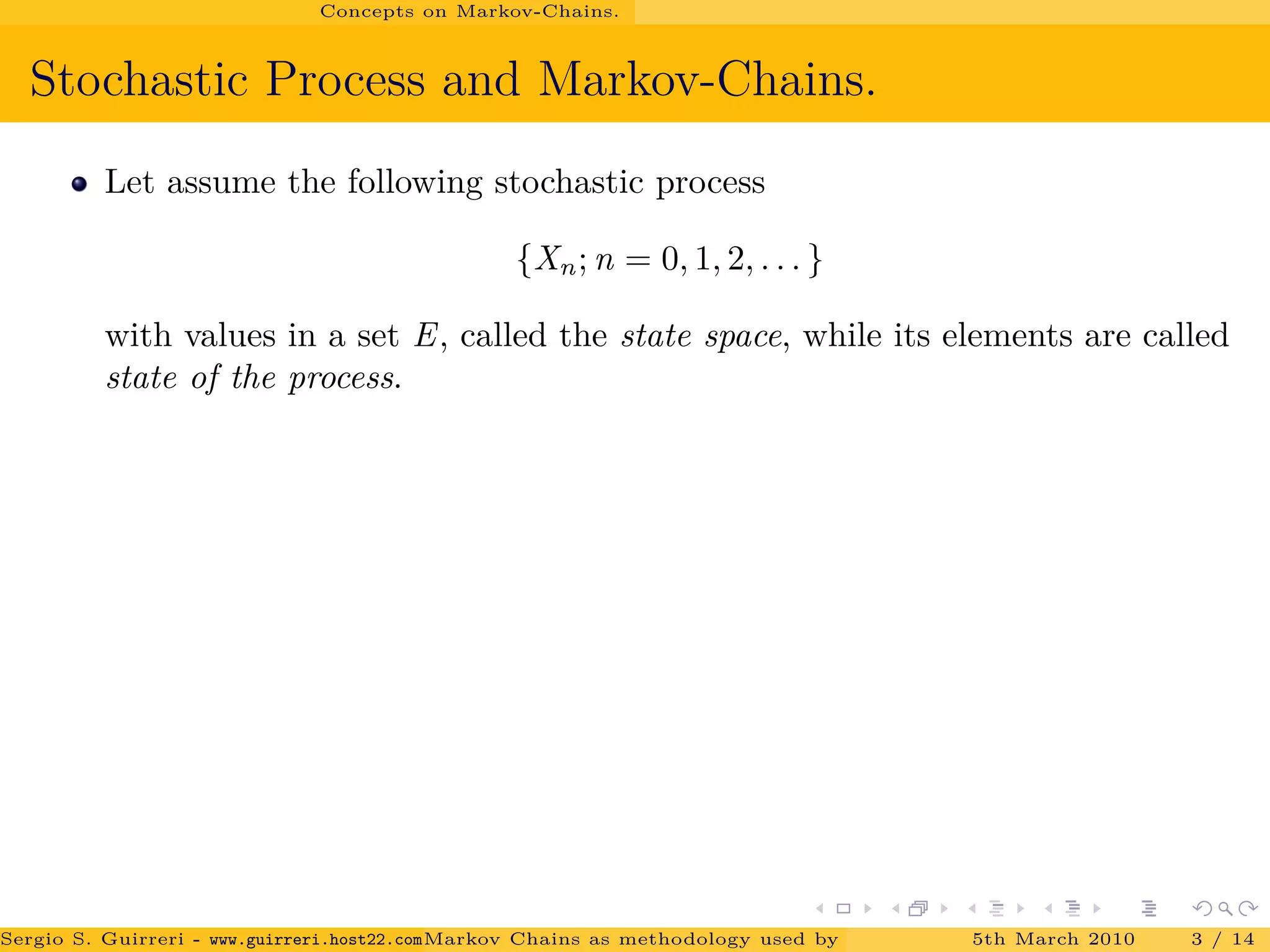
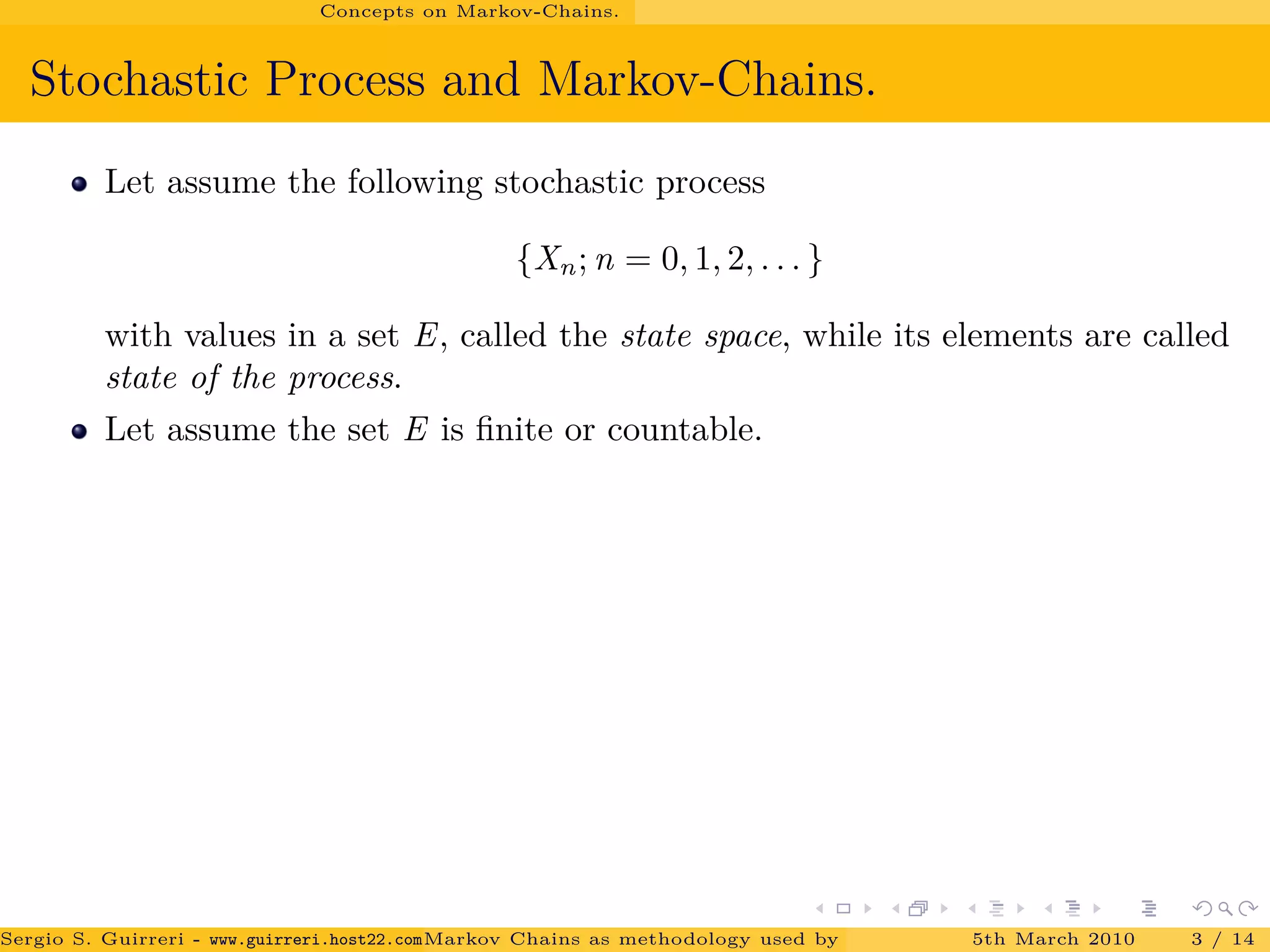
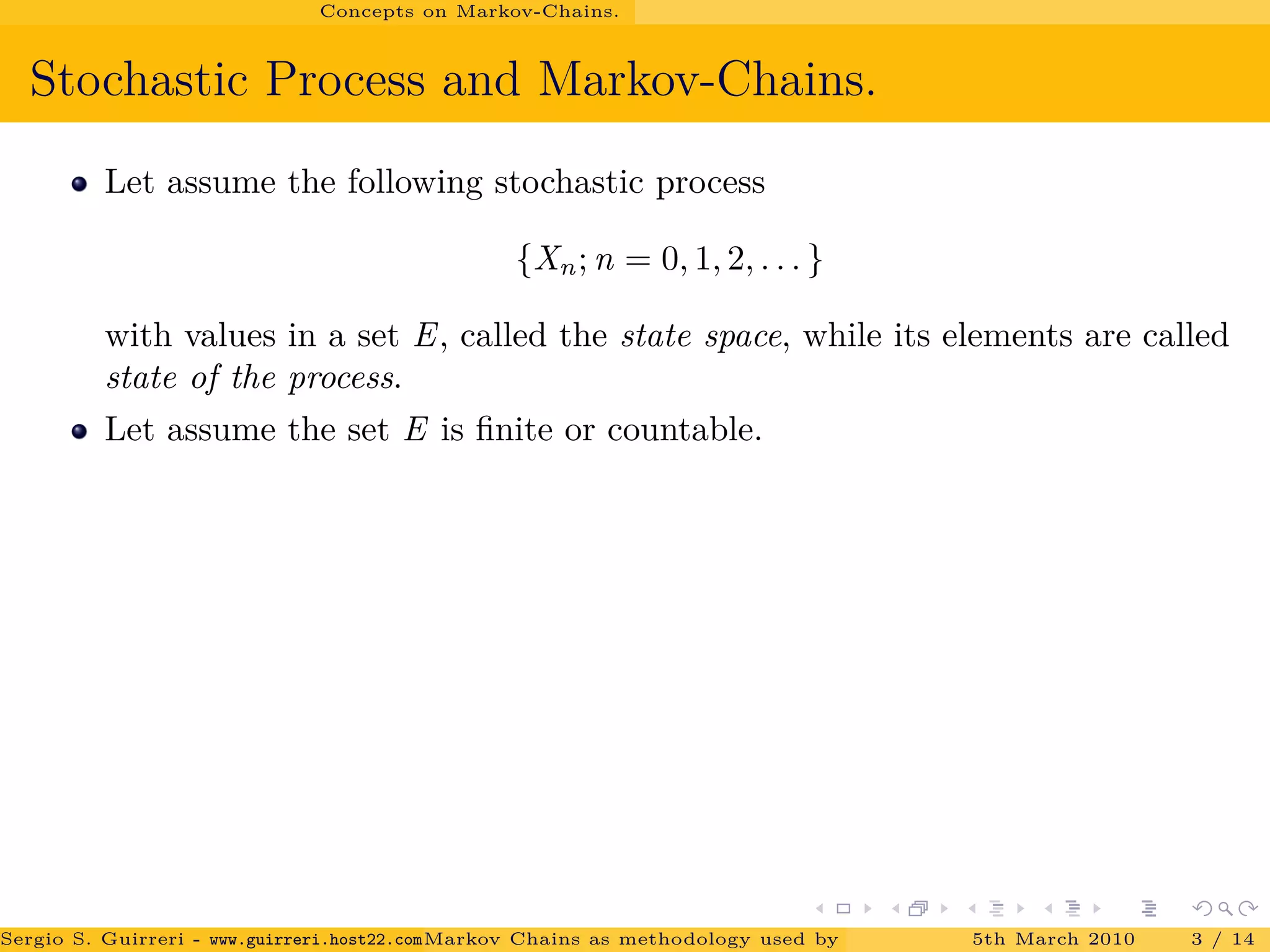
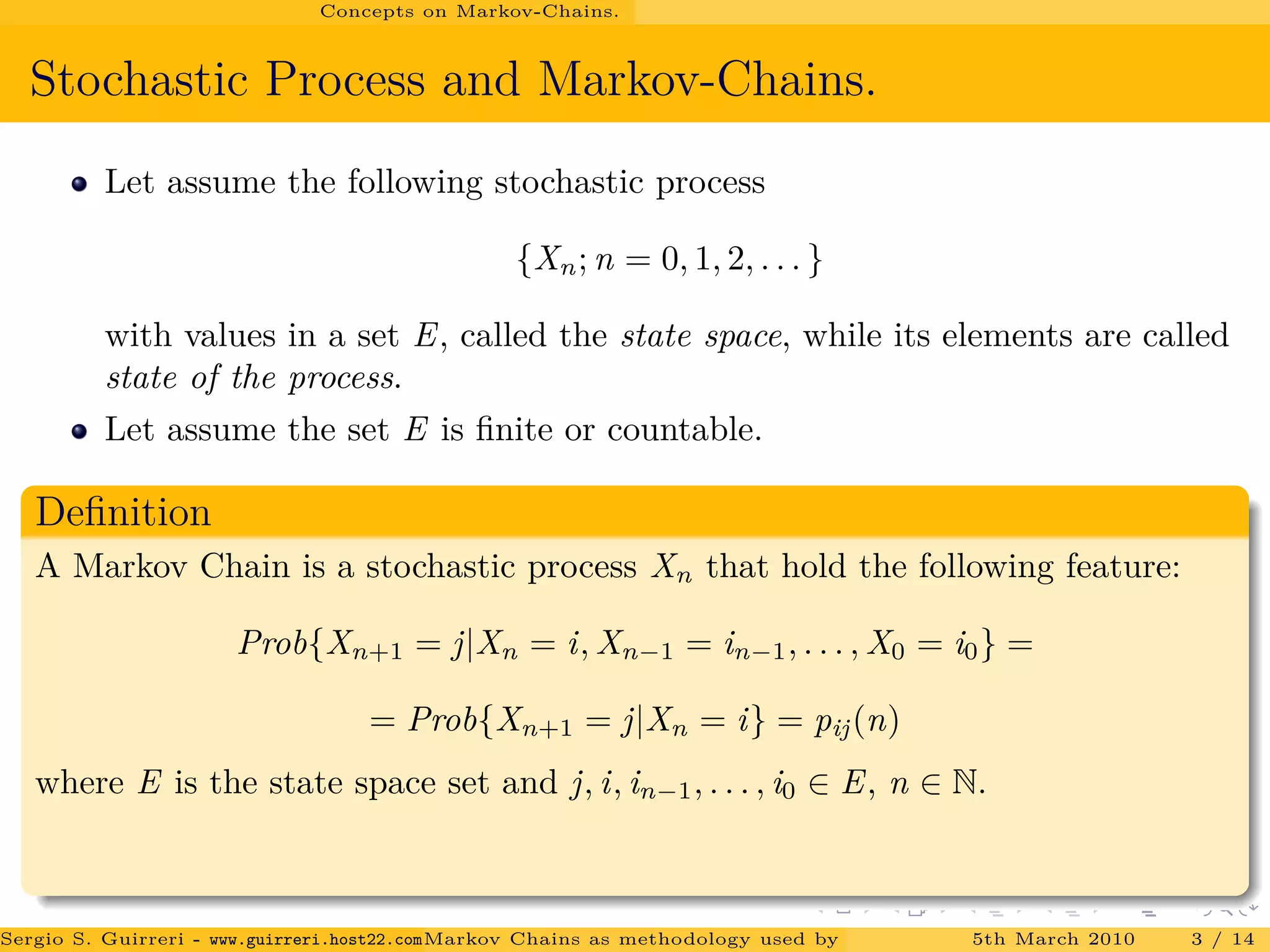
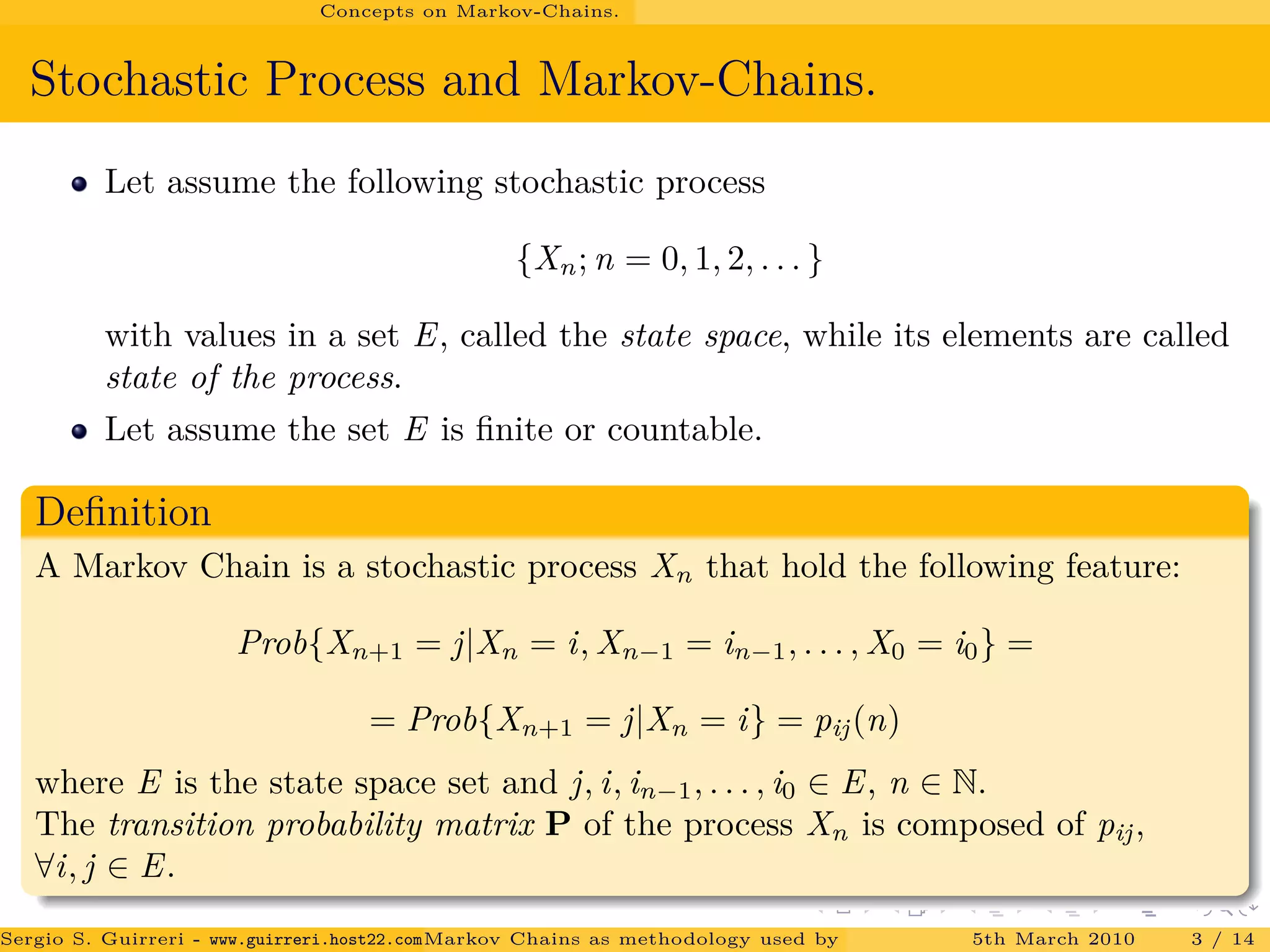
