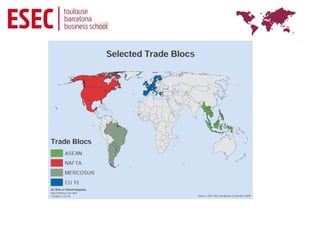
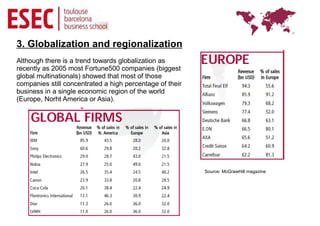
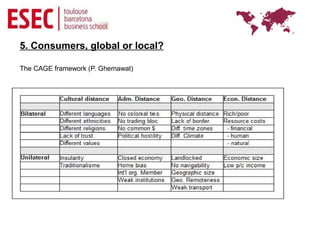
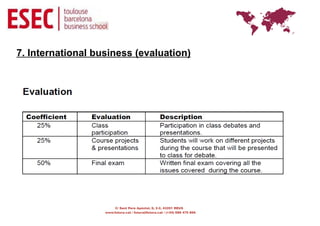
Globalization refers to the reduction of barriers between countries to facilitate the flow of goods, capital, services and labor across borders. It creates opportunities for businesses but also challenges as foreign competitors enter domestic markets. Key drivers of globalization include the decline of trade barriers after WWII, technological advances in communication and transportation, and the fall of political divisions. While some argue global consumer preferences are converging, others note local differences in culture, geography and economies still impact markets. Regional economic integration agreements like the EU and NAFTA have accelerated but most large multinationals still derive a high percentage of business from their home region. Managing international business requires recognizing differences from domestic operations.