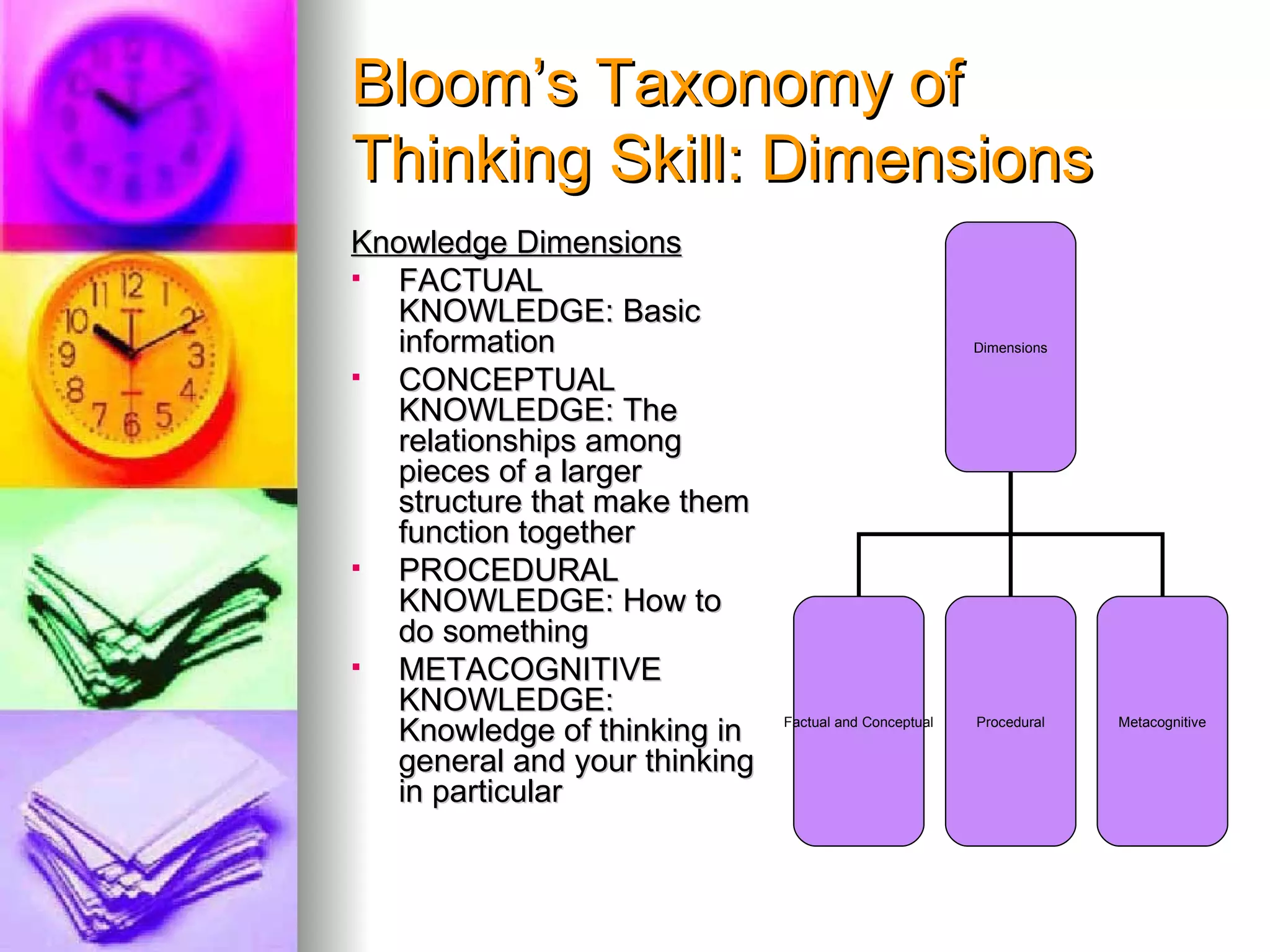
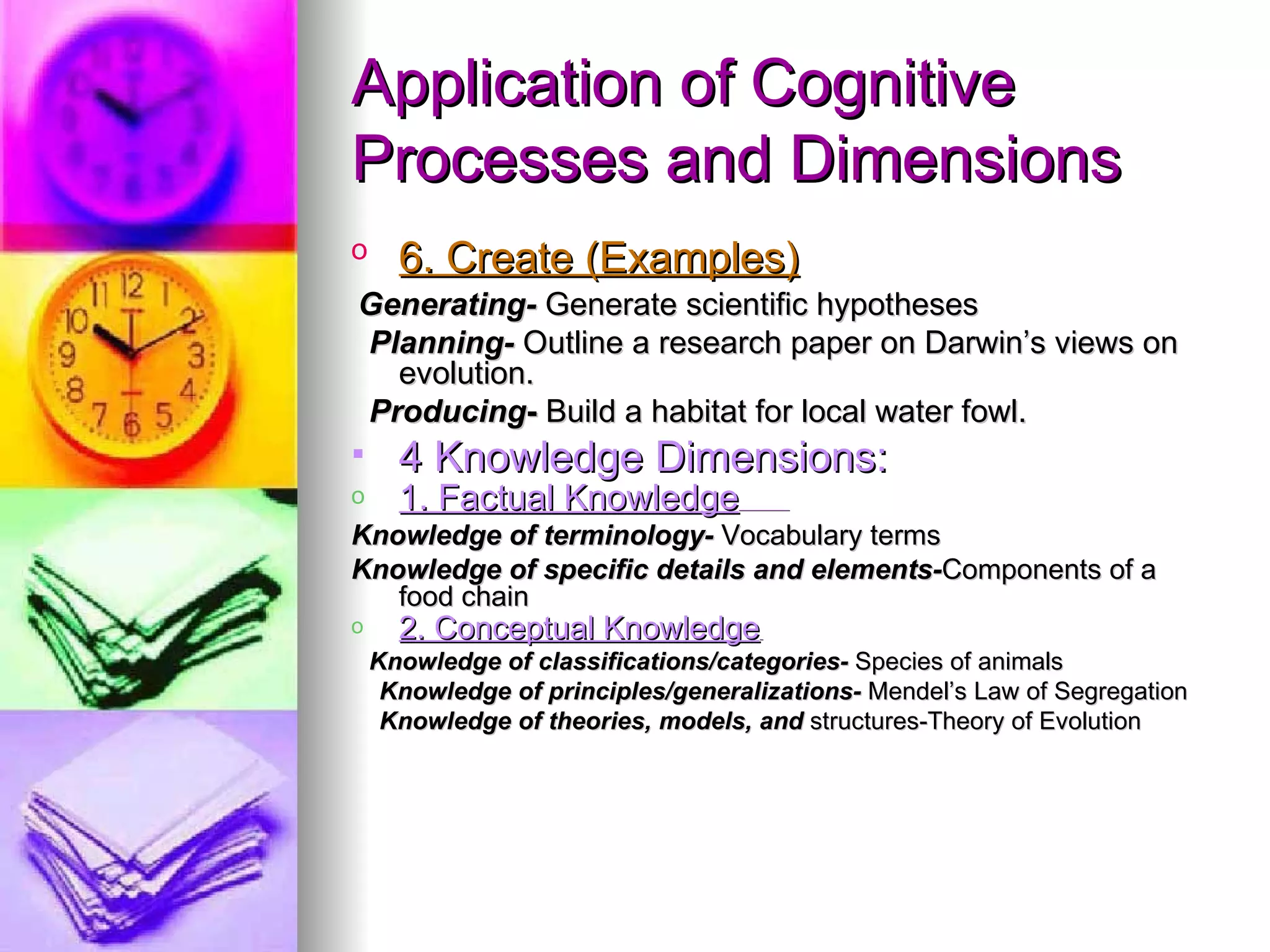
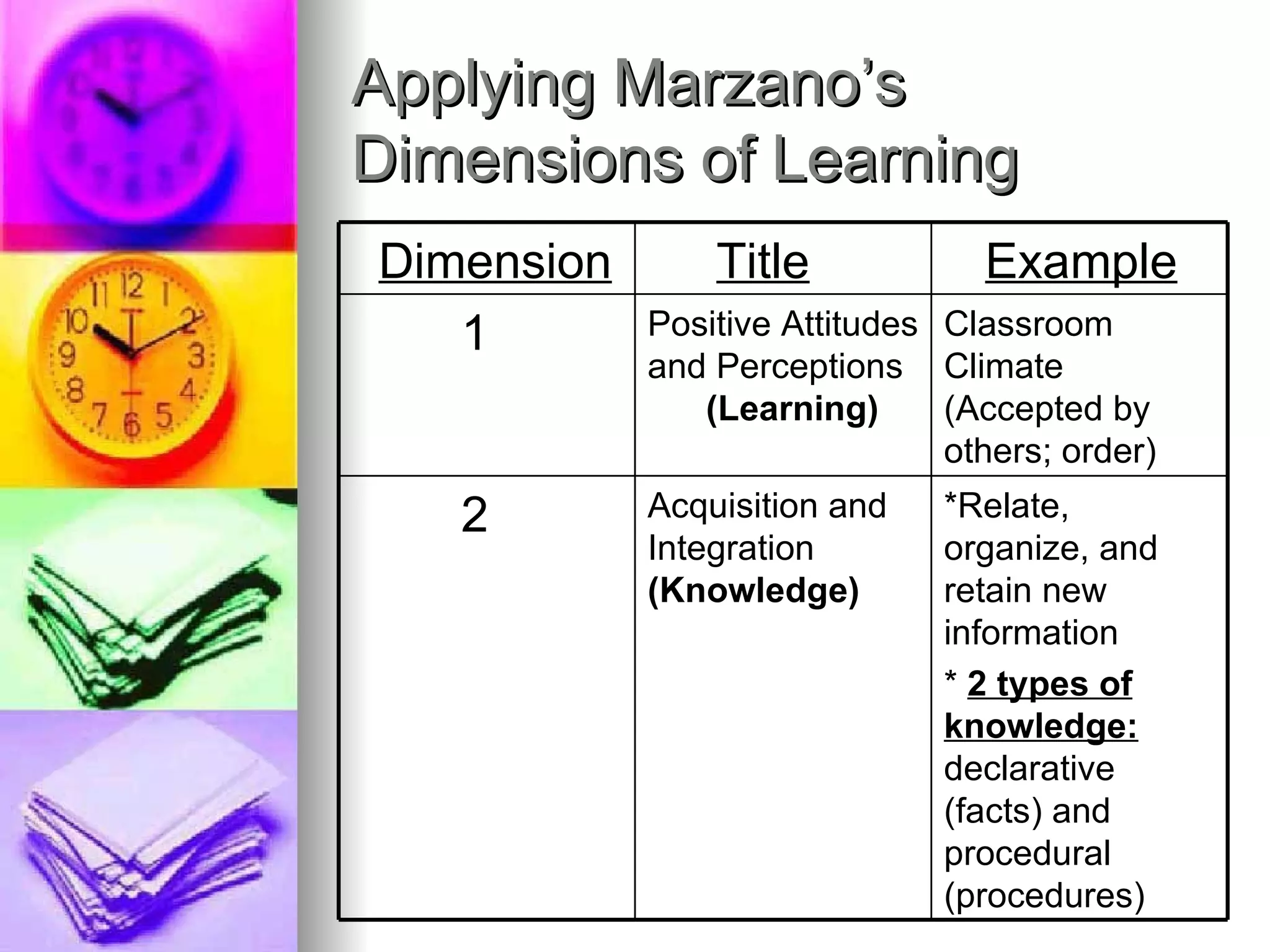
