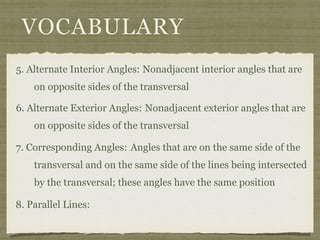
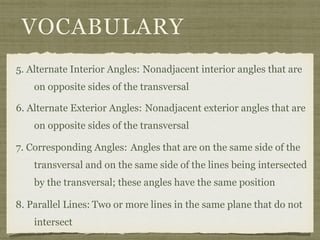
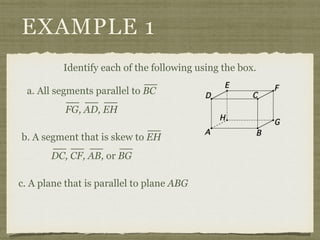
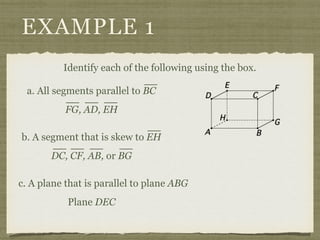
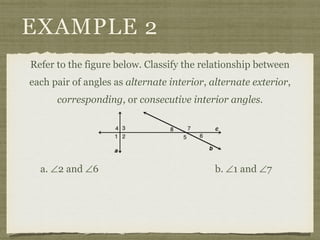
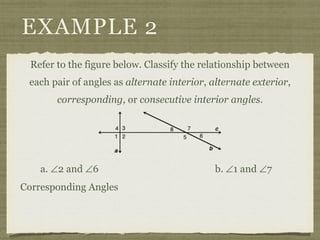
This document defines key terms and concepts related to parallel lines and transversals, including:
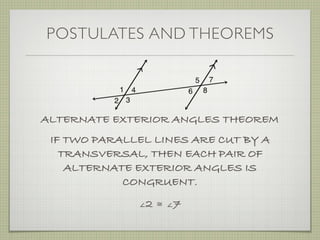
- A transversal is a line that intersects two other lines at two different points.
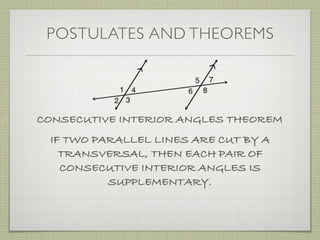
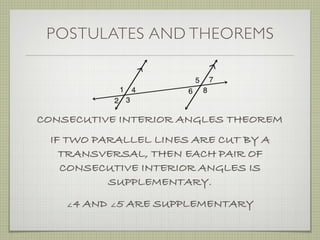
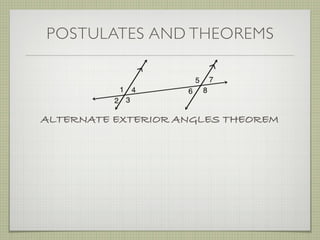
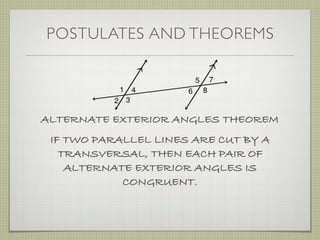
- Interior angles are formed between the two lines, while exterior angles are outside the lines.
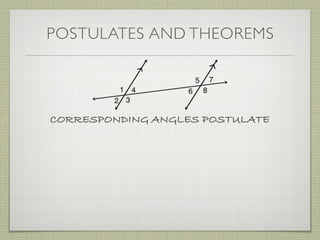
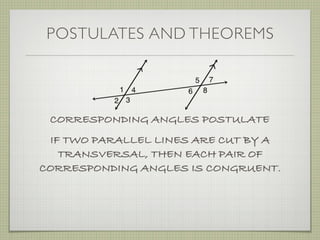
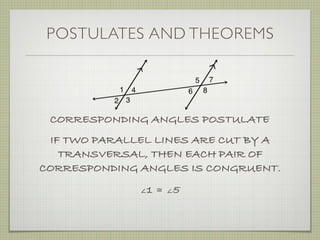
- Alternate interior angles, corresponding angles, and other angle relationships are defined.
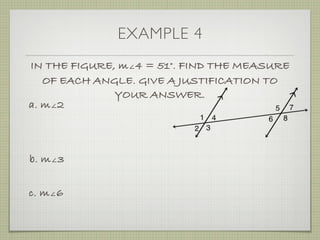
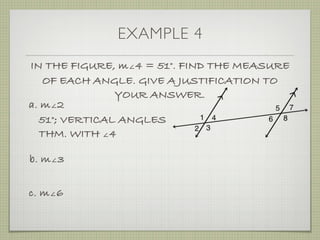
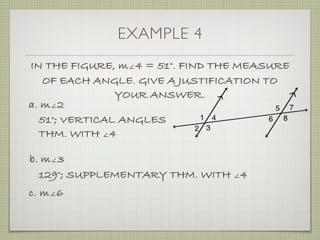
- Examples demonstrate identifying angle relationships and using properties of parallel lines to calculate unknown angle measures.













