping, military intelligence gathering, soil classification, and assessing crop damage.