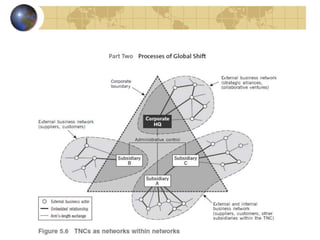
1. Transnational corporations (TNCs) operate across national borders through complex internal and external networks of relationships.
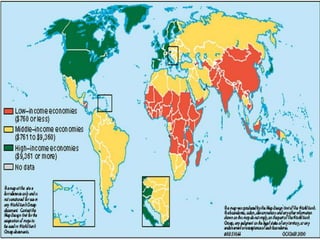
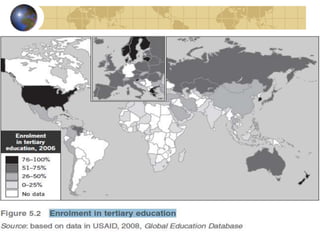
2. TNCs internationalize primarily for market access and to obtain resources like natural resources, labor, and knowledge. They enter foreign markets through exports, foreign direct investment, licensing, franchising, and management contracts.
3. As networks within networks, TNCs organize their internal operations and configure their external relationships based on industry forces, their own history and culture, and their home country influences. Their geographical embeddedness impacts how they operate globally.