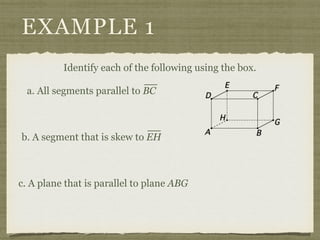
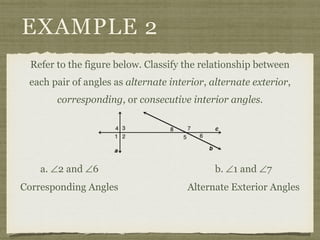
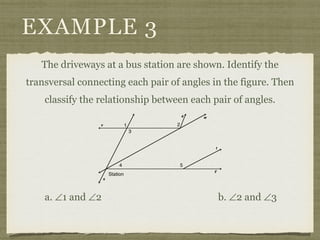
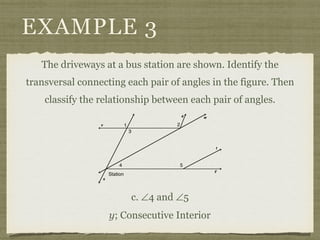
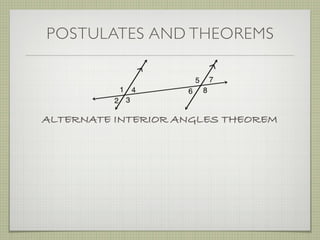
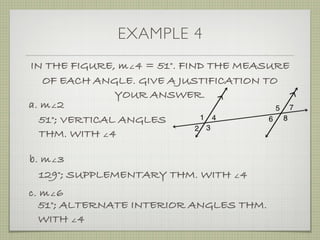
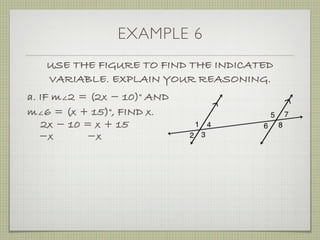
![EXAMPLE 6
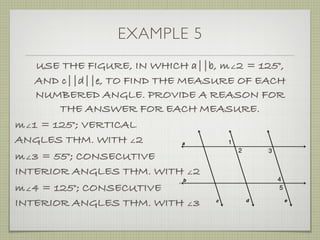
USE THE FIGURE TO FIND THE INDICATED
VARIABLE. EXPLAIN YOUR REASONING.
b. IF m∠7 = [4(y 25)]° AND
m∠1 = (4y)°, FIND y.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geosection2-7-180207051952/85/Geometry-Section-2-7-58-320.jpg)
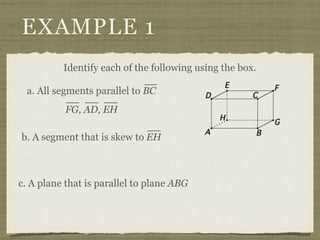
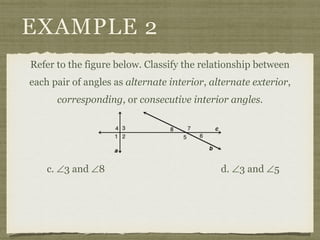
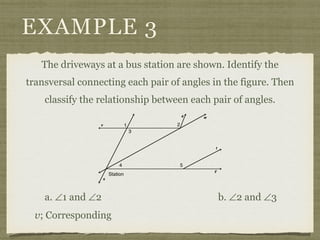
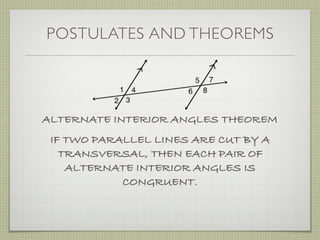
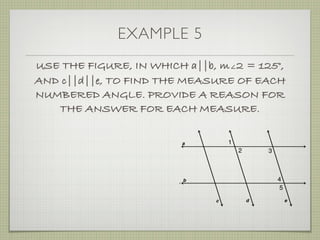
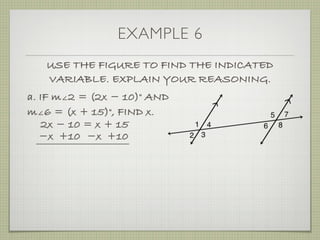
![EXAMPLE 6
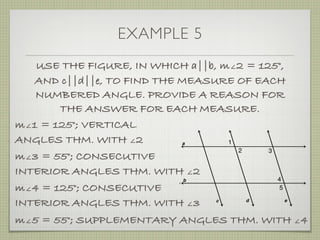
USE THE FIGURE TO FIND THE INDICATED
VARIABLE. EXPLAIN YOUR REASONING.
b. IF m∠7 = [4(y 25)]° AND
m∠1 = (4y)°, FIND y.
