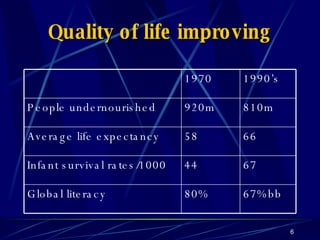
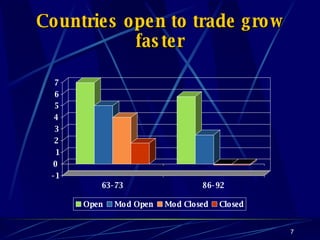
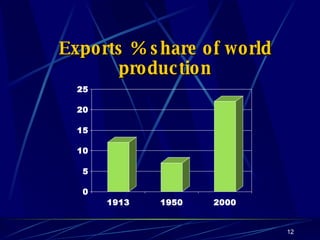
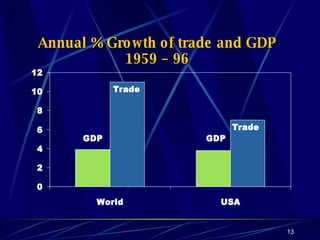
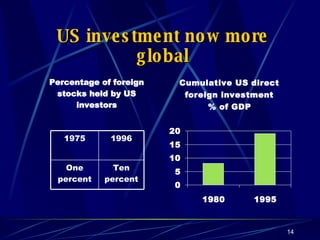
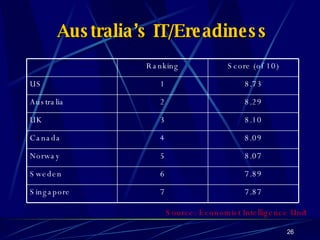
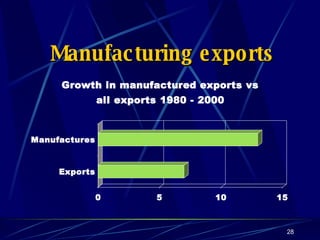
Globalization has led to reductions in global poverty and improvements in quality of life. While the wealth gap between the richest and poorest has narrowed, the proportion of people living in extreme poverty has fallen as national incomes have risen. Australia has embraced globalization through open trade policies, foreign investment, and immigration. It has competitive advantages in its openness, IT readiness, and culture that have supported the growth of globalized industries like mining, agriculture, manufacturing, and services. Looking ahead, Australia is well-positioned to continue thriving in an increasingly globalized world driven by information technology.