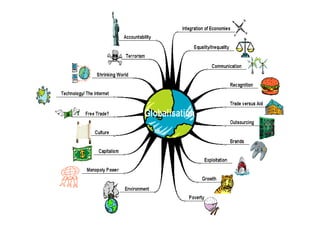
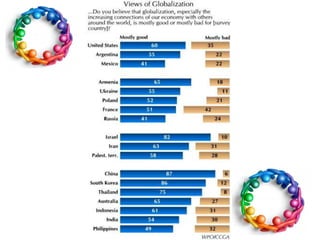
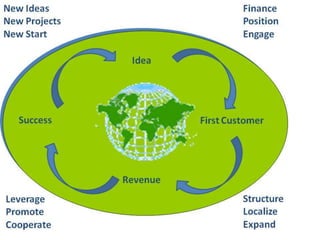
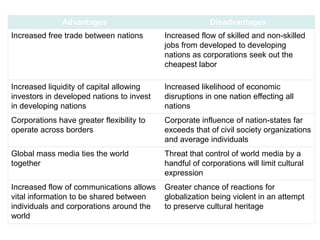
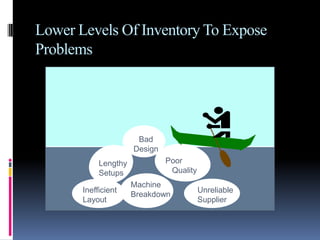
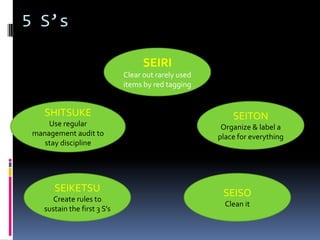
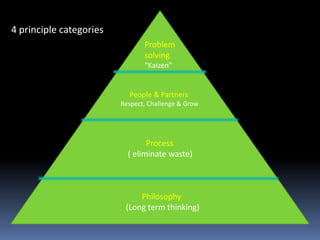
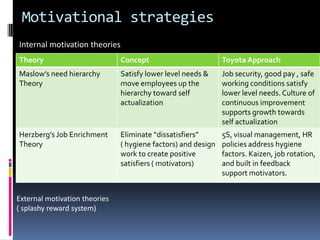
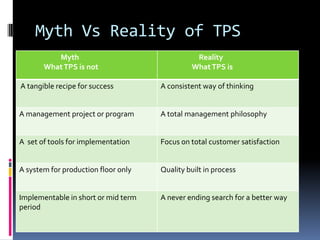
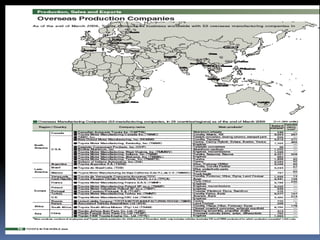
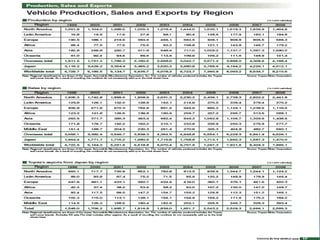
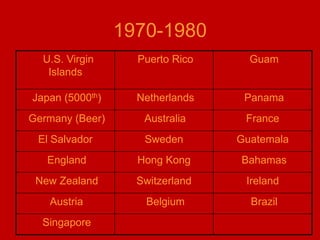
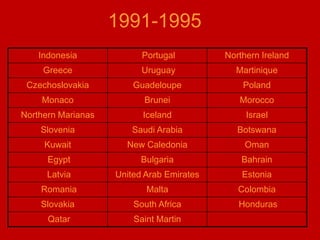
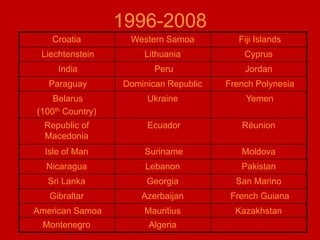
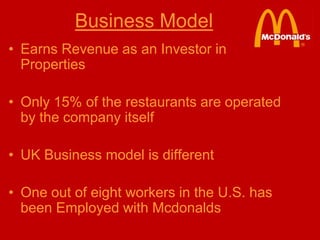
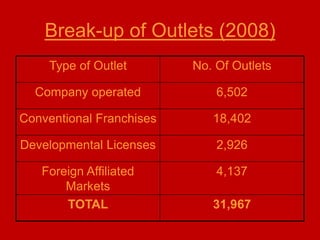
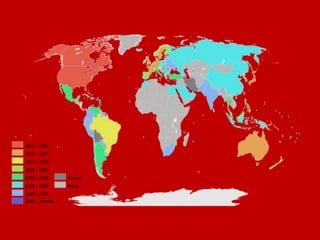
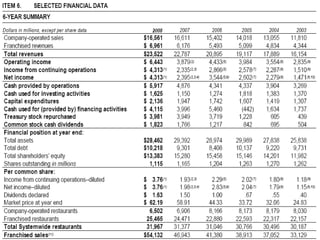
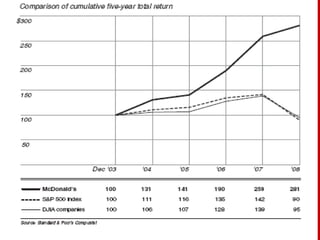