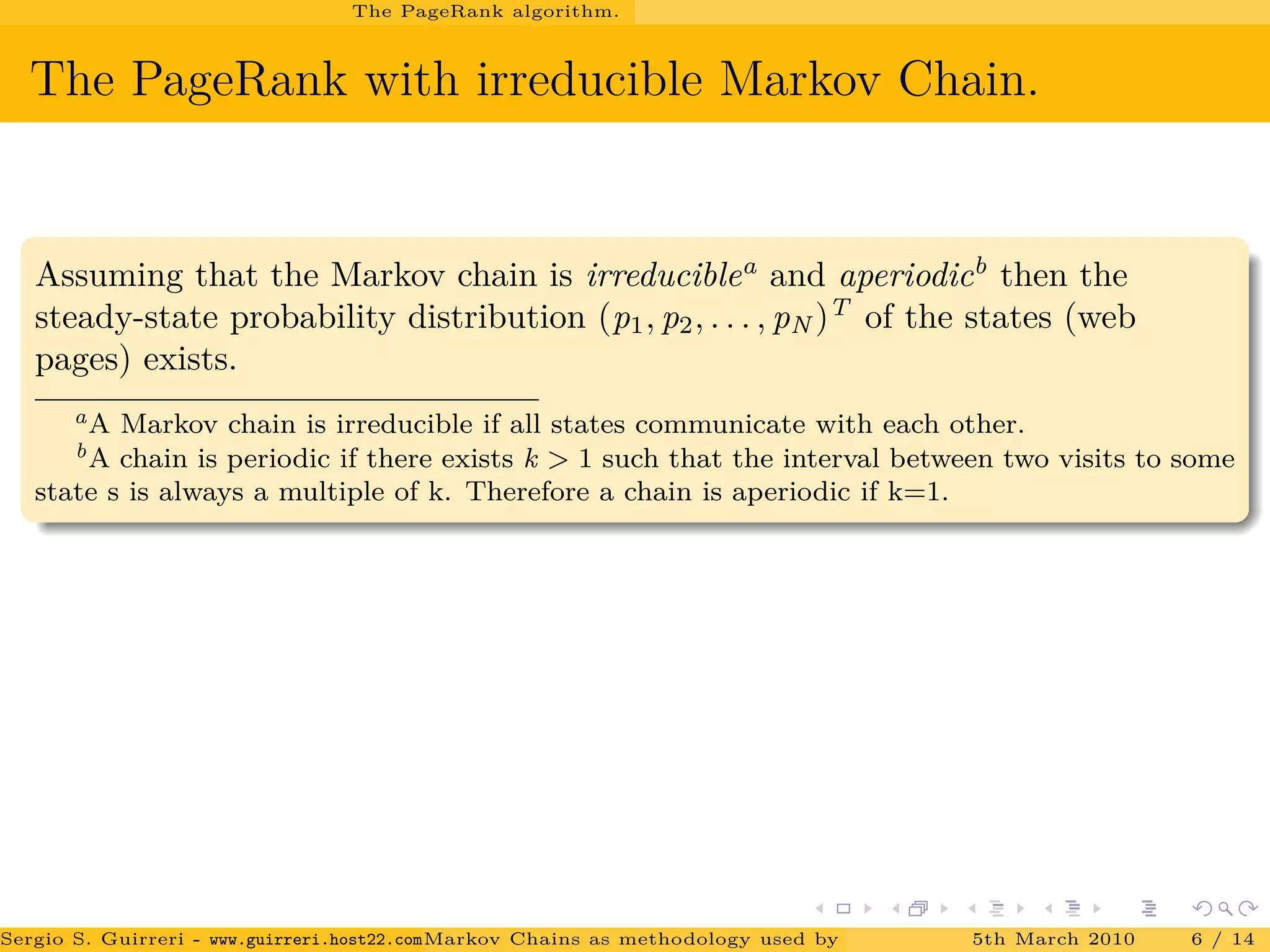
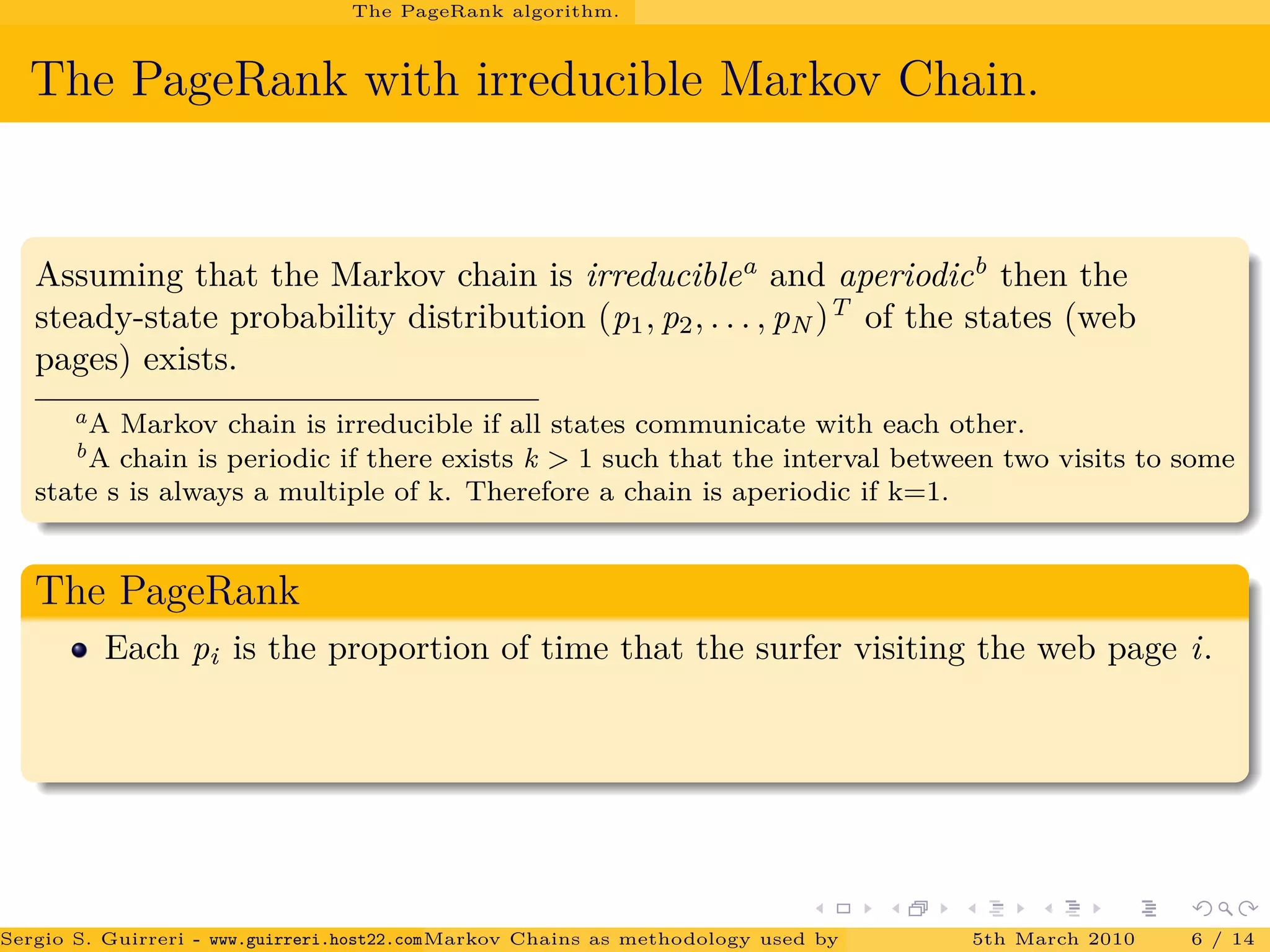
The document discusses how Markov chains are used as the methodology behind PageRank to rank web pages on the internet. It provides an overview of key concepts, including defining Markov chains and stochastic processes. It explains the idea behind PageRank, treating each web page as a journal and measuring importance based on the number of citations/links to other pages. The PageRank algorithm models web surfing as a Markov chain and the steady-state probabilities of the chain indicate the importance of each page.


