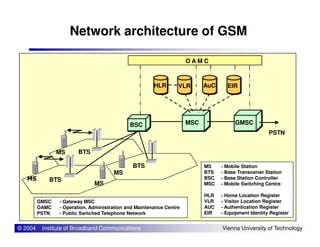
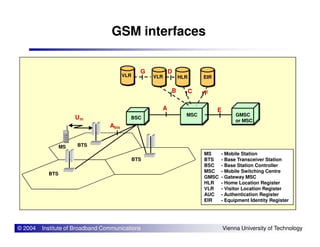
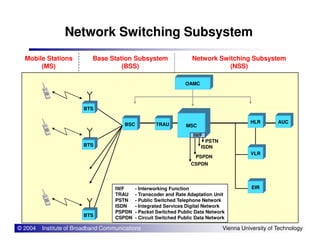
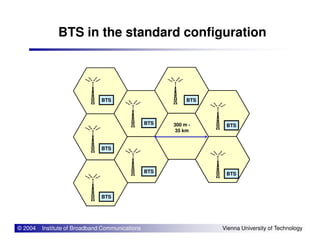
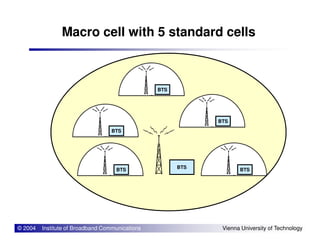
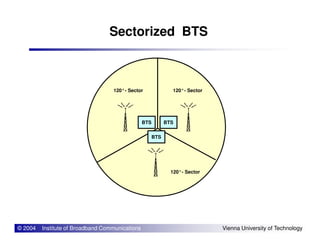
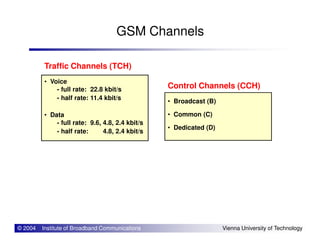
The document provides an overview of mobile communication networks and the GSM standard. It discusses the history and development of GSM in Europe. Key aspects of GSM network architecture are summarized, including the main network elements and interfaces. The coding and processing of information over the radio interface is also briefly described.