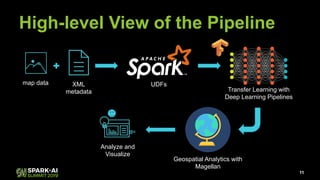
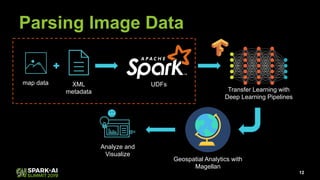
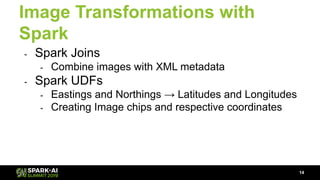
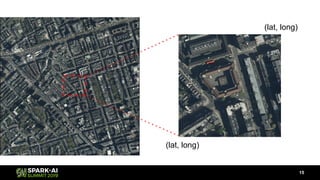
Raela Wang presented on geospatial analytics at scale using deep learning and Apache Spark. The talk covered ingesting image data with Spark, performing object detection on images using transfer learning models, and analyzing the results geospatially using Magellan. A pipeline was demonstrated that reads images with Spark, extracts predictions from a pre-trained model using Deep Learning Pipelines, and visualizes the objects identified on a heatmap while integrating with Magellan for geospatial analytics. The talk highlighted how Spark can tie together various technologies like deep learning frameworks, geospatial tools, and visualization libraries to perform end-to-end geospatial analytics at scale.