![The idea of the PageRank algorithm.
PageRank’s idea.
The idea behind the PageRank algorithm is similar to the idea of the impact
factor index used to rank the Journals [Page et al.(1999)]
[Brin and Page(1998)] [Langville et al.(2008)].
Sergio S. Guirreri - www.guirreri.host22.com (Google Technology User Group (GTUG) of Palermo.)Markov Chains as methodology used by PageRank to rank the Web Pages on Inte5th March 2010 4 / 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/guirreripagerank-12881971142656-phpapp01/75/PageRank-and-Markov-Chain-8-2048.jpg)
![The idea of the PageRank algorithm.
PageRank’s idea.
The idea behind the PageRank algorithm is similar to the idea of the impact
factor index used to rank the Journals [Page et al.(1999)]
[Brin and Page(1998)] [Langville et al.(2008)].
PageRank the impact factor of Internet.
The impact factor of a journal is defined as the average number of citations
per recently published papers in that journal.
By regarding each web page as a journal, this idea was then extended to
measure the importance of the web page in the PageRank Algorithm.
Sergio S. Guirreri - www.guirreri.host22.com (Google Technology User Group (GTUG) of Palermo.)Markov Chains as methodology used by PageRank to rank the Web Pages on Inte5th March 2010 4 / 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/guirreripagerank-12881971142656-phpapp01/75/PageRank-and-Markov-Chain-9-2048.jpg)
![The idea of the PageRank algorithm.
Elements of the PageRank.
To illustrate the PageRank algorithm I define the following variables
[Ching and Ng(2006)]:
let be N the total number of web pages in the web.
Sergio S. Guirreri - www.guirreri.host22.com (Google Technology User Group (GTUG) of Palermo.)Markov Chains as methodology used by PageRank to rank the Web Pages on Inte5th March 2010 5 / 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/guirreripagerank-12881971142656-phpapp01/75/PageRank-and-Markov-Chain-10-2048.jpg)
![The idea of the PageRank algorithm.
Elements of the PageRank.
To illustrate the PageRank algorithm I define the following variables
[Ching and Ng(2006)]:
let be N the total number of web pages in the web.
let be k the outgoing links of web page j.
Sergio S. Guirreri - www.guirreri.host22.com (Google Technology User Group (GTUG) of Palermo.)Markov Chains as methodology used by PageRank to rank the Web Pages on Inte5th March 2010 5 / 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/guirreripagerank-12881971142656-phpapp01/75/PageRank-and-Markov-Chain-11-2048.jpg)
![The idea of the PageRank algorithm.
Elements of the PageRank.
To illustrate the PageRank algorithm I define the following variables
[Ching and Ng(2006)]:
let be N the total number of web pages in the web.
let be k the outgoing links of web page j.
let be Q the so called hyperlink matrix with elements:
Qij =
1
k if web page i is an outgoing link of web page j;
0 otherwise;
Qi,i > 0 ∀i.
(1)
Sergio S. Guirreri - www.guirreri.host22.com (Google Technology User Group (GTUG) of Palermo.)Markov Chains as methodology used by PageRank to rank the Web Pages on Inte5th March 2010 5 / 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/guirreripagerank-12881971142656-phpapp01/75/PageRank-and-Markov-Chain-12-2048.jpg)
![The idea of the PageRank algorithm.
Elements of the PageRank.
To illustrate the PageRank algorithm I define the following variables
[Ching and Ng(2006)]:
let be N the total number of web pages in the web.
let be k the outgoing links of web page j.
let be Q the so called hyperlink matrix with elements:
Qij =
1
k if web page i is an outgoing link of web page j;
0 otherwise;
Qi,i > 0 ∀i.
(1)
Sergio S. Guirreri - www.guirreri.host22.com (Google Technology User Group (GTUG) of Palermo.)Markov Chains as methodology used by PageRank to rank the Web Pages on Inte5th March 2010 5 / 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/guirreripagerank-12881971142656-phpapp01/75/PageRank-and-Markov-Chain-13-2048.jpg)
![The idea of the PageRank algorithm.
Elements of the PageRank.
To illustrate the PageRank algorithm I define the following variables
[Ching and Ng(2006)]:
let be N the total number of web pages in the web.
let be k the outgoing links of web page j.
let be Q the so called hyperlink matrix with elements:
Qij =
1
k if web page i is an outgoing link of web page j;
0 otherwise;
Qi,i > 0 ∀i.
(1)
The hyperlink matrix Q can be regarded as a transition probability matrix of
a Markov chain.
One may regard a surfer on the net as a random walker and the web pages as
the states of the Markov chain.
