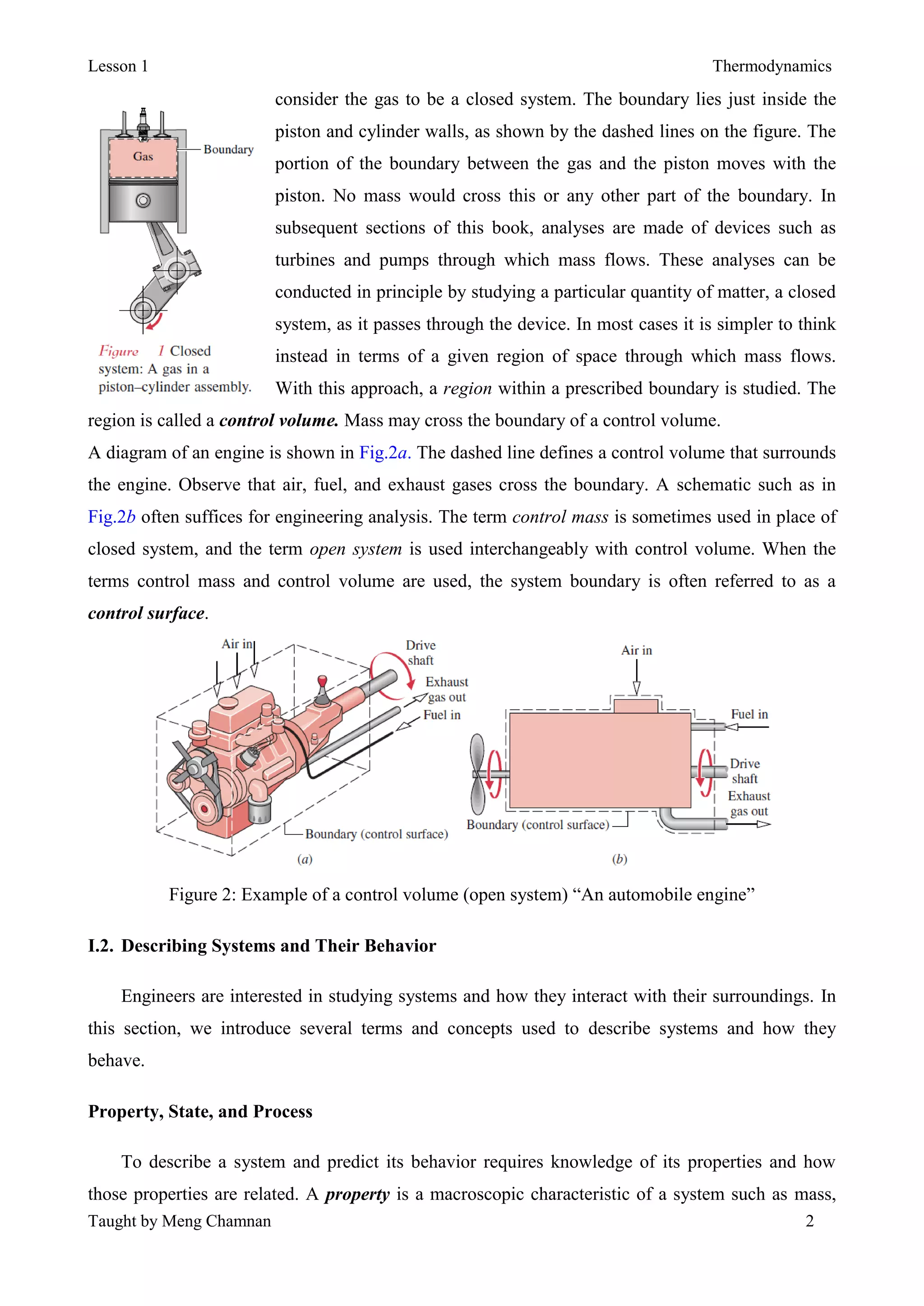
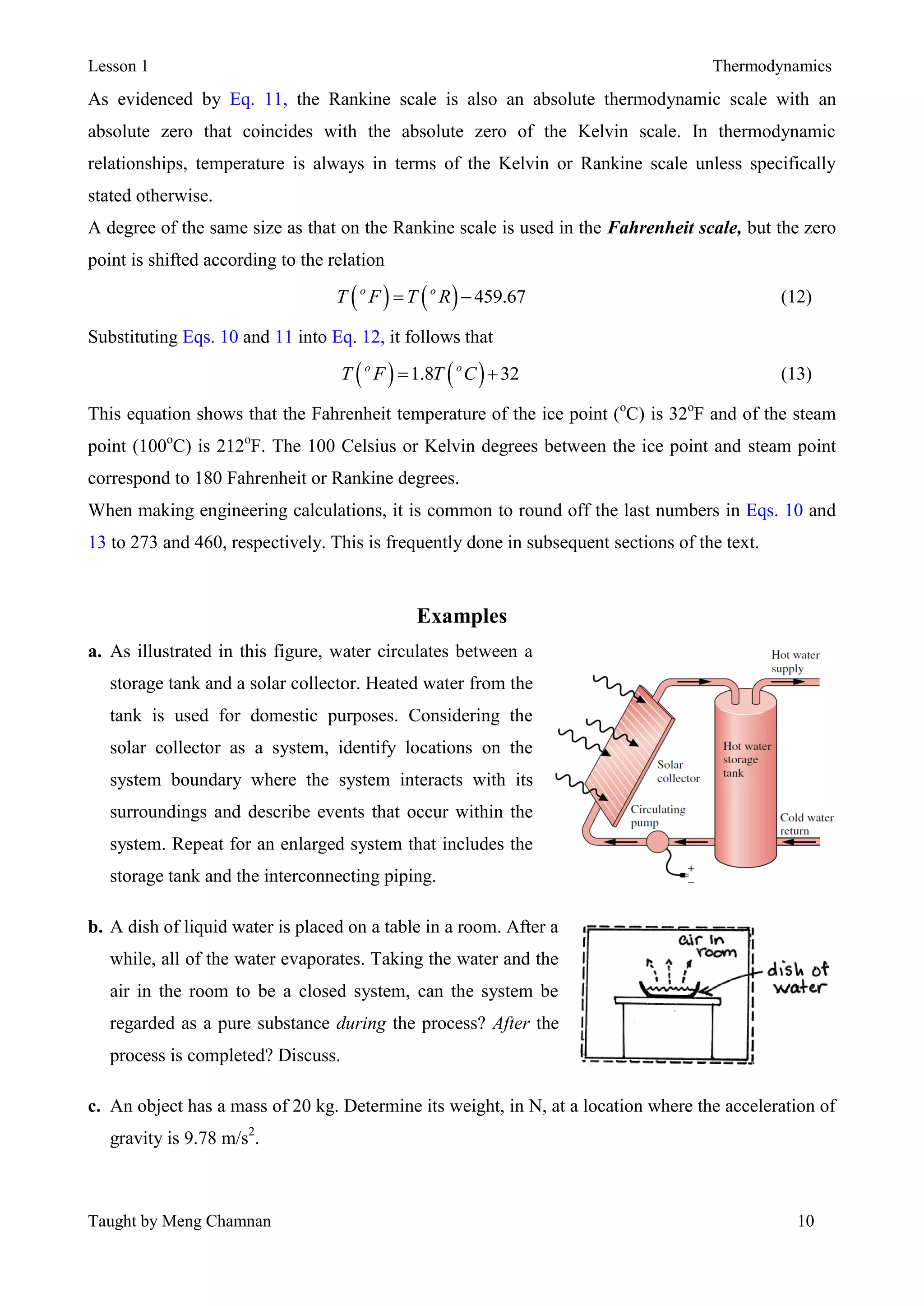
Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations between thermal and mechanical forms. A system is defined as the subject of analysis, which has specified boundaries and properties that may change as it undergoes processes or reaches equilibrium states. Thermodynamic properties are either extensive, meaning their values depend on system size, or intensive, with values independent of system size. Temperature, pressure, and specific volume are important intensive properties. The SI system of units is commonly used, with the pascal and kelvin as units of pressure and temperature. A system reaches thermal equilibrium when its intensive properties become uniform throughout.