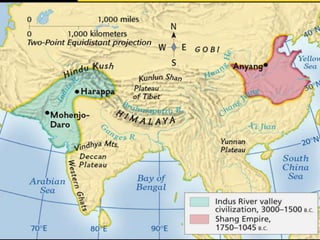
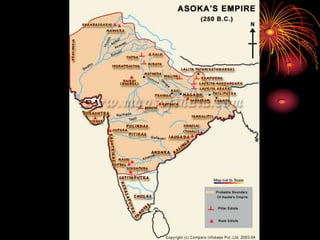
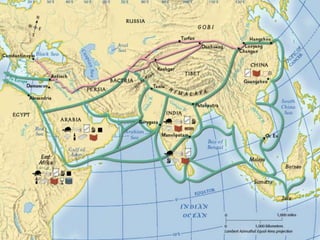
Ancient India developed advanced civilizations like the Indus Valley Civilization between 3000-1500 BC. The Aryans later invaded and established a caste system by 1500 BC. Hinduism and Buddhism emerged as major religions promoting dharma and escaping suffering. China also saw early dynasties like Shang and Zhou centralized around the Yellow River Valley. Confucianism emphasized social harmony through filial piety while Daoism focused on living naturally. Both India and China made scientific advances and established empires during their Golden Ages.