Sergio S. Guirreri - www.guirreri.host22.com (Google Technology User Group (GTUG) of Palermo.)Markov Chains as methodology used by PageRank to rank the Web Pages on Inte5th March 2010 5 / 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/guirreripagerank-12881971142656-phpapp01/75/PageRank-and-Markov-Chain-14-2048.jpg)
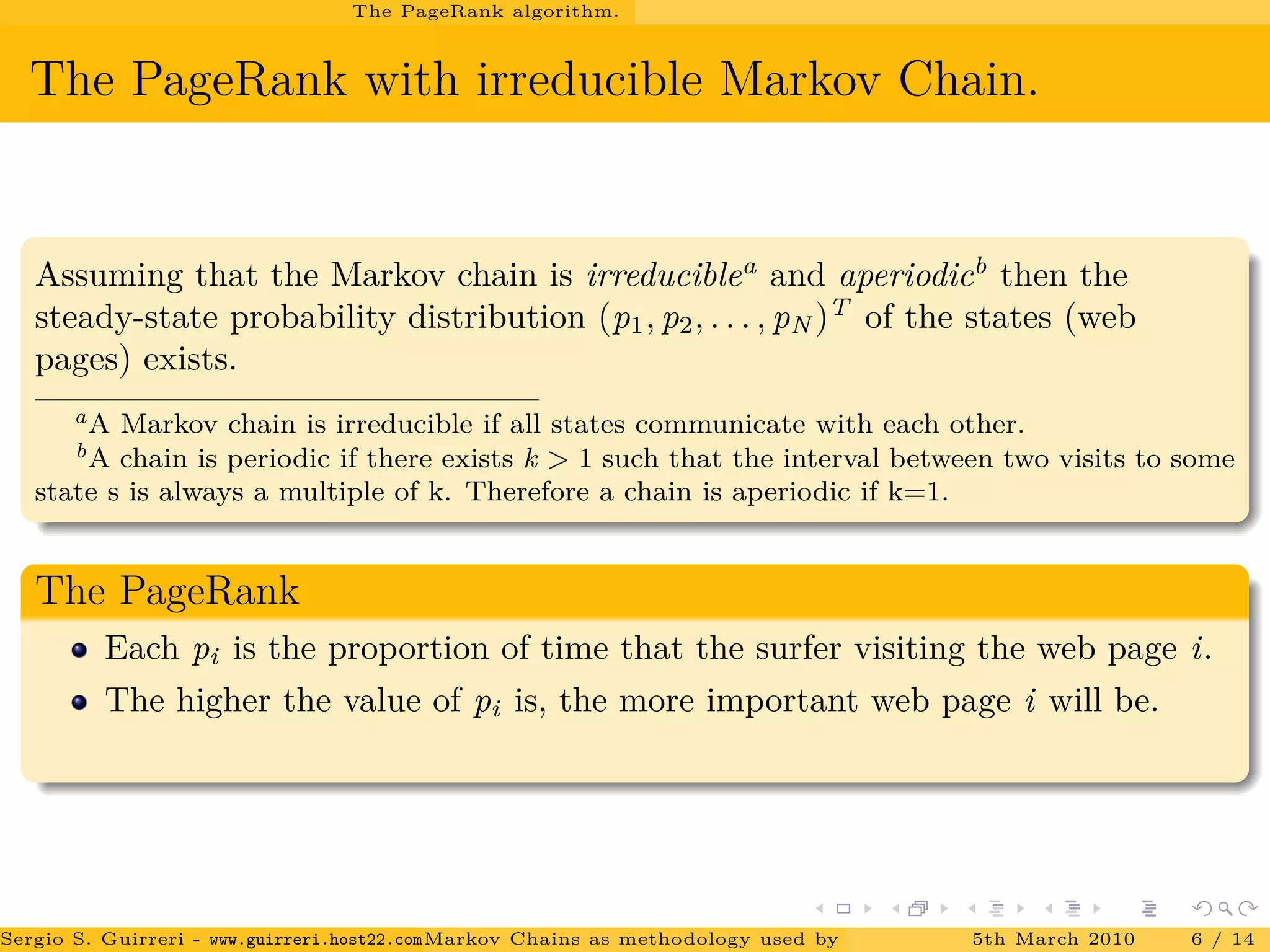
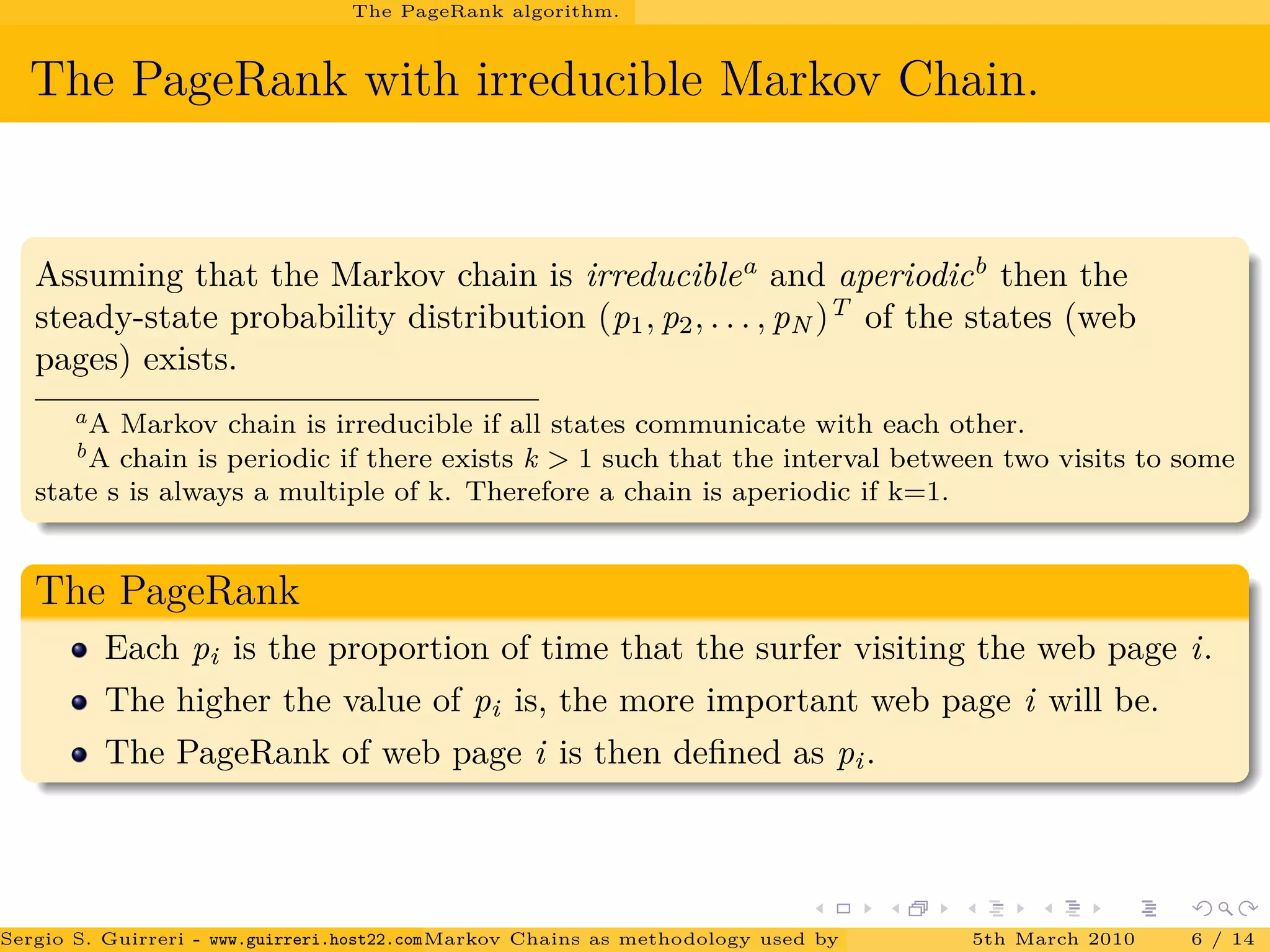
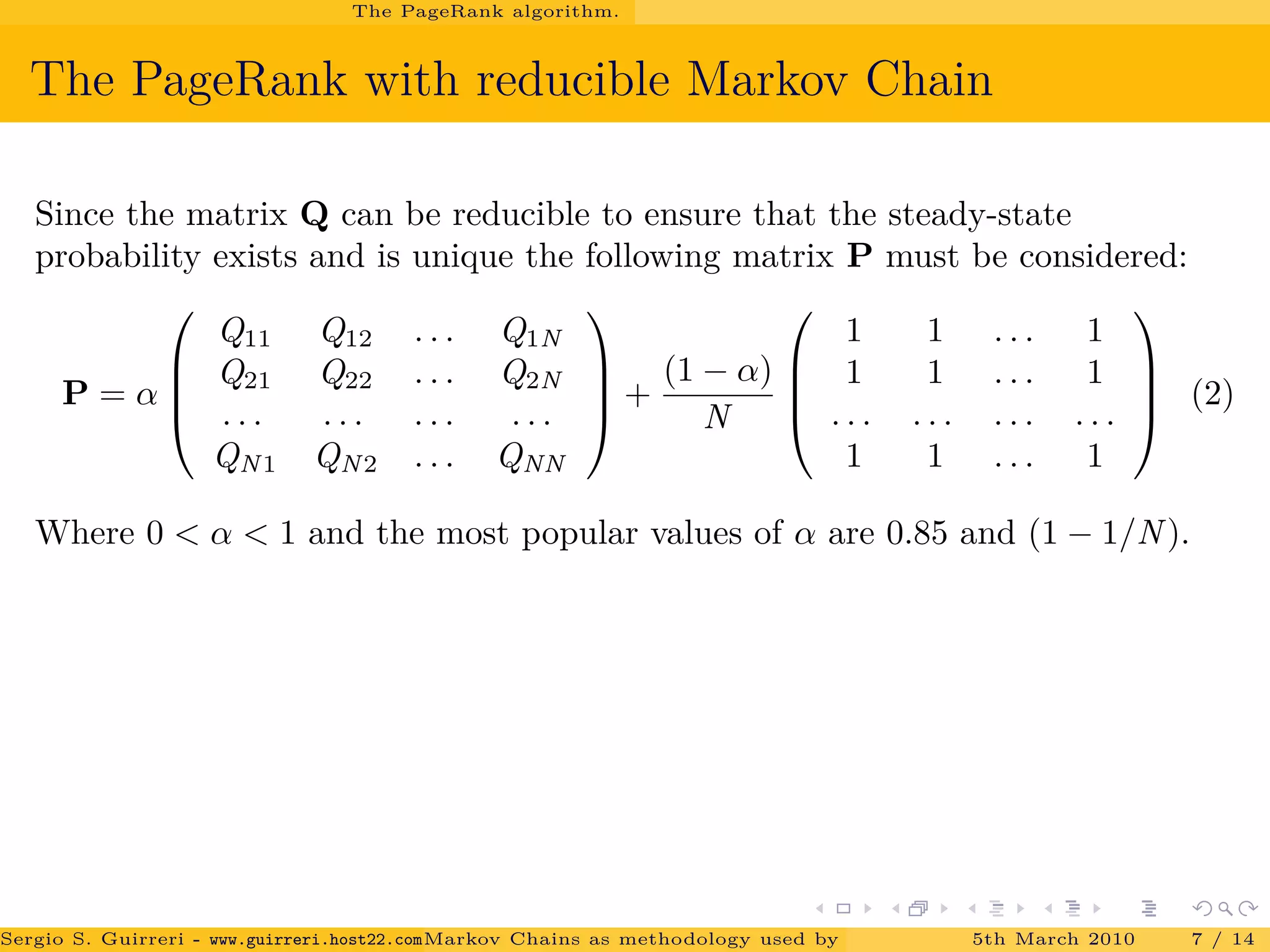
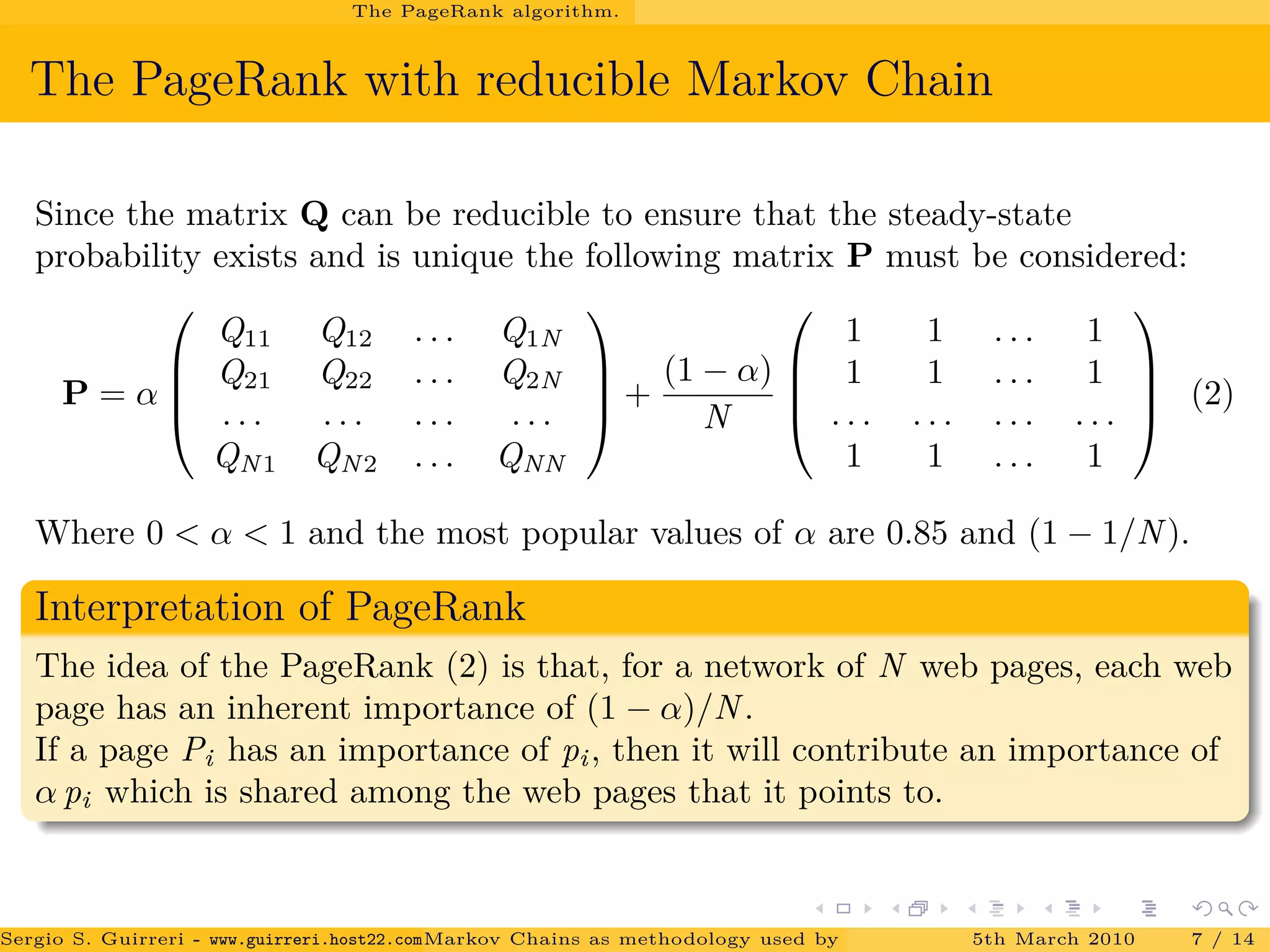
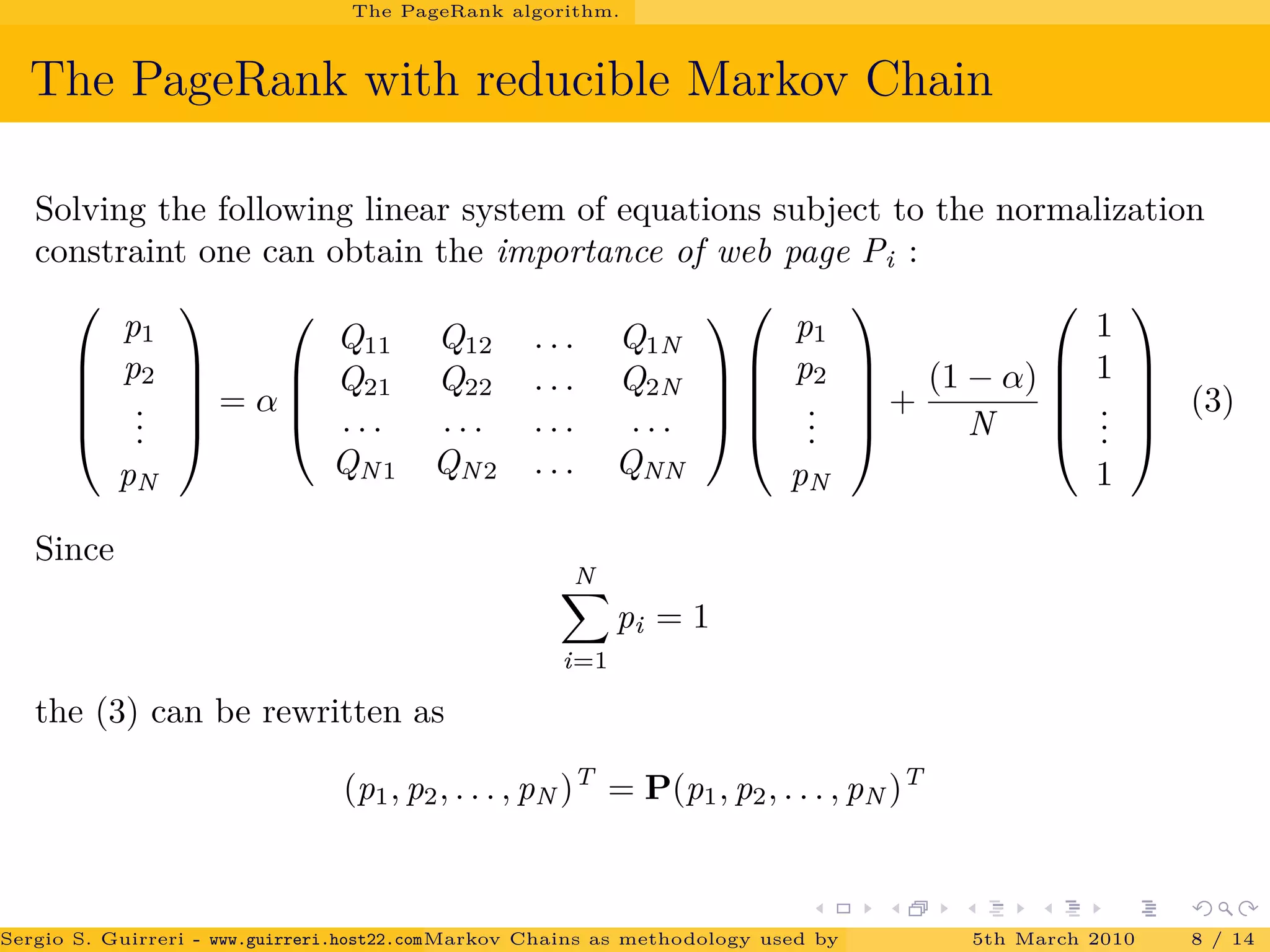














![Conclusions.
The power method and PageRank.
Results.
The matrix P of the PageRank algorithm is a stochastic matrix therefore
the largest eigenvalue is 1.
The convergence rate of the power method depends on the ratio of λ2
λ1
.
It has been showed by [Haveliwala and Kamvar(2003)] that for the second
largest eigenvalue of P, we have
|λ2| ≤ α 0 ≤ α ≤ 1.