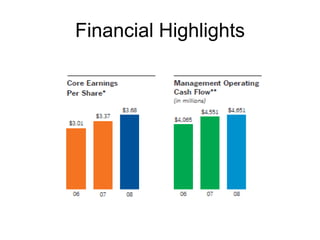
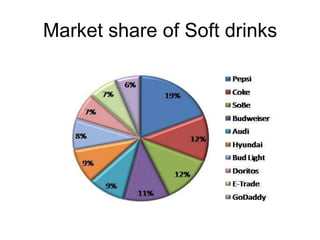
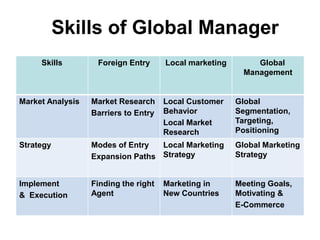
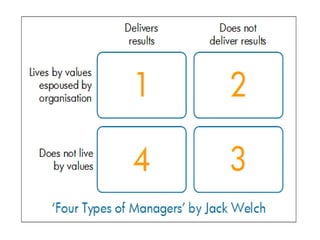
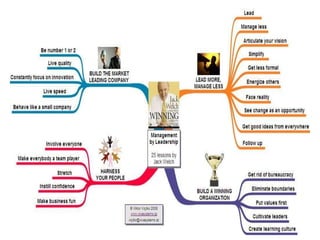
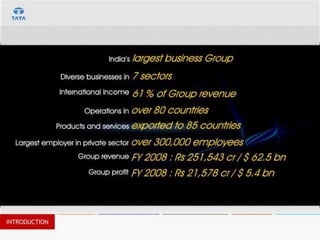
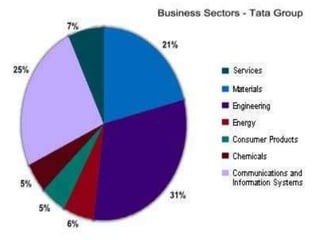
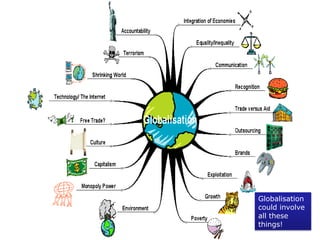
This document provides an introduction and overview of an international business project presented by a group of students to their professor. It includes the names and student IDs of the group members, as well as brief sections on globalization, global companies and global managers. Specific companies discussed include Toyota, McDonald's, PepsiCo, and managers such as Jack Welch and Indian businessman Lakshmi Mittal.