4(y 25) + 4y = 180](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geosection2-7-180207051952/85/Geometry-Section-2-7-59-320.jpg)
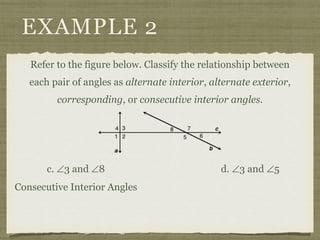
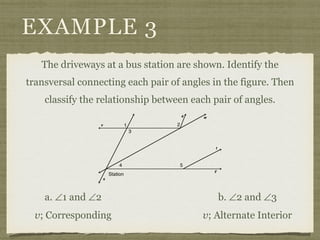
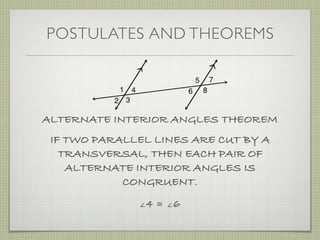
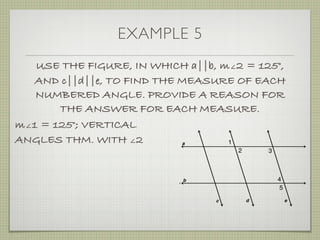
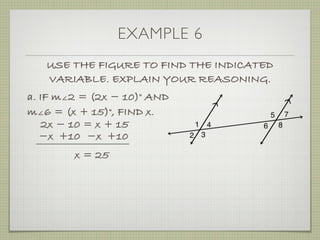
![EXAMPLE 6
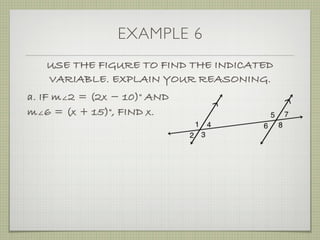
USE THE FIGURE TO FIND THE INDICATED
VARIABLE. EXPLAIN YOUR REASONING.
b. IF m∠7 = [4(y 25)]° AND
m∠1 = (4y)°, FIND y.
4(y 25) + 4y = 180
4y 100 + 4y = 180](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geosection2-7-180207051952/85/Geometry-Section-2-7-60-320.jpg)
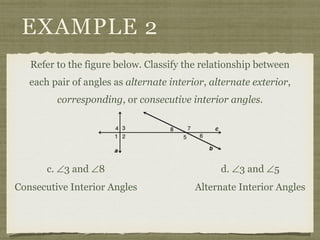
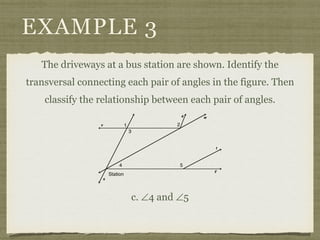
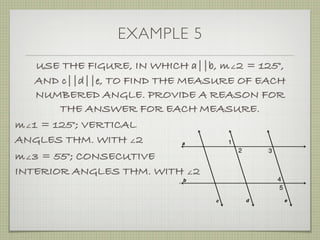
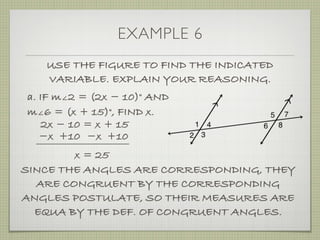
![EXAMPLE 6
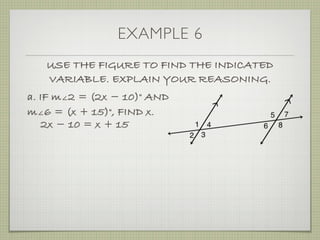
USE THE FIGURE TO FIND THE INDICATED
VARIABLE. EXPLAIN YOUR REASONING.
b. IF m∠7 = [4(y 25)]° AND
m∠1 = (4y)°, FIND y.
4(y 25) + 4y = 180
4y 100 + 4y = 180
8y 100 = 180](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geosection2-7-180207051952/85/Geometry-Section-2-7-61-320.jpg)
![EXAMPLE 6
USE THE FIGURE TO FIND THE INDICATED
VARIABLE. EXPLAIN YOUR REASONING.
b. IF m∠7 = [4(y 25)]° AND
m∠1 = (4y)°, FIND y.
4(y 25) + 4y = 180
4y 100 + 4y = 180
8y 100 = 180
8y = 280](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geosection2-7-180207051952/85/Geometry-Section-2-7-62-320.jpg)
![EXAMPLE 6
USE THE FIGURE TO FIND THE INDICATED
VARIABLE. EXPLAIN YOUR REASONING.
b. IF m∠7 = [4(y 25)]° AND
m∠1 = (4y)°, FIND y.
4(y 25) + 4y = 180
4y 100 + 4y = 180
8y 100 = 180
8y = 280
y = 35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geosection2-7-180207051952/85/Geometry-Section-2-7-63-320.jpg)