Sergio S. Guirreri - www.guirreri.host22.com (Google Technology User Group (GTUG) of Palermo.)Markov Chains as methodology used by PageRank to rank the Web Pages on Inte5th March 2010 11 / 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/guirreripagerank-12881971142656-phpapp01/75/PageRank-and-Markov-Chain-36-2048.jpg)
![Conclusions.
The power method and PageRank.
Results.
The matrix P of the PageRank algorithm is a stochastic matrix therefore
the largest eigenvalue is 1.
The convergence rate of the power method depends on the ratio of λ2
λ1
.
It has been showed by [Haveliwala and Kamvar(2003)] that for the second
largest eigenvalue of P, we have
|λ2| ≤ α 0 ≤ α ≤ 1.
Since λ1 = 1 the converge rate depends on α.
Sergio S. Guirreri - www.guirreri.host22.com (Google Technology User Group (GTUG) of Palermo.)Markov Chains as methodology used by PageRank to rank the Web Pages on Inte5th March 2010 11 / 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/guirreripagerank-12881971142656-phpapp01/75/PageRank-and-Markov-Chain-37-2048.jpg)
![Conclusions.
The power method and PageRank.
Results.
The matrix P of the PageRank algorithm is a stochastic matrix therefore
the largest eigenvalue is 1.
The convergence rate of the power method depends on the ratio of λ2
λ1
.
It has been showed by [Haveliwala and Kamvar(2003)] that for the second
largest eigenvalue of P, we have
|λ2| ≤ α 0 ≤ α ≤ 1.
Since λ1 = 1 the converge rate depends on α.
The most popular value for α is 0.85. With this value it has been proved
that the power method on web data set of over 80 million pages converges
in about 50 iterations.
Sergio S. Guirreri - www.guirreri.host22.com (Google Technology User Group (GTUG) of Palermo.)Markov Chains as methodology used by PageRank to rank the Web Pages on Inte5th March 2010 11 / 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/guirreripagerank-12881971142656-phpapp01/75/PageRank-and-Markov-Chain-38-2048.jpg)