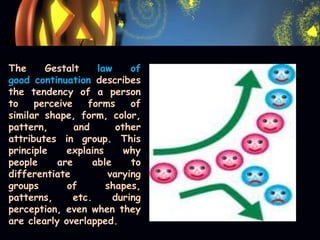
Gestalt psychology is a philosophy of mind that views the mind as forming global wholes. It emphasizes that people actively organize sensory information into unified perceptions. Some key principles of Gestalt psychology include: proximity, similarity, closure, good continuation, and simplicity. Insight learning involves problem solving through understanding relationships rather than trial and error. Lifespace refers to the psychological and behavioral environment that affects an individual's thoughts and behaviors at a given time.