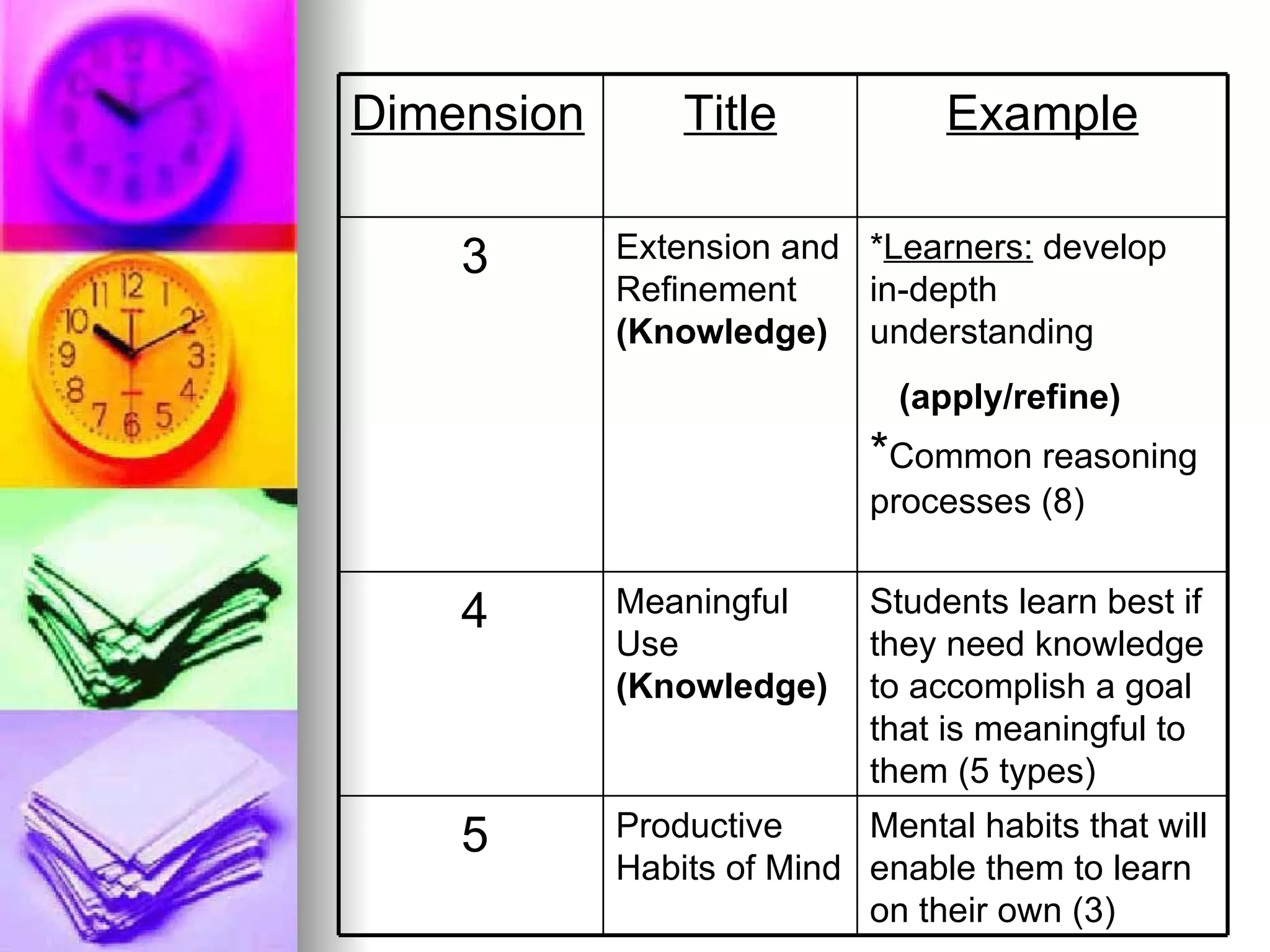
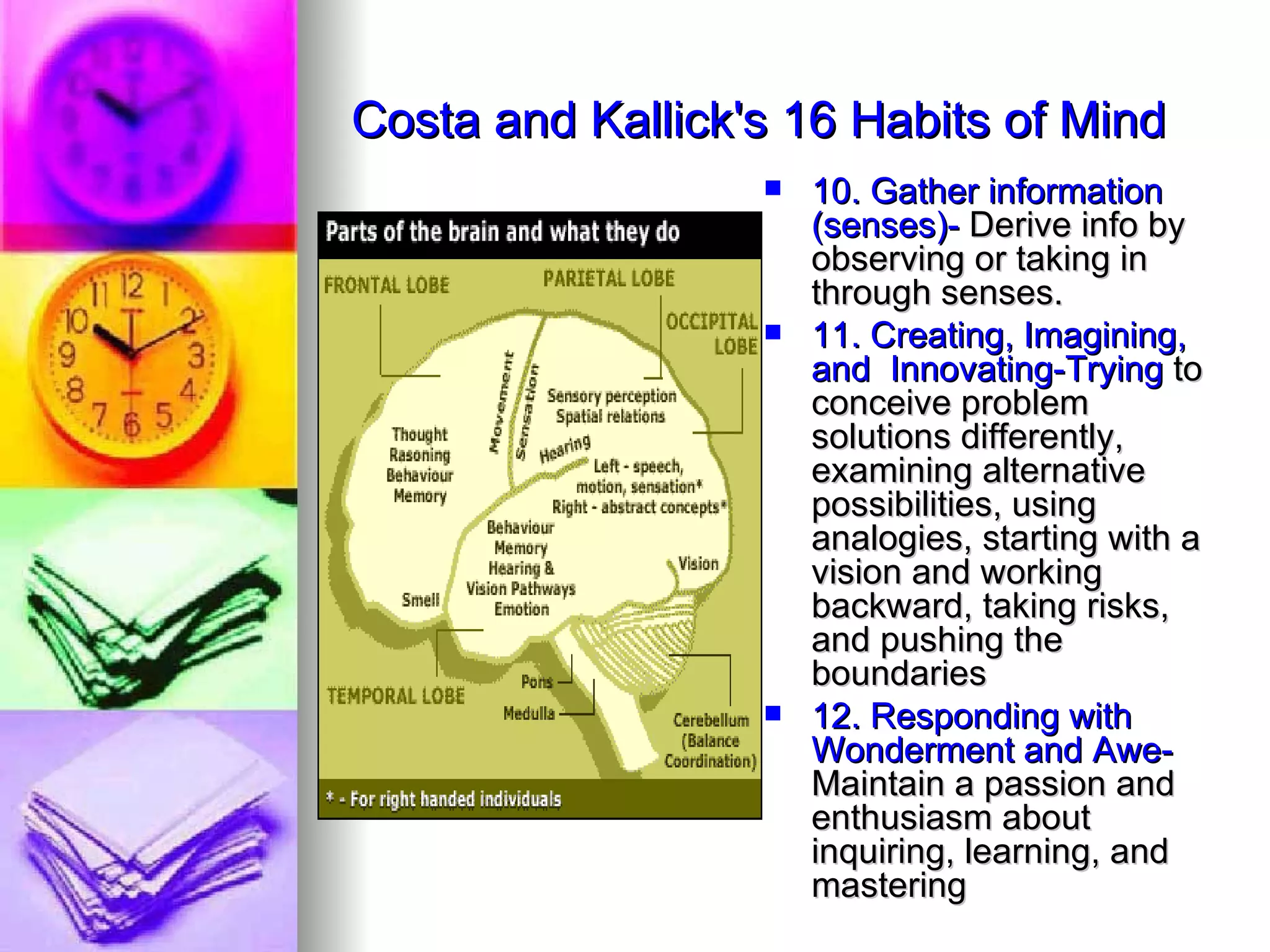
The document provides an overview of various models of thinking that can be applied in educational settings. It summarizes Bloom's Taxonomy of cognitive processes and knowledge dimensions, demonstrates how the taxonomy can be applied, and discusses other models including Marzano's Dimensions of Learning and Costa and Kallick's 16 Habits of Mind. The purpose is to show parents how these thinking models guide teaching practices and student assessment.