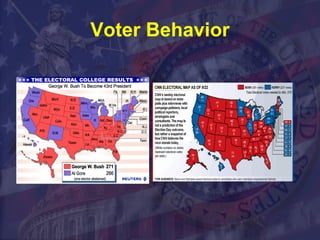
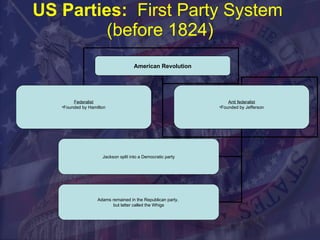
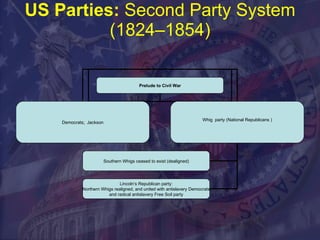
Political parties are important in a democracy to organize candidates, present alternative policy options to voters, and help mobilize public support. The main US political parties today are the Republican Party and Democratic Party. They emerged from the early Federalist and Anti-Federalist parties and evolved through various political eras and realignments related to issues like slavery and economic policies. Parties help structure government and provide accountability to voters.